Reread procedures outlined in manuals from before the experiment and your own reflective write up of the experimental steps. Recall the mechanisms you used and any problems that may have come up. This may include measurements in weighing and alterations of steps as necessary. Mark down changes from procedure.
What is error in lab report?
Differences between single measurements are due to error. Errors are differences between observed values and what is true in nature. Error causes results that are inaccurate or misleading and can misrepresent nature. Scientifically accepted values are scientists’ current best approximations, or descriptions, of nature.
What are the 3 types of errors in science?
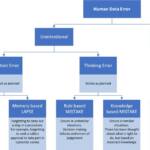
Three general types of errors occur in lab measurements: random error, systematic error, and gross errors. Random (or indeterminate) errors are caused by uncontrollable fluctuations in variables that affect experimental results.
What is the most common laboratory error?
The most common lab errors in the collection of the samples and reporting are: Wrong labeling of the sample. The technique of the blood sample: This is very important to follow an excellent technique to collect good quality blood.
What are 3 sources of error in an experiment?
Physical and chemical laboratory experiments include three primary sources of error: systematic error, random error and human error.
What is human error in a lab?
Human error in chemical analysis is any action or lack thereof that leads to exceeding the tolerances of the conditions required for the normative work of the measuring/testing (chemical analytical) system with which the human interacts.
What types of errors can cause invalid test results?
Three main reasons that incorrect data is provided as a result of lab testing is that the specimen is associated with the wrong person, possibly because a patient is misidentified, a specimen is mislabeled, or information is entered incorrectly into the computer.
What are the 4 steps of error analysis?
Error Analysis Steps For instance, Corder in (1974) mentions five steps, they are Selection, identification, classification, explanation and evaluation. In (1997), Ellis proposes four main steps, identification, description, explanation, and evaluation.
How do you explain error analysis?
Error analysis is a method commonly used to identify the cause of student errors when they make consistent mistakes. It is a process of reviewing a student’s work and then looking for patterns of misunderstanding. Errors in mathematics can be factual, procedural, or conceptual, and may occur for a number of reasons.
What is human error in a lab?
Human error in chemical analysis is any action or lack thereof that leads to exceeding the tolerances of the conditions required for the normative work of the measuring/testing (chemical analytical) system with which the human interacts.
How often do lab errors occur?
Laboratory errors have a reported frequency of 0.012–0.6 % of all test results. Patient safety is a managerial issue which can be enhanced by implementing active system to identify and monitor quality failures.
What can happen if a laboratory result is incorrect due to technical error?
What can happen if a laboratory result is incorrect due to technician error? If they are not correct, you could cause a patient to receive medication that is unnecessary or to receive other procedures that the patients don’t need. This could lead to legal action from the patient against the physician and/or facility.
What do you call error in research?
In scientific research, measurement error is the difference between an observed value and the true value of something. It’s also called observation error or experimental error.
What type of error is accuracy?
Accuracy has two definitions: More commonly, it is a description of only systematic errors, a measure of statistical bias of a given measure of central tendency; low accuracy causes a difference between a result and a true value; ISO calls this trueness.
What types of errors can cause invalid test results?
Three main reasons that incorrect data is provided as a result of lab testing is that the specimen is associated with the wrong person, possibly because a patient is misidentified, a specimen is mislabeled, or information is entered incorrectly into the computer.
Why do lab errors occur?
Many mistakes in the Total Testing Process are called “laboratory errors”, although these may be due to poor communication, action taken by others involved in the testing process (e.g., physicians, nurses and phlebotomists), or poorly designed processes, all of which are beyond the laboratory’s control.
What is an example of human error?
Human Error is an action or inaction Human error is a generic term that involves all those instances where a planned activity fails to achieve its intended outcome. For example, forgetting to set your park brake in your car or misapplying your vehicle brakes in wet and slippery road conditions.
What is total allowable error?
Quality goals, also expressed as total allowable error (TEa), specify the maximum amount of error—both imprecision and bias combined—that is allowed for an assay.
What are the negative consequences of laboratory error?
Any error during the laboratory testing process can affect patient care, including delay in reporting, unnecessary redraws, misdiagnosis, and improper treatment. Sometimes, these errors may even be fatal (e.g., acute hemolytic reaction after incompatible blood transfusion caused by an error in patient identification).
What is the difference between error and mistake?
Mistakes are an accident. You know it’s wrong, but the wrong word slips out. An error, on the other hand, is something you don’t know. It’s grammar you haven’t learned yet or vocabulary you haven’t learned the nuance of yet.
What is an error analysis in chemistry?
What is an error. “Error” in Chemistry is defined as the difference between the true result (or accepted true result) and the measured result. If the error in the analysis is large, serious consequences may result. As reliability, reproducibility, and accuracy are the basis of analytical chemistry.
What are the stages of error analysis?
Corder (1974) discusses the error analysis in five stages: collection of data containing errors, classification of errors, identification of errors, disclosure of errors and evaluation of errors.