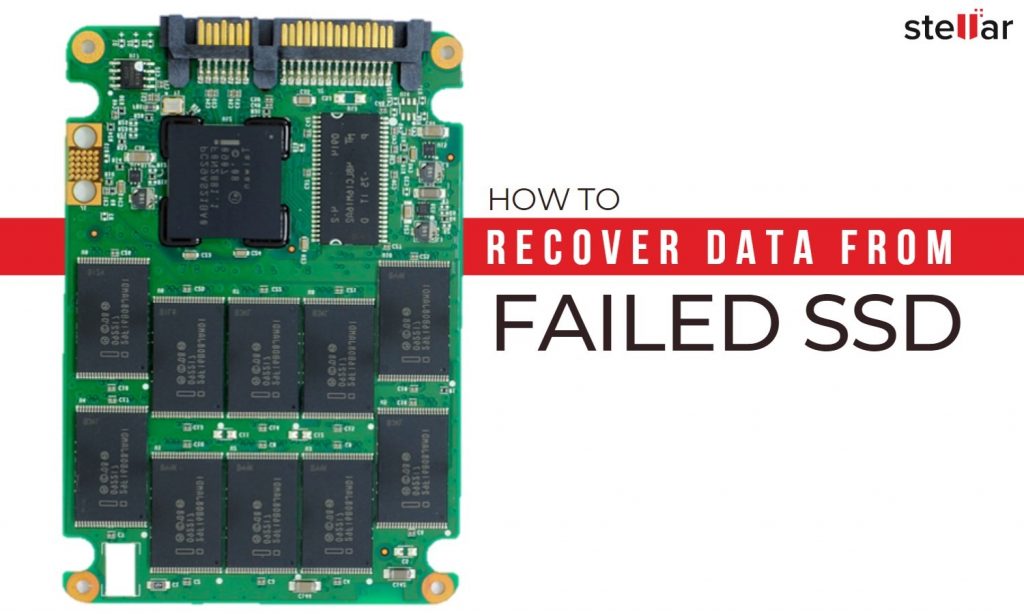
When the SSD is a data disk, you can fix it directly after formatting and wiping. If the SSD is a system disk, you can reinstall the system.
Can a dead SSD be recovered?
It’s possible to recover data from dead SSD if the SSD died of natural causes (memory cells stopped working). A simple way to recover data from a dead SSD is to simply clone it to a new drive, although you can also connect it to another PC as a secondary device.
How do you diagnose a dead SSD?
Type “chkdsk” in Command Prompt (running as administrator) for a quick look at your file system integrity, and if your SSD came with any proprietary management software, there are often built-in tools for monitoring its health. Sudden power loss can still result in damage to your SSD, even if it seems healthy.
How do I know if my SSD is corrupted?
The easiest way to keep track of the number of bad sectors on an SSD is to run ChkDsk (short for “check disk”) in Windows®. After checking the drive, ChkDsk will report the number of bad sectors it found. Make a note of what that number is and run ChkDsk again after a couple of days.
Is it harder to recover data from SSD?
And while they might not last as long and are vulnerable to physical damage, recovering data from a failed HDD is reportedly easier than from SSDs. SSDs on the other hand use a different type of technology that doesn’t rely on the moving parts of an HDD.
How long do SSD hold data?
Most SSDs will retain your data without power for 5 to 10 years. HDDs have a similar lifespan, but they are more likely to get damaged because they consist of moving parts. Flash drives, for example, can retain data for more than ten years. The more advanced ones have a lifespan of 10 years minimum.
Can SSD fail suddenly?
Compared to hard drives, SSDs are remarkably reliable; yet, no storage technology is perfect. Even the latest NVMe SSDs are susceptible to a sudden or gradual breakdown.
Why did my SSD suddenly stop working?
A sudden loss of power or rare software events can cause a system to fail to recognize an SSD. In most cases, the SSD can be returned to normal operating condition by completing our power cycle procedure.
Why is my SSD not being detected?
The BIOS will not detect a SSD if the data cable is damaged or the connection is incorrect. Serial ATA cables, in particular, can sometimes fall out of their connection. Be sure to check your SATA cables are tightly connected to the SATA port connection.
Which lasts longer SSD or HDD?
Will SSD degrade if not used?
The JEDEC standards stipulate that an SSD must be able to retain data unpowered for 1 year in up to 30 degrees Celcius.
Can SSDs lose data without power?
Debunked: Your SSD won’t lose data if left unplugged after all.
Are SSDs prone to failure?
In short, yes, SSDs do fail – all drives do. However, the problems associated with HDDs and SSDs are different. Generally, SSD’s can be described as more durable than HDDs, because they contain no moving parts. HDDs are mechanical devices, with fast-moving components like the platters and spindle motor.
How often does SSD fail?
SSDs aren’t that far behind hard drives in failure rate, with a 1.05% annualized failure rate compared to 1.38%.
How often do SSD drives fail?
How long will a 1TB SSD last?
The 1TB model of the Samsung 850 EVO series, which is equipped with the low-priced TLC storage type, can expect a life span of 114 years. If your SSD is already in usage for a while, then you can calculate the anticipated remaining life time with the help of special tools.
Are cheap SSDs worth it?
The cheaper SSDs tend to have worse performance than expensive ones with extensive write file operations, though it may or may not be a problem depending on how often said operations are done. Also since cheaper SSDs tend to exclude DRAM, there’s the potential to wear out faster due to using flash to cache things.
Is it OK to defrag SSD drives?
To summarize, do not defrag an SSD The answer is short and simple — do not defrag a solid state drive. At best it won’t do anything, at worst it does nothing for your performance and you will use up write cycles. If you have done it a few times, it isn’t going to cause you much trouble or harm your SSD.
Do SSD drives get slower over time?
The more data on the drive, the more time it takes the SSD to find the right spot to move that data, regardless of whether you’re writing brand new data or just changing a file that already exists. To put it as simply as possible: The more an SSD fills up, the more it slows down.
Why is my SSD degrade over time?
As discussed earlier, once SSDs are full, they can only write new information by erasing older information. Over time, this creates wear and tear on flash cells and ultimately renders them unusable.
How often should you power an SSD?
SSDs (Solid State Drives) have a reputation for having a very low data retention rate. Numbers commonly cited suggest one year for consumer grade SSDs, and as low as one week for enterprise class SSDs.
What is the lifespan of an SSD?
In addition, there’s not as much information on how long SSDs will last simply because they’re newer devices. However, some estimates say that the typical SSD will last for 10 years under normal workloads. That’s an increase from the five to six years that was once used as an estimate.