ERROR_LINE returns the line number at which the error occurred. This happens regardless of the location of the ERROR_LINE call within the scope of the CATCH block, and regardless of the number of calls to ERROR_LINE .
How do I find the error line in SQL Server?
ERROR_LINE returns the line number at which the error occurred. This happens regardless of the location of the ERROR_LINE call within the scope of the CATCH block, and regardless of the number of calls to ERROR_LINE .
How do I find SQL database errors?
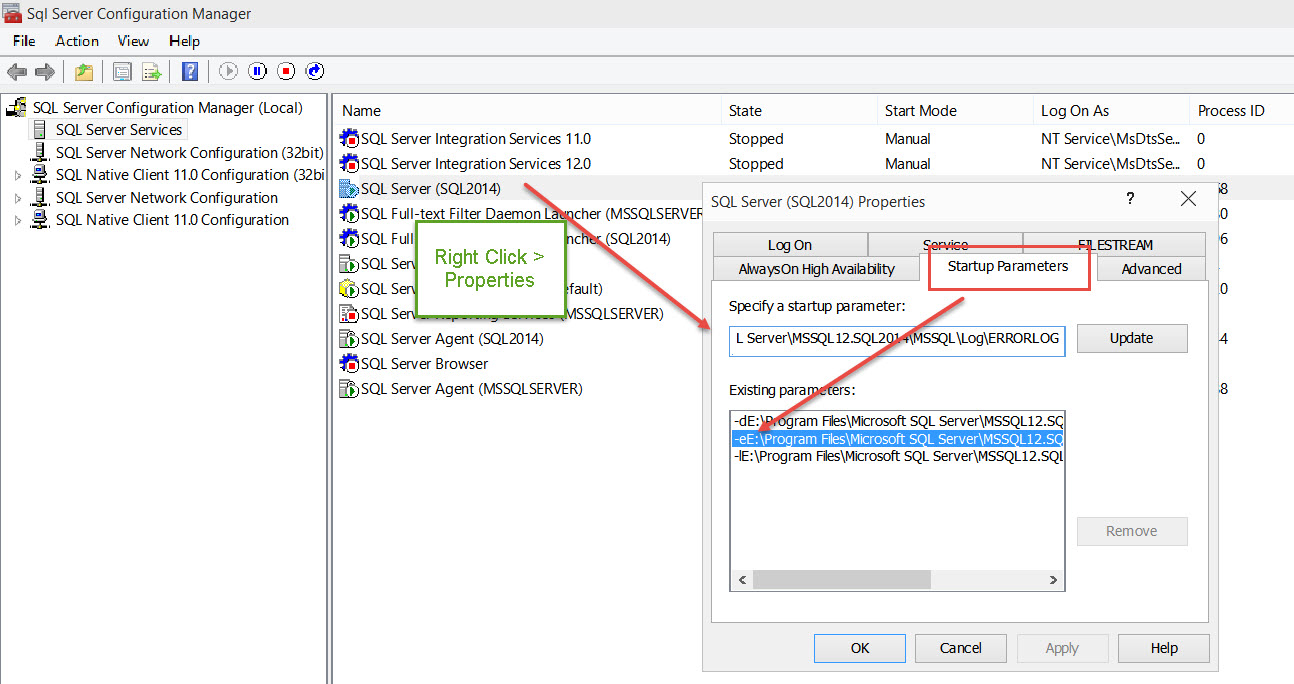
View the SQL Server error log by using SQL Server Management Studio or any text editor. For more information about how to view the error log, see Open Log File Viewer. By default, the error log is located at Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL. n \MSSQL\LOG\ERRORLOG and ERRORLOG.
Where is error line in SSMS?
This is a simple process by either pasting your code into a query window or opening the query file. You can then click the check mark or press Ctrl+F5 to parse the code. If your code is free of any syntax errors SSMS will return the message “The command(s) completed successfully”.
How do I find the error line in SQL Server?
ERROR_LINE returns the line number at which the error occurred. This happens regardless of the location of the ERROR_LINE call within the scope of the CATCH block, and regardless of the number of calls to ERROR_LINE .
