The most common technique for detecting faults is the time-frequency analysis technique. For a rotating machine, the rotational speed of the machine (often known as the RPM), is not a constant, especially not during the start-up and shutdown stages of the machine.
How do you check for system faults?
The most common technique for detecting faults is the time-frequency analysis technique. For a rotating machine, the rotational speed of the machine (often known as the RPM), is not a constant, especially not during the start-up and shutdown stages of the machine.
What are system faults?
System Fault means a malfunction or error in UNISS such that the System is unable to perform the functions it is required to perform for the time being.
What is fault diagnosis system?
Fault diagnosis is determining which fault occurred, in other words, determining the root(s) of the out of control status. Process fault diagnosis involves interpreting the current status of the plant given sensor readings and process knowledge.
How would you isolate a fault in a system?
Isolating the location of electrical faults It is accomplished by building in test circuits and/or by dividing operations into multiple regions or components that can be monitored separately. After fault isolation is accomplished, parts can be replaced manually or automatically.
How do you check for system faults?
The most common technique for detecting faults is the time-frequency analysis technique. For a rotating machine, the rotational speed of the machine (often known as the RPM), is not a constant, especially not during the start-up and shutdown stages of the machine.
What is an example of a system failure?
Recent examples of how companies have been impacted by systems failure include: An airline facing a computer outage caused by a fire impacting its data centre at the group’s headquarters. Around 2,300 flights were cancelled and hundreds of thousands of passengers were delayed.
What does system failure mean?
A system failure is a problem either with hardware (other than disk) or with operating system software that causes your system to end abnormally. After your service representative has corrected the problem, follow the procedure to start your system after an abnormal end.
Why do we diagnose faults?
Fault diagnosis has become an area of primary importance in modern process automation. It provides the prerequisites for fault tolerance, reliability or security, which constitute fundamental design features in complex engineering systems.
What’s the meaning of fault finding?
faultfinding. noun. Definition of faultfinding (Entry 2 of 2) : petty, nagging, or unreasonable criticism.
What is fault in software testing with example?
Fault : It is an incorrect step in any process and data definition in computer program which is responsible of the unintended behavior of any program in the computer. Faults or bugs in a hardware or software may cause errors. An error can be defined as a part of the system which will lead to the failure of the system.
What are the causes of faults?
The movement of the plates is incredibly slow, but since the plates are so big, when they bump into and rub against each other, we get massive events like volcanoes and earthquakes. And along these plate boundaries, we find faults. Faults are cracks in the earth’s crust where movement occurs on at least one side.
What causes fault computer?
Wear and tear – A computer with case fans, heat sinks, and hard drives that have moving parts can all experience wear and tear that over time and will eventually fail. Bad interface board or IC – A circuit board used to control hardware can become bad because of any of the reasons mentioned above.
What does a fault condition mean?
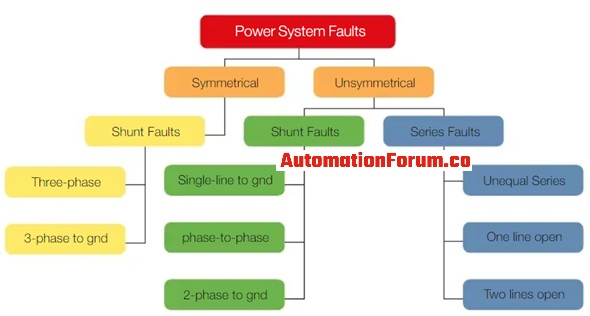
A fault condition occurs when one or more electrical conductors short to each other or to ground. The fault types are classified as: phase to ground, double phase to ground, three phase to ground, phase to phase, and three phase.
How do you check for system faults?
The most common technique for detecting faults is the time-frequency analysis technique. For a rotating machine, the rotational speed of the machine (often known as the RPM), is not a constant, especially not during the start-up and shutdown stages of the machine.
What is systematic troubleshooting?
Maintenance troubleshooting usually follows a systematic, four-step approach; identify the problem, plan a response, test the solution, and resolve the problem. Steps one to three are often repeated multiple times before a resolution is reached.
What is the main cause of failure of the system?
System failures may result from a hard drive with bad sectors, causing the operating system to not be able to read data from the hard drive. A failing motherboard can cause a system failure because the computer is not able to process requests or operate in general.
What causes operating system failure?
An operating system failure can be caused by a hardware malfunction or a software crash, and it usually results in the inability of the operating system to boot. The OS may repeatedly reboot and freeze with an error message displayed on the screen, or it may completely stop running with no notifications.
What is the risk of system failure?
Risk of systems failure and communication network failure due to power fluctuations and absence of effective UPS protection. Hardware or LAN Failure. Loss of data due to inadequate backup facility or procedure. Poorly trained, poorly skilled IT staff that lack sufficient knowledge.
What are the types of computer system failure?
Today, we talked about the 3 types of computer failures, minor, major, catastrophic, and how to have a plan in place to protect your office.
What is diagnostic system in computer?
A diagnostic program (also known as a Test Mode) is an automatic computer program sequence that determines the operational status within the software, hardware, or any combination thereof in a component, a system, or a network of systems.
Why do we need to diagnose faults of computer systems and networks?
Diagnosis is an important function in computer systems, both for manual repair and for automatic reconfiguration in fault-tolerant systems. A fault may cause the system to violate its requirements, i.e., to fail.