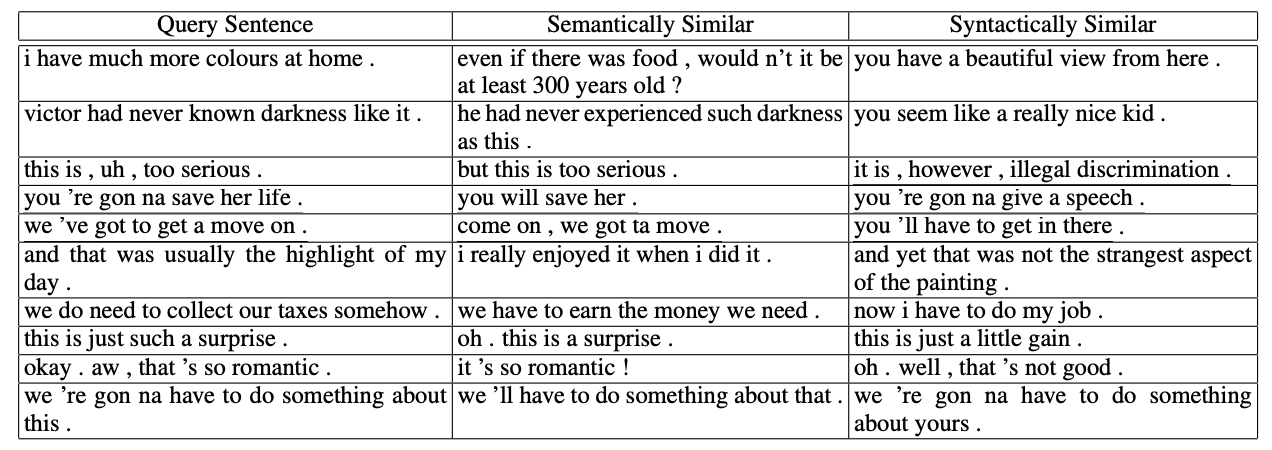
Syntax has to do with the form and order of words within the sentence. Semantics has to do with the meaning. Syntax is language dependent, whereas the semantics remains the same if the same sentence were expressed in another language.
Does syntax depend on semantics?
Syntax has to do with the form and order of words within the sentence. Semantics has to do with the meaning. Syntax is language dependent, whereas the semantics remains the same if the same sentence were expressed in another language.
What would happen without semantics?
Without proper semantics—and a thoughtful, grammatically correct ordering of words—the meaning of a sentence would be completely different. Linguists break semantics down into various categories, including lexical semantics, which is the study of word meanings and relations.
Do computers have syntax but no semantics?
More generally it can use its knowledge base for manipulating symbols and for transforming semantic information into instructions for the manipulation. Searle (1980, p. 423), writes: “The computer, to repeat, has a syntax but no semantics.
Is syntax part of semantic?
Syntax refers to the set of rules that create sentence structure. Writers can also call these the grammar rules. Semantics refers to the study of the meaning of sentences. Sometimes, grammatically correct words do not make sense, even when they are correct grammatically.
What would happen without semantics?
Without proper semantics—and a thoughtful, grammatically correct ordering of words—the meaning of a sentence would be completely different. Linguists break semantics down into various categories, including lexical semantics, which is the study of word meanings and relations.
Do computers have syntax but no semantics?
More generally it can use its knowledge base for manipulating symbols and for transforming semantic information into instructions for the manipulation. Searle (1980, p. 423), writes: “The computer, to repeat, has a syntax but no semantics.
Why is semantics needed?
The aim of semantics is to discover why meaning is more complex than simply the words formed in a sentence.
Why is semantics important in language?
Semantics is the study of the meaning of words. Many words have very similar meanings and it is important to be able to distinguish subtle differences between them. For example, ‘anger’ and ‘rage’ are similar in meaning (synonyms) but ‘rage’ implies a stronger human reaction to a situation than ‘anger.
Why is semantics important in writing?
Semantics aims to determine meanings and explain relationships between patterns of language and what is referred to. “In dealing with meaning, a distinction is generally made between grammatical meaning, which is treated in the grammar, and referential meaning, which is treated in the lexicon,” Lehmann writes.
Who said syntax is not sufficient for semantics?
Does syntax suffice for semantics? John Searle famously says that it does not. 1 I have argued that it does. 2 More precisely, I have argued that semantics is nothing but syntax.
Do all languages have syntax?
Not only does every language have syntax, but similar syntactic principles are found over and over again in languages.
Can a language exist without syntax?
It is not possible to find any language in the world without grammar.
What is the difference between syntax and a semantic error?
The syntax error is an incorrect construction of the source code, whereas a semantic error is erroneous logic that produces the wrong result when executed.
What is the interface between syntax and semantics?
The study of the syntax–semantics interface is concerned with linguistic phenomena that are the product of interactions between principles of syntactic organization and principles of semantic interpretation. Such interactions abound in natural language and can be found in all subsystems of the grammar.
Is vocabulary syntax or semantics?
Expressive vocabulary refers to all the words a person uses when speaking. Not understanding words or using words incorrectly is very common among children with language problems. Syntax refers to the way words are arranged in a sentence to convey meaning. Semantics refers to the meaning of words and how they are used.
What determines syntax?
Syntax FAQ In linguistics, syntax is the arrangement or order of words, determined by both the writer’s style and grammar rules.
Who said syntax is not sufficient for semantics?
Does syntax suffice for semantics? John Searle famously says that it does not. 1 I have argued that it does. 2 More precisely, I have argued that semantics is nothing but syntax.
What is difference between syntactic and semantic?
Semantic focuses on the meaning of words. On the other hand, syntactic focuses on the arrangement of words and phrases when forming a sentence. As you can see, there is a key difference between semantic and syntactic as each focuses on a different component in language.
What would happen without semantics?
Without proper semantics—and a thoughtful, grammatically correct ordering of words—the meaning of a sentence would be completely different. Linguists break semantics down into various categories, including lexical semantics, which is the study of word meanings and relations.
Do computers have syntax but no semantics?
More generally it can use its knowledge base for manipulating symbols and for transforming semantic information into instructions for the manipulation. Searle (1980, p. 423), writes: “The computer, to repeat, has a syntax but no semantics.
Is syntax part of semantic?
Syntax refers to the set of rules that create sentence structure. Writers can also call these the grammar rules. Semantics refers to the study of the meaning of sentences. Sometimes, grammatically correct words do not make sense, even when they are correct grammatically.