How do I find a specific line in SQL?
If this feature is not turned and you need to go to a particular line number press CTRL + G to open the Go To Line dialog box, enter line number and click OK as shown below.
How do I repair SQL Server?
Launch the SQL Server Setup program (setup.exe) from SQL Server installation media. After prerequisites and system verification, the Setup program will display the SQL Server Installation Center page. Click Maintenance in the left-hand navigation area, and then click Repair to start the repair operation.
How do I view a stored procedure error in SQL Server?
Retrieving Error Information ERROR_STATE() returns the error state number. ERROR_PROCEDURE() returns the name of the stored procedure or trigger where the error occurred. ERROR_LINE() returns the line number inside the routine that caused the error. ERROR_MESSAGE() returns the complete text of the error message.
How do I recall a line in SQL?
To recall commands, choose Command | Recall from the menu bar to activate the command recall window. The command recall window displays the first line of the last 15 commands executed. and press Enter.
What is error command in SQL?
SQL keyword errors occur when one of the words that the SQL query language reserves for its commands and clauses is misspelled. For example, writing “UPDTE” instead of “UPDATE” will produce this type of error.
Is error function in SQL Server?
ERROR FUNCTIONS in Sql Server ERROR_SEVERITY() : Returns the Severity of the Error. ERROR_STATE() : Returns the State of the Error. ERROR_PROCEDURE(): Returns the name of the SP/UDF in which the error occurred. ERROR_LINE() : Returns the line number of the Sql statement which raised the error.
How do I find the error line in SQL Server?
ERROR_LINE returns the line number at which the error occurred. This happens regardless of the location of the ERROR_LINE call within the scope of the CATCH block, and regardless of the number of calls to ERROR_LINE .
Where is error line in SSMS?
This is a simple process by either pasting your code into a query window or opening the query file. You can then click the check mark or press Ctrl+F5 to parse the code. If your code is free of any syntax errors SSMS will return the message “The command(s) completed successfully”.
What is error command in SQL?
SQL keyword errors occur when one of the words that the SQL query language reserves for its commands and clauses is misspelled. For example, writing “UPDTE” instead of “UPDATE” will produce this type of error.
Is error function in SQL Server?
ERROR FUNCTIONS in Sql Server ERROR_SEVERITY() : Returns the Severity of the Error. ERROR_STATE() : Returns the State of the Error. ERROR_PROCEDURE(): Returns the name of the SP/UDF in which the error occurred. ERROR_LINE() : Returns the line number of the Sql statement which raised the error.
What is the error in SQL query?
The most common SQL error is a syntax error. What does syntax mean? Basically, it means a set arrangement of words and commands. If you use improper syntax, the database does not know what you’re trying to tell it.
How do I view a line in SQL Server?
Show/Hide Line Numbers in SSMS Click Tools–>Options as highlighted in green color below. In Options Dialog Box, Under Text Editor, in Transact-SQL, General –>Line Numbers . Enable the checkbox, If you want to Display/Show Line Numbers in SSMS.
How do I recall a line in SQL?
To recall commands, choose Command | Recall from the menu bar to activate the command recall window. The command recall window displays the first line of the last 15 commands executed. and press Enter.
How do I find a specific string in SQL Server?
SQL Server CHARINDEX() Function The CHARINDEX() function searches for a substring in a string, and returns the position. If the substring is not found, this function returns 0. Note: This function performs a case-insensitive search.
How do I know if my SQL Server database is corrupted?
There is a very general single line query to check the corruption in the database – SELECT * FROM msdb. dbo. suspect_pages. If there is no error in the database, then the result will show no rows.
How do I investigate SQL Server performance issues?
To establish that you have query performance issues on your SQL Server instance, start by examining queries by their execution time (elapsed time). Check if the time exceeds a threshold you have set (in milliseconds) based on an established performance baseline.
How do I view SQL errors in event viewer?
On the Search bar, type Event Viewer, and then select the Event Viewer desktop app. In Event Viewer, expand the Windows Logs folder, and select the Application event log. SQL Server events are identified by the entry MSSQLSERVER (named instances are identified with MSSQL$