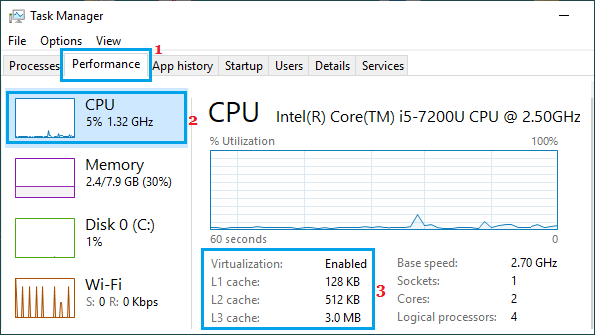
It’s hard to say how much processor cache you need, but 3-6MB is typical in current laptops and PCs. But given the performance benefits, more cache and a slower clock speed is likely to be faster than the opposite.
What is a good cache memory size?
The higher the demand from these factors, the larger the cache needs to be to maintain good performance. Disk caches smaller than 10 MB do not generally perform well. Machines serving multiple users usually perform better with a cache of at least 60 to 70 MB.
Is 8 MB cache good in laptop?
It holds frequently-used data and instructions so that they are immediately available to the CPU when used again. The higher the cache memory, the faster your computer. Cache memory is typically measured in Megabytes (MB). An 8 MB of cache memory is recommended.
Is 8MB cache good?
So, 8MB doesn’t speed up all your data access all the time, but it creates (4 times) larger data “bursts” at high transfer rates. Benchmarking finds that these drives perform faster – regardless of identical specs.” “8mb cache is a slight improvement in a few very special cases.
Is 12 MB cache good?
Some people say that you need about 1MB of cache if you are just browsing the Internet, whereas others say that 8MB should be more than enough. It really depends on what you do with your computer most of the time. If you are a gamer, then you might want to increase the cache to 12MB at least.
What is normal cache size?
Common cache line sizes are 32, 64 and 128 bytes. A cache can only hold a limited number of lines, determined by the cache size.
Is bigger cache always better?
In multiprocess environment with several active processes bigger cache size is always better, because of decrease of interprocess contention.
Is 6 MB L3 cache good?
It’s a decent amount of L3 cache for a multicore desktop processor, up to about 4 cores, I’d reckon. From 4 to 8 you’re pushing it, and above 8 it seems undersized.
Which is better 6MB cache or 8MB cache?
Larger caches can store more data and can lead to faster performance in some applications. Larger cache size however does not necessarily mean faster performance in all tasks.
Is 8MB cache good for gaming?
Honorable. 6MB, 8MB only help those doing very CPU intensive processes (IE: heavy duty video editing). In gaming you’ll see absolutely no difference at all.
Is 16MB cache memory good?
Overall, most CPUs with 16MB L3 cache are good gaming CPUs. For example, a Ryzen 5 5600G is an excellent gaming CPU and only has 16MB L3 cache.
Does cache size matter?
Cache size is important as it reduces the probability that there will be a cache miss. Cache miss’ are expensive because the CPU has to go to the main memory to access the memory address, this takes much longer and hence results in a slower computer.
How cache affects performance?
Cache memory is a large determinant of system performance. The larger the cache, the more instructions can be queued and carried out. Storing instructions in cache reduces the amount of time it takes to access that instruction and pass it to a CPU core.
Is 32 MB of L3 cache good?
> 32MB L3 Cache is going to be very useful for certain types of Application. Are there applications where more cache is actively detrimental? General rule of thumb is that bigger caches are slower to access.
Is cache memory good for gaming?
More cache means that the CPU doesn’t need to fetch data from your system RAM, which could increase latency by 10 times or more. That doesn’t mean more cache is inherently better for gaming. It largely depends on the game, but more importantly, when the game was made.
Is 32MB cache good for gaming?
There is virtually no difference in performance.
Is 6 MB cache good?
It is much better than 4mb of cache but much worse than 8 mb of cache.
Is 8MB cache good for gaming?
Honorable. 6MB, 8MB only help those doing very CPU intensive processes (IE: heavy duty video editing). In gaming you’ll see absolutely no difference at all.
What is 8 MB cache in processor?
The 8 MB you are talking about, is the amount of L3 cache found in some high level CPUs like i7 and some xeons. The optimal amount of cache is obtained by a calculus between the maximum amount of RAM for the system, the number of physical cores and the CPU cycles.
Which cache memory is faster?
Level 1 (L1) is the fastest type of cache memory since it is smallest in size and closest to the processor. Level 2 (L2) has a higher capacity but a slower speed and is situated on the processor chip.
Is 64mb cache good for gaming?
It won’t make a huge difference. Games are generally optimized to do large sequential reads, instead of small random reads, so the cache doesn’t help very much.
What are the 3 levels of cache memory?
The more cache there is, the more data can be stored closer to the CPU. Cache is graded as Level 1 (L1), Level 2 (L2) and Level 3 (L3): L1 is usually part of the CPU chip itself and is both the smallest and the fastest to access. Its size is often restricted to between 8 KB and 64 KB.