Enter sudo -i to switch to the root user. If you do not have root access, use the commands with appending sudo . Use the groupadd command. Use command useradd .
How do I change from root to user?
Enter sudo -i to switch to the root user. If you do not have root access, use the commands with appending sudo . Use the groupadd command. Use command useradd .
How do I change permissions on a root directory?
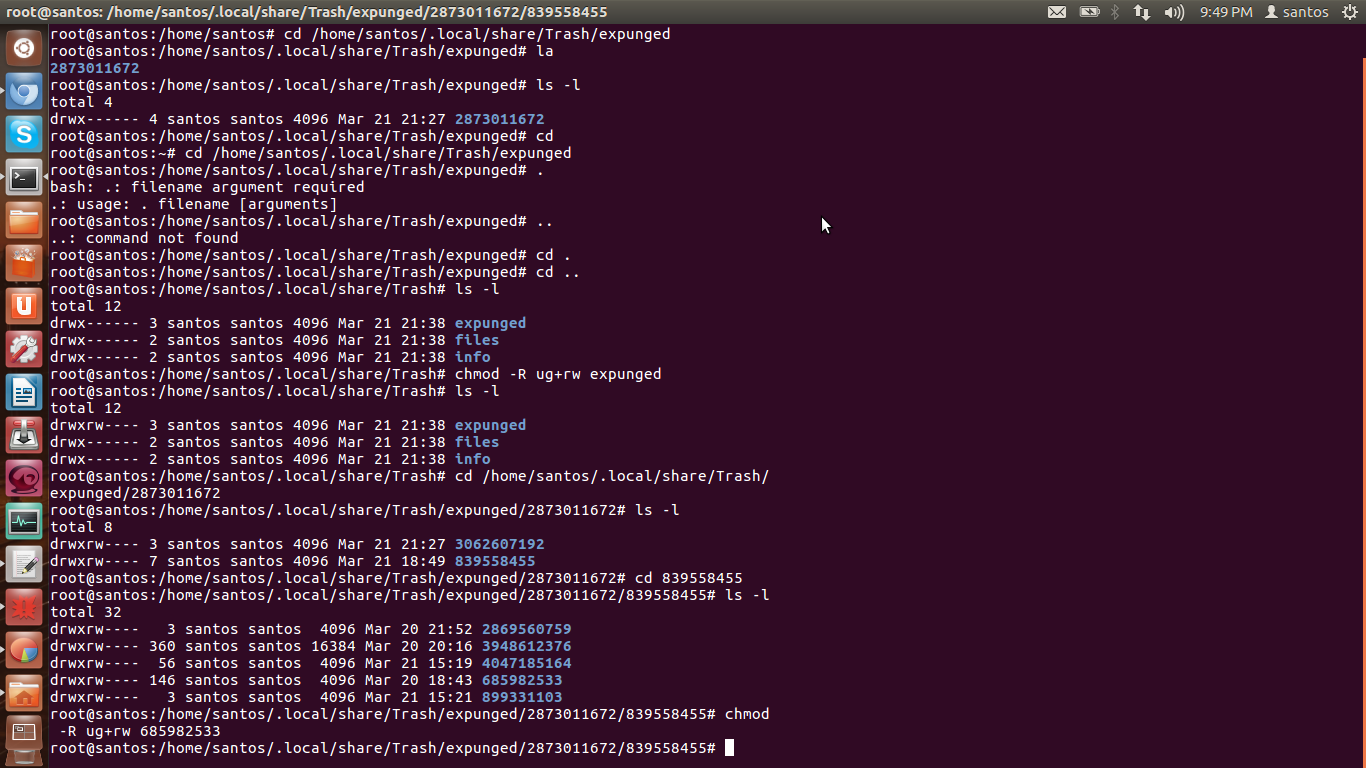
To change the permissions on a file, you use the command chmod. (chmod stands for “change mode;” a file’s permissions are also known as its mode.) As with chown, and chgrp, only the owner of a file or the superuser (root) can change the permissions of a file.
How do I change permissions from root to user in Ubuntu?
