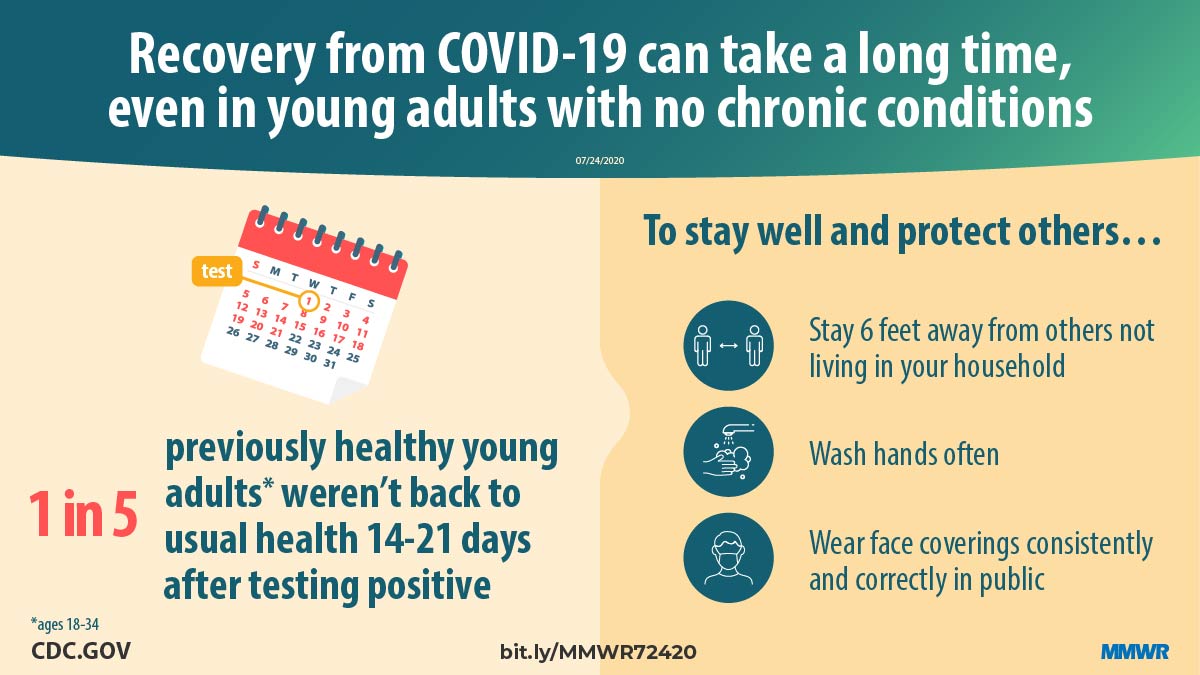
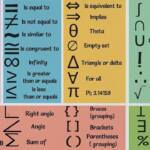
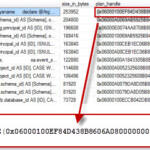
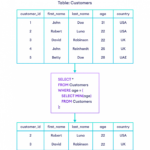
“We have seen these viruses that have been lingering for three to four weeks, so patients have been symptomatic for that long and often they don’t’ respond to antibiotics right away.”
Can you have a viral infection for weeks?
Most people will be infectious for around 2 weeks. Symptoms are usually worse during the first 2 to 3 days, and this is when you’re most likely to spread the virus.
How long do viruses take to get over?
last up to 14 days, sometimes even longer. people, the worst is over in about 10 days, although the cough may last for 3 weeks. Remember, antibiotics won’t make a viral illness get better faster. Usually, they just need to run their course.
Can viruses last over a month?
The Differences Between a Virus and Bacterial Infection A lot of times the symptoms last for maybe three days to a week and then slowly get better over time. Sometimes the cough can be persistent up to a month.
When should I be worried about a viral infection?
A viral fever refers to any fever that results from a viral infection, such as the flu or dengue fever. While most viral fevers resolve on their own within a day or two, some are more severe and require medical treatment. If your temperature starts reading 103°F (39°C) or higher, it’s time to call a doctor.
