MySQL: Error Handling. If an expected error is specified and that error occurs, mysqltest continues reading input. If the command is successful or a different error occurs, mysqltest aborts. If no expected error is specified, mysqltest aborts unless the command is successful.
How do I handle errors in MySQL?
MySQL: Error Handling. If an expected error is specified and that error occurs, mysqltest continues reading input. If the command is successful or a different error occurs, mysqltest aborts. If no expected error is specified, mysqltest aborts unless the command is successful.
How do you handle database errors?
We will look at three situations, using database exception handling options to manage errors in different ways: On the first error, roll back all changes and stop mapping execution. Roll back only the transaction with the error and continue. Roll back the top transaction and continue.
How do I view MySQL errors?
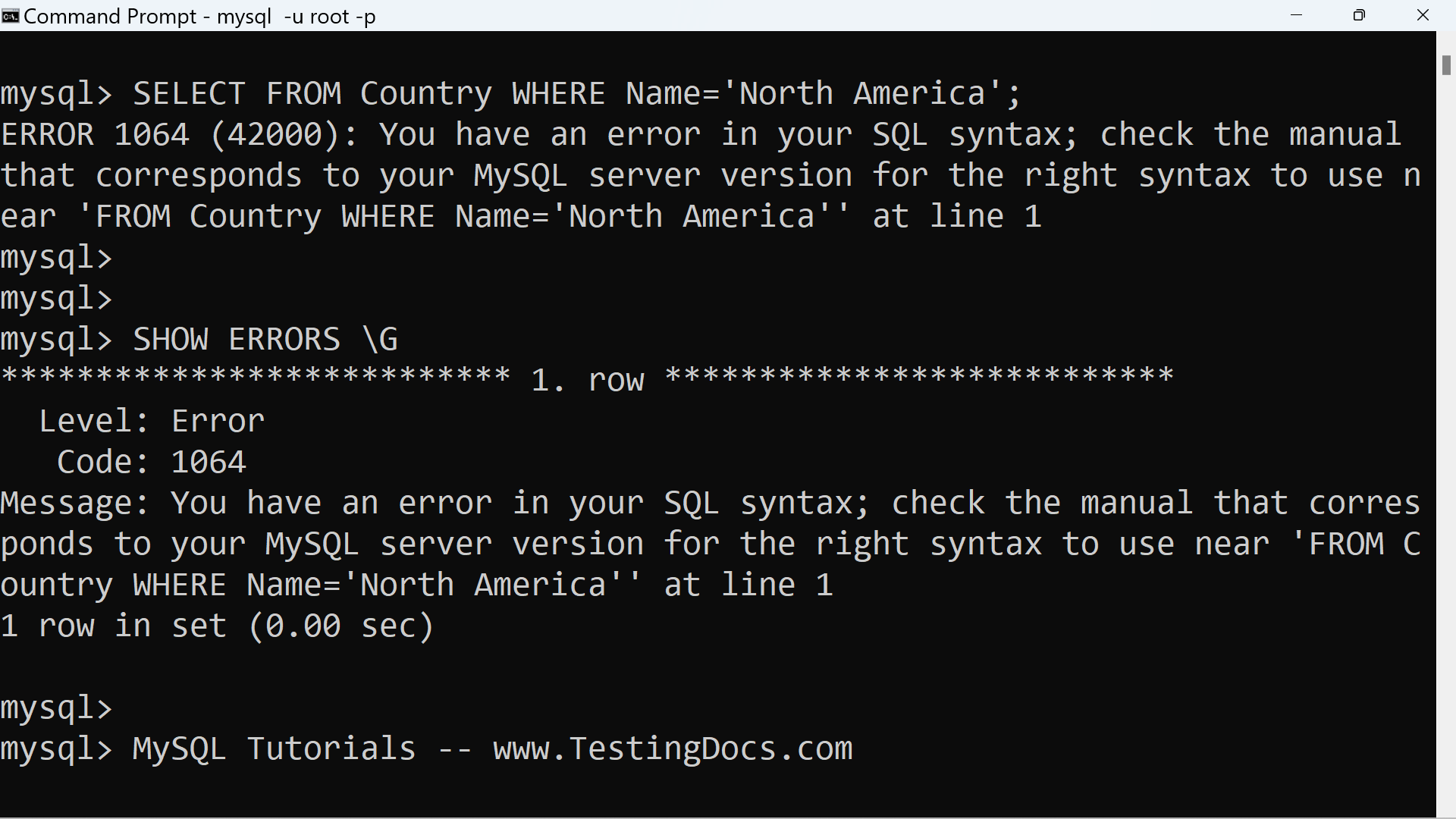
The SHOW COUNT(*) ERRORS statement displays the number of errors. You can also retrieve this number from the error_count variable: SHOW COUNT(*) ERRORS; SELECT @@error_count; SHOW ERRORS and error_count apply only to errors, not warnings or notes.