Type “sudo chmod a+rwx /path/to/file” into the terminal, replacing “/path/to/file” with the file you want to give permissions to everyone for, and press “Enter.” You can also use the command “sudo chmod -R a+rwx /path/to/folder” to give permissions to the selected folder and its files.
How do I change from root to user?
Enter sudo -i to switch to the root user. If you do not have root access, use the commands with appending sudo . Use the groupadd command. Use command useradd .
How do I change permissions on a root directory?
To change the permissions on a file, you use the command chmod. (chmod stands for “change mode;” a file’s permissions are also known as its mode.) As with chown, and chgrp, only the owner of a file or the superuser (root) can change the permissions of a file.
Is root user same as admin?
In Untangle, and in general English, “admin” is abbreviation for “administrator.” If an admin creates a new set of admin credentials (a username/password) and provides those credentials to a person, then that person now has administrator access. This level of access is also called “root” or “superuser” in some cases.
Does root user have all permissions?
The root account has root privileges. This means it can read and write any files on the system, perform operations as any user, change system configuration, install and remove software, and upgrade the operating system and/or firmware. In essence, it can do pretty much anything on the system.
Why do I get permission denied as root?
This error occurs when the user does not have the privileges to make edits to a file. Root has access to all files and folders and can make any edits. Other users, however, may not be allowed to make such edits. Remember that only root or users with Sudo privileges can change permissions for files and folders.
What is chmod R 777?
The command chmod -R 777 / makes every single file on the system under / (root) have rwxrwxrwx permissions. This is equivalent to allowing ALL users read/write/execute permissions.
How do I give permission to user?
Go to Dashboard > User Management > Users, and click the name of the user to view. Click the Permissions tab, and click Assign Permissions. Select the API from which you want to assign permissions, then select the permissions to assign to the user, and click Add Permissions.
How do I give permission to run a user?
To give the owner all permissions and world execute you would type chmod 701 [filename]. To give the owner all permissions and world read and execute you would type chmod 705 [filename].
How do I run as non root user?
sudo (superuser do) allows you to configure non-root users to run root level commands without being root. Access can be given by the root level administrator through configuration of the /etc/sudoers file.
How do I log out of root?
If you want to save the configuration of your panel, as well as any programs which are running, check the Save current setup option, as well. Similarly, in KDE, you can log out of root by going to Main Menu => Logout or by simply typing exit at the shell prompt.
How do I change from root to user?
Enter sudo -i to switch to the root user. If you do not have root access, use the commands with appending sudo . Use the groupadd command. Use command useradd .
How do I change permissions on a root directory?
To change the permissions on a file, you use the command chmod. (chmod stands for “change mode;” a file’s permissions are also known as its mode.) As with chown, and chgrp, only the owner of a file or the superuser (root) can change the permissions of a file.
Why should you disable root?
The Bad. The root is the superuser account in Unix and Linux based systems. Once we have access to the root account, we have complete system access. Because the username is always root and the access rights are unlimited, this account is the most valuable target for hackers.
What is meant by root permission?
Thus, rooting gives the ability (or permission) to alter or replace system applications and settings, run specialized applications (“apps”) that require administrator-level permissions or perform other operations that are otherwise inaccessible to a normal Android user.
What are root permissions?
Rooting is a process that allows you to attain root access to the Android operating system code (the equivalent term for Apple devices is jailbreaking). It gives you privileges to modify the software code on the device or install other software that the manufacturer wouldn’t normally allow you to.
What is the difference between root user and normal user?
The root user is basically equivalent to the administrator user on Windows — the root user has maximum permissions and can do anything to the system. Normal users on Linux run with reduced permissions — for example, they can’t install software or write to system directories.
How do I know if I am the root user?
If you are able to use sudo to run any command (for example passwd to change the root password), you definitely have root access. A UID of 0 (zero) means “root”, always.
How do you check if a user is a root user?
The “root” user’s UID is always 0 on the Linux systems. Instead of using the UID, you can also match the logged-in user name. The whoami command provides the currently logged user name.