How long do viruses take to get over?
last up to 14 days, sometimes even longer. people, the worst is over in about 10 days, although the cough may last for 3 weeks. Remember, antibiotics won’t make a viral illness get better faster. Usually, they just need to run their course.
Can viruses last over a month?
The Differences Between a Virus and Bacterial Infection A lot of times the symptoms last for maybe three days to a week and then slowly get better over time. Sometimes the cough can be persistent up to a month.
What are the 5 stages of viral infection?
The life cycle of viruses can differ greatly between species and category of virus, but they follow the same basic stages for viral replication. The viral life cycle can be divided into several major stages: attachment, entry, uncoating, replication, maturation, and release.
How do you get rid of a virus in your body?
Antiviral drugs can ease symptoms and shorten how long you are sick with viral infections like the flu and Ebola. They can rid your body of these viruses. Viral infections like HIV, hepatitis and herpes are chronic. Antivirals can’t get rid of the virus, which stays in your body.
How long does Omicron symptoms last?
How long do omicron symptoms last? Most people who test positive with any variant of COVID-19 typically experience some symptoms for a couple weeks. People who have long COVID-19 symptoms can experience health problems for four or more weeks after first being infected, according to the CDC.
Can viruses last 6 weeks?
It’s a virus, different from a common cold, flu or allergies for that matter. And according to Doctor Gary Gross, who is on staff with Texas Health Dallas, it can last four to six weeks, maybe even longer.
Can a doctor do anything for a virus?
For most viral infections, treatments can only help with symptoms while you wait for your immune system to fight off the virus. Antibiotics do not work for viral infections. There are antiviral medicines to treat some viral infections. Vaccines can help prevent you from getting many viral diseases.
How long does a virus last in adults?
In general, healthy people usually get over a cold in 7 to 10 days. Flu symptoms, including fever, should go away after about 5 days, but you may still have a cough and feel weak a few days longer. All your symptoms should be gone within 1 to 2 weeks.
What are 3 types of viral infections?
Viral infections include: the common cold, which mainly occurs due to rhinovirus, coronavirus, and adenovirus. encephalitis and meningitis, resulting from enteroviruses and the herpes simplex virus (HSV), as well as West Nile Virus. warts and skin infections, for which HPV and HSV are responsible.
What are 3 types of viral infections?
Viral infections include: the common cold, which mainly occurs due to rhinovirus, coronavirus, and adenovirus. encephalitis and meningitis, resulting from enteroviruses and the herpes simplex virus (HSV), as well as West Nile Virus. warts and skin infections, for which HPV and HSV are responsible.
How do you get rid of a viral infection?
For most viral infections, treatments can only help with symptoms while you wait for your immune system to fight off the virus. Antibiotics do not work for viral infections. There are antiviral medicines to treat some viral infections. Vaccines can help prevent you from getting many viral diseases.
Can you have a viral infection for weeks?
Most people will be infectious for around 2 weeks. Symptoms are usually worse during the first 2 to 3 days, and this is when you’re most likely to spread the virus.
How long do viruses take to get over?
last up to 14 days, sometimes even longer. people, the worst is over in about 10 days, although the cough may last for 3 weeks. Remember, antibiotics won’t make a viral illness get better faster. Usually, they just need to run their course.
Can viruses last over a month?
The Differences Between a Virus and Bacterial Infection A lot of times the symptoms last for maybe three days to a week and then slowly get better over time. Sometimes the cough can be persistent up to a month.
What is the last stage of a viral infection?
Convalescence. The final stage of infection is known as convalescence. During this stage, symptoms resolve, and a person can return to their normal functions. Depending on the severity of the infection, some people may have permanent damage even after the infection resolves.
How does the body fight a virus?
If an antigen enters the body and B-cells recognize it (either from having had the disease before or from being vaccinated against it), B-cells will produce antibodies. When antibodies attach to an antigen (think a lock–key configuration), it signals other parts of the immune system to attack and destroy the invaders.
Why do doctors give antibiotics for viral infections?
Antibiotics do kill specific bacteria. Some viruses cause symptoms that resemble bacterial infections, and some bacteria can cause symptoms that resemble viral infections. Your healthcare provider can determine what type of illness you have and recommend the proper type of treatment.