How do I handle errors in MySQL?
MySQL: Error Handling. If an expected error is specified and that error occurs, mysqltest continues reading input. If the command is successful or a different error occurs, mysqltest aborts. If no expected error is specified, mysqltest aborts unless the command is successful.
Does SQL have error handling?
Error handling in SQL Server gives us control over the Transact-SQL code. For example, when things go wrong, we get a chance to do something about it and possibly make it right again. SQL Server error handling can be as simple as just logging that something happened, or it could be us trying to fix an error.
What causes most error in database?
Hardware failures may include memory errors, disk crashes, bad disk sectors, and disk full of errors among others. Hardware failures can also be attributed to design errors, inadequate or poor quality control during fabrication, overloading (use of under-capacity components) and wear out of mechanical parts.
How do I find out why MySQL crashed?
The most common cause of crashes in MySQL is that it stopped or failed to start due to insufficient memory. To check this, you will need to review the MySQL error log after a crash. First, attempt to start the MySQL server by typing: sudo systemctl start mysql.
Where are MySQL error logs stored?
The MySQL server uses the error log to record information relevant to the error that prevents the server from starting. The error log is located in the data directory specified in your my. ini file.
What is MySQL error?
Lost connection to MySQL server Network conditions should be checked if this is a frequent error. If an error message like “Lost connection to MySQL server” appears while querying the database, it is certain that the error has occurred because of network connection issues.
How do I handle errors in MySQL?
MySQL: Error Handling. If an expected error is specified and that error occurs, mysqltest continues reading input. If the command is successful or a different error occurs, mysqltest aborts. If no expected error is specified, mysqltest aborts unless the command is successful.
How do you fix a random error?
While you can’t eradicate it completely, you can reduce random error by taking repeated measurements, using a large sample, and controlling extraneous variables. You can avoid systematic error through careful design of your sampling, data collection, and analysis procedures.
What are the 2 types of errors?
What are Type I and Type II errors? In statistics, a Type I error means rejecting the null hypothesis when it’s actually true, while a Type II error means failing to reject the null hypothesis when it’s actually false.
How many types of errors are there in SQL?
There are two types of errors in SQL Server: system errors and custom errors. System errors can be viewed in the sys. messages system view and are defined by SQL server. Therefore, when a system error occurs, SQL Server will log a system error and may take actions to fix the error.
What are the 3 types of SQL commands?
There are 3 main types of commands. DDL (Data Definition Language) commands, DML (Data Manipulation Language) commands, and DCL (Data Control Language) commands.
How do I check if a SQL query is correct?
To check syntax code: First, Drag and drop your SQL file or copy / paste your request directly into the editor above. Finally, you must click on “Check SQL syntax” button to display if there is an syntax error in your code.
What are the 4 sources of error?
Common sources of error include instrumental, environmental, procedural, and human. All of these errors can be either random or systematic depending on how they affect the results.
How do you check if a database is corrupted?
First, enable it by going to the database and choosing Properties from the right-click menu. Go to Recovery option, Choose Page Verify, and write CHECKSUM. Then Choose the Target Recovery Time in Seconds and click OK. The modern SQL Server versions enable the verify with CHECKSUM by default.
How do I restart MySQL?
First, open the Run window by using the Windows+R keyboard. Second, type services. msc and press Enter : Third, select the MySQL service and click the restart button.
Does MySQL have a log file?
MySQL Server has several logs that can help you find out what activity is taking place. By default, no logs are enabled, except the error log on Windows. (The DDL log is always created when required, and has no user-configurable options; see Section 5.4. 6, “The DDL Log”.)
How do I know if MySQL is running on port 3306?
To verify the port configuration for MySql DB use the ss command. You can also display the MySQL port by logging in to the MySQL database, use the -p flag to make remote connections to the MySQL database.
How do I handle errors in MySQL?
MySQL: Error Handling. If an expected error is specified and that error occurs, mysqltest continues reading input. If the command is successful or a different error occurs, mysqltest aborts. If no expected error is specified, mysqltest aborts unless the command is successful.