Systematic error can be minimized by routinely calibrating equipment, using controls in experiments, warming up instruments prior to taking readings, and comparing values against standards. While random errors can be minimized by increasing sample size and averaging data, it’s harder to compensate for systematic error.
How can systematic error be eliminated or reduced?
Systematic error, as stated above, can be eliminated—not totally, but usually to a sufficient degree. This elimination process is called “calibration.” Calibration is simply a procedure where the result of measurement recorded by an instrument is compared with the measurement result of a standard.
What causes systematic error?
The two primary causes of systematic error are faulty instruments or equipment and improper use of instruments. There are other ways systematic error can happen in your experiments, and these could be the research data, confounding, the procedure you used to gather your data, and even your analysis method.
How can we minimize random errors and systematic errors?
While you can’t eradicate it completely, you can reduce random error by taking repeated measurements, using a large sample, and controlling extraneous variables. You can avoid systematic error through careful design of your sampling, data collection, and analysis procedures.
What are the types of systematic errors?
There are four types of systematic error: observational, instrumental, environmental, and theoretical.
How can systematic errors be minimized or eliminated answers?
Systematic errors can be minimised by improving experimental techniques, selecting better instruments and removing personal bias as far as possible. For a given set up, these errors may be estimated to a certain extent and the necessary corrections may be applied to the readings.
How can systematic errors be reduced in chemistry?
Calibration, when feasible, is the most reliable way to reduce systematic errors. To calibrate your experimental procedure, you perform it upon a reference quantity for which the correct result is already known.
What is one way to eliminate error in an experiment?
Solution. There are several ways to avoid experimental errors in a scientific investigation. These ways include taking the measurements accurately, conducting a controlled laboratory experiment with a large sample size, and testing the validity of the investigation through peer review and replication.
How are systematic errors eliminated Mcq?
How systematic errors are eliminated? Explanation: The possible way of eliminating systematic error is the replacement of instruments. Systematic errors are caused by poor instrument calibration.
What does systematic error affect?
Systematic errors are errors that affect the accuracy of a measurement. Systematic errors cause readings to differ from the true value by a consistent amount each time a measurement is made, so that all the readings are shifted in one direction from the true value.
What is meaning of systematic error?
: an error that is not determined by chance but is introduced by an inaccuracy (as of observation or measurement) inherent in the system.
What do you mean by systematic error?
: an error that is not determined by chance but is introduced by an inaccuracy (as of observation or measurement) inherent in the system.
What could reduce systematic errors Quizizz?
Random errors can be reduced by taking the average of several measurements. Random errors are always caused by the person taking the measurement. A systematic error cannot be reduced by adjusting the apparatus.
How systematic errors are eliminated ?( COA?
Solution : Systematic errors can be eliminated by finding the cause of errors and then removing them.
What is a systematic error Mcq?
The difference between a sample statistic and the corresponding parameter is known as. Standard error. Sampling error. Systematic error.
How many systematic errors are eliminated?
How systematic errors are eliminated? Explanation: The possible way of eliminating systematic error is the replacement of instruments. Systematic errors are caused by poor instrument calibration.
How do you handle systematic errors?
Systematic error can be minimized by routinely calibrating equipment, using controls in experiments, warming up instruments prior to taking readings, and comparing values against standards. While random errors can be minimized by increasing sample size and averaging data, it’s harder to compensate for systematic error.
What are 3 types of systematic errors?
There are four types of systematic error: observational, instrumental, environmental, and theoretical.
What are some of the causes of random error systematic error?
Random Errors. Systematic errors are usually caused by measuring instruments that are incorrectly calibrated or are used incorrectly. However, they can creep into your experiment from many sources, including: A worn out instrument.
Which of the following is not a systematic error?
Personal error is not a systematic error.
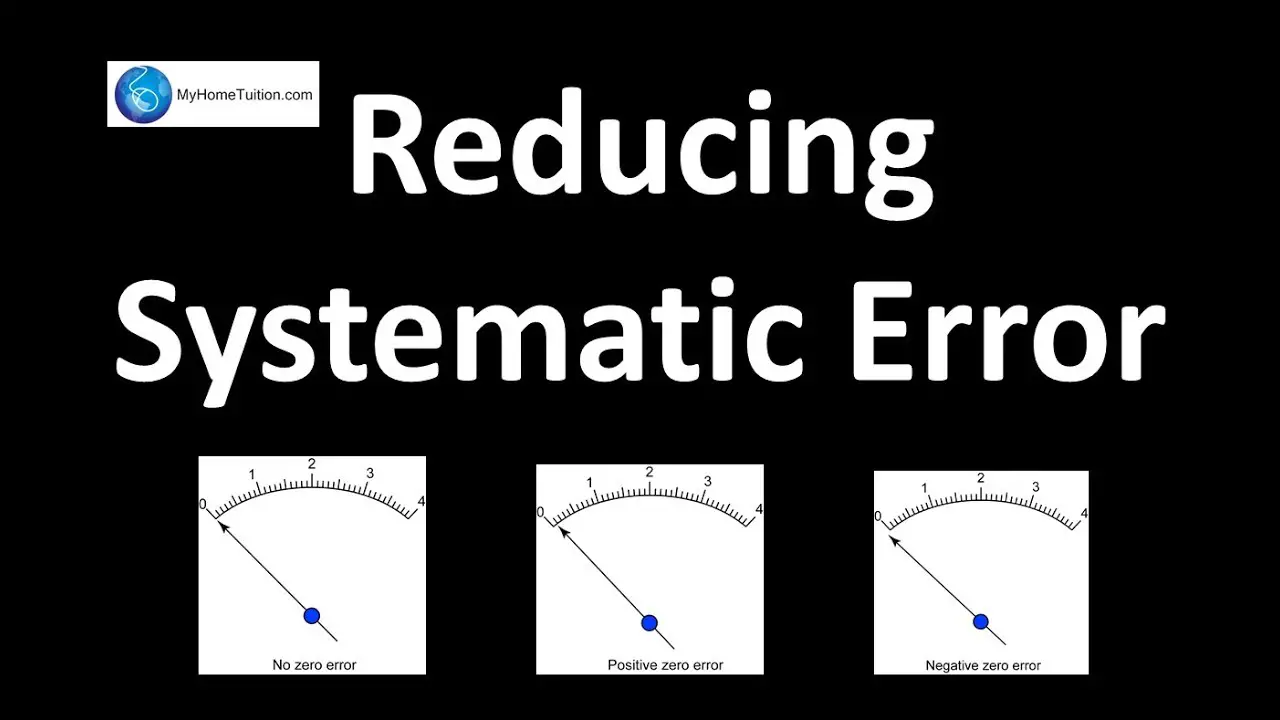
What is the difference between a systematic error and a zero error?
The magnitude of systematic error remains constant because the defect is inbuilt inside the apparatus. Whereas, the magnitude of the random error is variable. The zero error and the incorrect calibration of apparatus cause the systematic error.
How symptomatic errors are eliminated?
Explanation: Systematic errors can also be detected by measuring already known quantities. … Such errors cannot be removed by repeating measurements or averaging large numbers of results. A common method to remove systematic error is through calibration of the measurement instrument.