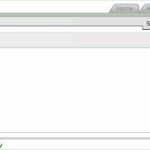
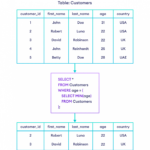
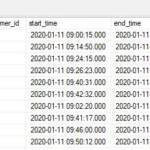
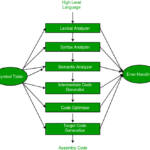
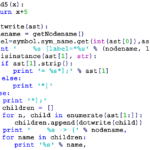Generally errors are classified into three types: systematic errors, random errors and blunders.
What are types of errors?
There are three types of errors: systematic, random, and human error.
How many types of error are there in physics?
Basically, there are three types of errors in physics, random errors, blunders, and systematic errors.
What are types of errors?
There are three types of errors: systematic, random, and human error.
How many types of error are there in physics?
Basically, there are three types of errors in physics, random errors, blunders, and systematic errors.
What is called error?
An error is something you have done which is considered to be incorrect or wrong, or which should not have been done.
What is Type 2 error in statistics?
A Type II error means not rejecting the null hypothesis when it’s actually false. This is not quite the same as “accepting” the null hypothesis, because hypothesis testing can only tell you whether to reject the null hypothesis.
What are errors in computer?
An error in computer data is called Bug. A software bug is an error, flaw, failure or fault in a computer program or system that causes it to produce an incorrect or unexpected result, or to behave in unintended ways. …
What is method error?
They can be defined as the difference between the value obtained during the process of measurement and the real value of the magnitude of measurement. 5. These errors, when significant and of great magnitude, affect the reliability of results by increasing or decreasing the real differences among the studied variables.
How many types of error are there in physics class 11?
There are mainly six types of errors, which can occur while measuring physical quantities.
What are types of errors?
There are three types of errors: systematic, random, and human error.
How many types of error are there in physics?
Basically, there are three types of errors in physics, random errors, blunders, and systematic errors.
What is an zero error?
Answer: It is a type of error in which an instrument gives a reading when the true reading at that time is zero. For example needle of ammeter failing to return to zero when no current flows through it.
What type of error is accuracy?
Accuracy has two definitions: More commonly, it is a description of only systematic errors, a measure of statistical bias of a given measure of central tendency; low accuracy causes a difference between a result and a true value; ISO calls this trueness.
What is source of error?
Common sources of error include instrumental, environmental, procedural, and human. All of these errors can be either random or systematic depending on how they affect the results. Instrumental error happens when the instruments being used are inaccurate, such as a balance that does not work (SF Fig.
What are Type 1 and Type 2 errors in statistics?
A type I error (false-positive) occurs if an investigator rejects a null hypothesis that is actually true in the population; a type II error (false-negative) occurs if the investigator fails to reject a null hypothesis that is actually false in the population.
What causes type1 error?
Type 1 errors can result from two sources: random chance and improper research techniques. Random chance: no random sample, whether it’s a pre-election poll or an A/B test, can ever perfectly represent the population it intends to describe.
What are 3 sources of error in an experiment?
Physical and chemical laboratory experiments include three primary sources of error: systematic error, random error and human error.
Is Type 1 or Type 2 error worse?
Hence, many textbooks and instructors will say that the Type 1 (false positive) is worse than a Type 2 (false negative) error. The rationale boils down to the idea that if you stick to the status quo or default assumption, at least you’re not making things worse. And in many cases, that’s true.
How do you find a Type 2 error?
How to Calculate the Probability of a Type II Error for a Specific Significance Test when Given the Power. Step 1: Identify the given power value. Step 2: Use the formula 1 – Power = P(Type II Error) to calculate the probability of the Type II Error.
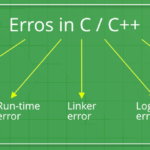
What is error in C language?
Error is an illegal operation performed by the user which results in abnormal working of the program. Programming errors often remain undetected until the program is compiled or executed. Some of the errors inhibit the program from getting compiled or executed.
What is software error?
Software Error means a reproducible defect or combination thereof in the Software that results in a failure of the Software when used in accordance with the Documentation.