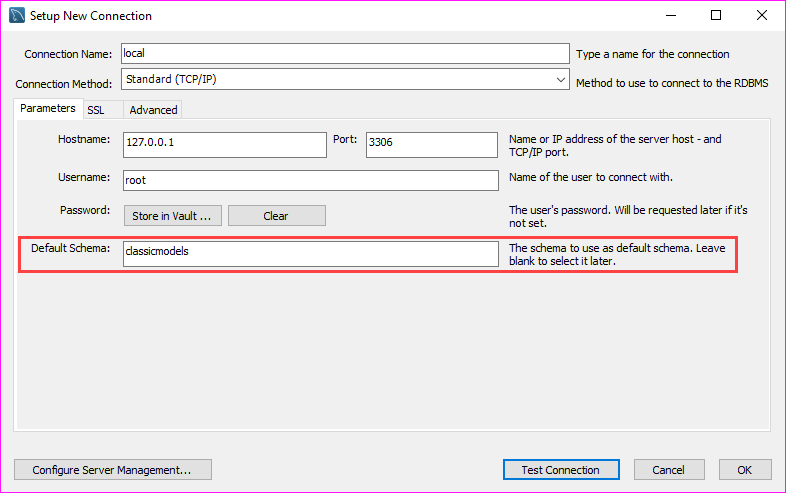
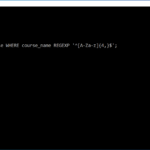
In MySQL, you can use the <> or != operators to test for inequality in a query. For example, we could test for inequality using the <> operator, as follows: SELECT * FROM contacts WHERE last_name <> ‘Johnson’;
What does != Mean in a query?
<> means not equal to, != also means not equal to.
How do you use not equal to in query?
The SQL Not Equal comparison operator (!=) is used to compare two expressions. For example, 15 != 17 comparison operation uses SQL Not Equal operator (!=) between two expressions 15 and 17.
How do I exclude something in MySQL?
To check records which are NULL, use IS NULL. However, to exclude any of the records, use the NOT IN clause. Use both of them in the same query.
Is != Valid in SQL?
There is no != operator according to the ANSI/SQL 92 standard.
Is not vs <> in SQL?
In terms of performance , the two queries almost the same. if you can check the actual execution plan in SQL Server, there is no difference of the two query. NOT is a negation and the other (<>) is an operator used for comparison.
Is != The same as ==?
The equal-to operator ( == ) returns true if both operands have the same value; otherwise, it returns false . The not-equal-to operator ( != ) returns true if the operands don’t have the same value; otherwise, it returns false .
Is != The correct comparison operator for not equal to?
Not equal to ( !== ) — returns true if the value on the left is not equal to the value on the right, otherwise it returns false .
Is not equal to null in SQL?
In SQL null is not equal ( = ) to anything—not even to another null . According to the three-valued logic of SQL, the result of null = null is not true but unknown. SQL has the is [not] null predicate to test if a particular value is null .
How do I exclude a condition in SQL?
EXCLUDE conditions in SQL usually appear in the WHERE clause of the statement or in the HAVING clause of an aggregate query. Some commonly used EXCLUDE operators in SQL are NOT, NOT IN, NOT LIKE, ‘! =’, EXCEPT, NOT NULL, etc.
What are the 3 types of SQL commands?
There are 3 main types of commands. DDL (Data Definition Language) commands, DML (Data Manipulation Language) commands, and DCL (Data Control Language) commands.
Is SQL hard to learn?
Because SQL is a relatively simple language, learners can expect to become familiar with the basics within two to three weeks. That said, if you’re planning on using SQL skills at work, you’ll probably need a higher level of fluency.
Is SQL a coding?
Given the definition of a programming language as having a certain vocabulary and a specific syntax, SQL definitely qualifies as a programming language. However, it does not qualify as a General Purpose Language (GPL) and is, in fact, a Domain-Specific Language (DSL).
What is null in MySQL?
The NULL value means “no data.” NULL can be written in any lettercase. Be aware that the NULL value is different from values such as 0 for numeric types or the empty string for string types.
Which is not valid in SQL type?
2) Which of the following is not a valid SQL type? Explanation: DECIMAL is not a valid SQL type because it is nothing but numeric only in SQL. NUMERIC has fixed precision, and scale numbers range from -10^38+1 to 10^38-1.
Which datatype is not valid SQL?
So, float is not valid.
Is not VS != NULL?
The main difference between e != null and e is not null is the way the the compiler executes the comparison. Microsoft: “The compiler guarantees that no user-overloaded equality operator == is invoked when expression x is null is evaluated.”
IS NOT NULL vs <> NULL SQL?
The IS NULL condition is satisfied if the column contains a null value or if the expression cannot be evaluated because it contains one or more null values. If you use the IS NOT NULL operator, the condition is satisfied when the operand is column value that is not null, or an expression that does not evaluate to null.
Does not exist in MySQL?
In MySQL 8.0. 19 and later, you can also use NOT EXISTS or NOT EXISTS with TABLE in the subquery, like this: SELECT column1 FROM t1 WHERE EXISTS (TABLE t2); The results are the same as when using SELECT * with no WHERE clause in the subquery.
What can I use instead of same?
Some common synonyms of same are equal, equivalent, identical, selfsame, and very.
How can I use same same?
Describing something as ‘same same’ (even if it’s significantly different) is a way to answer a question vaguely, without actually saying “no” (or “it’s different”).
What does same Y mean?
/ˈseɪ.mi/ not interesting because of being very similar: His paintings all look a bit samey.