Whether or not the performance is affected by the difference in collation is likely dependent on how tempdb is used. The biggest impact of different collations is when for example tables are joined on columns with different collations and the collation is explicitly stated in the “ON” clause.
Does collation matter in SQL?
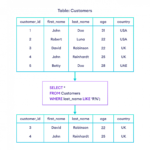
Data always follows collation constraint rules, which are configured when creating an object. When retrieving data using a T-SQL query, collation plays a fundamental role in the execution. It matters which collation is associated with a column when ordering clause is applied to that column.
Why do we need collation?
A collation allows character data for a given language to be sorted using rules that define the correct character sequence, with options for specifying case-sensitivity, accent marks, kana character types, use of symbols or punctuation, character width, and word sorting.
Does query store affect performance?
Query Store performance impact a user concern Because the tool runs all the time if it’s on, it can take system resources away from other programs. According to Warren, DBAs are likely to assume that running Query Store will increase processing overhead in their database servers — and often with good reason.
What is the difference between SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS and Latin1_General_CI_AS?
The SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS collation is a SQL collation and the rules around sorting data for unicode and non-unicode data are different. The Latin1_General_CI_AS collation is a Windows collation and the rules around sorting unicode and non-unicode data are the same.
What collation should I use for SQL Server?
Server-level collation for Microsoft SQL Server If you don’t choose a different collation, the server-level collation defaults to SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS. The server collation is applied by default to all databases and database objects.
What causes SQL to be slow?
WAITING: Queries can be slow because they’re waiting on a bottleneck for a long time. See a detailed list of bottlenecks in types of Waits. RUNNING: Queries can be slow because they’re running (executing) for a long time. In other words, these queries are actively using CPU resources.
What is collation sensitivity?
Collation refers to a set of rules that determine how data is sorted and compared. Character data is sorted using rules that define the correct character sequence, with options for specifying case-sensitivity, accent marks, kana character types and character width. Case sensitivity: If A and a, C and c, etc.
What is collation and example?
: a light meal allowed on fast days in place of lunch or supper. : a light meal. [Middle English, from Latin collation-, collatio] : the act, process, or result of collating.
What is collation rule?
Collation is the assembly of written information into a standard order. Many systems of collation are based on numerical order or alphabetical order, or extensions and combinations thereof. Collation is a fundamental element of most office filing systems, library catalogs, and reference books.
Does normalization improve performance SQL?
Normalization, also known as database normalization or data normalization, is an important part of relational database design because it helps to improve the speed, accuracy, and efficiency of the database.
Does DBCC Checkdb affect performance?
DBCC CHECKDB regular database maintenance commands T-SQL command below only checks the database physical structure. The command lessens run time and performance impact.
Do capitalizations matter in SQL?
Keywords in SQL are case-insensitive for the most popular DBMSs. The computer doesn’t care whether you write SELECT , select, or sELeCt ; so, in theory, you can write however you like.
Is SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS deprecated?
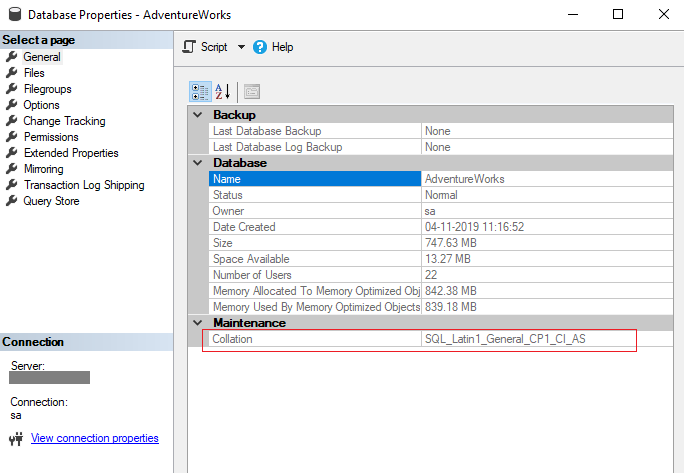
What does it mean by the As in the default collation SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS?
The server collation is specified during SQL Server installation. The default server-level collation is based upon the locale of the operating system. For example, the default collation for systems using US English (en-US) is SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS.
Is != Or <> better in SQL?
If != and <> both are the same, which one should be used in SQL queries? Here is the answer – You can use either != or <> both in your queries as both technically same but I prefer to use <> as that is SQL-92 standard.
What does collate SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS do?
The collate clause is used for case sensitive and case insensitive searches in the columns of the SQL server. There are two types of collate clause present: SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CS_AS for case sensitive. SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS for case insensitive.
Why collation is important in SQL Server?
Collations in SQL Server provide sorting rules, case, and accent sensitivity properties for your data. Collations that are used with character data types, such as char and varchar, dictate the code page and corresponding characters that can be represented for that data type.
What should database collation?
Collation is a set of rules that tell database engine how to compare and sort the character data in SQL Server. Collation can be set at different levels in SQL Server.
What is SQL default collation?
Default server-level collation is SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS. If you are migrating databases from SQL Server to Managed Instance, check the server collation in the source SQL Server using SERVERPROPERTY(N’Collation’) function and create a Managed Instance that matches the collation of your SQL Server.
Is SSD good for SQL Server?
Solid state drives (SSDs) can significantly enhance the ability to consume large amounts of data rapidly, enabling performance to make decisions faster. For SQL databases, NVMe™ SSDs offer high IOPS and bandwidth, as well as faster response times, which can directly impact speed of processing.
What is the fastest SQL Server?
Named Pipes is the fastest SQL Server protocol.