Cache is a small amount of memory which is a part of the CPU – closer to the CPU than RAM . It is used to temporarily hold instructions and data that the CPU is likely to reuse.
Is cache on the CPU or motherboard?
Some systems also have a third layer of cache L3 which again could be located on either the CPU or the motherboard. Older 486 systems, for example, had L1 in the CPU and an optional L2 on the motherboard. Most modern systems have all the cache on the CPU. Around that time all cache on the motherboard was also common.
Is cache stored in RAM or CPU?
RAM is the main type of computer data storage that stores information and program processes. It’s farther away from the CPU than cache memory and isn’t as fast; cache is actually 100 times faster than standard RAM. If cache is so fast, why isn’t all data stored there?
Where is the CPU cache located?
The cache memory is located very close to the CPU, either on the CPU chip itself or on the motherboard in the immediate vicinity of the CPU and connected by a dedicated data bus.
Do all CPUs have cache?
Every processor has a small amount of cache, with smaller CPUs getting perhaps just a few kilobytes while large CPUs can have many megabytes worth of cache. But you might be wondering why cache is necessary at all when we have RAM, especially when a single stick of RAM can have several gigabytes of memory.
Is cache on the CPU or motherboard?
Some systems also have a third layer of cache L3 which again could be located on either the CPU or the motherboard. Older 486 systems, for example, had L1 in the CPU and an optional L2 on the motherboard. Most modern systems have all the cache on the CPU. Around that time all cache on the motherboard was also common.
Does motherboard have cache?
The data or instruction the CPU needs to operate on is usually found in one of three places: cache memory, the motherboard memory (main memory), or the hard drive. Cache memory is a very fast type of memory designed to increase the speed of processor operations.
Where does cache sit between?
Cache memory sits between the CPU and main memory, which allows it to be accessed relatively quickly. Depending on the processor, cache memory may be split into multiple levels, including L1 and L2 (and possibly L3).
Where is cache stored?
The data in a cache is generally stored in fast access hardware such as RAM (Random-access memory) and may also be used in correlation with a software component. A cache’s primary purpose is to increase data retrieval performance by reducing the need to access the underlying slower storage layer.
Is cache a part of RAM?
The RAM that is used for the temporary storage is known as the cache. Since accessing RAM is significantly faster than accessing other media like hard disk drives or networks, caching helps applications run faster due to faster access to data.
How do I increase my CPU cache?
With newer systems, the most effective way to increase cache memory is to replace the current CPU with one that has a higher capacity. This will automatically make it possible to increase the size of the cache memory, as well as enhance the processor speed and overall performance of the system.
Is cache the same as memory?
RAM stands for random access memory. Any file or application actively in use on a computer is stored in RAM primary memory. Cache is a smaller memory configuration reserved from main memory to make computer operations more efficient.
Is 8 MB cache good?
So, 8MB doesn’t speed up all your data access all the time, but it creates (4 times) larger data “bursts” at high transfer rates. Benchmarking finds that these drives perform faster – regardless of identical specs.” “8mb cache is a slight improvement in a few very special cases.
Is 12 MB cache good?
Some people say that you need about 1MB of cache if you are just browsing the Internet, whereas others say that 8MB should be more than enough. It really depends on what you do with your computer most of the time. If you are a gamer, then you might want to increase the cache to 12MB at least.
Does CPU cache affect gaming?
More cache means that the CPU doesn’t need to fetch data from your system RAM, which could increase latency by 10 times or more. That doesn’t mean more cache is inherently better for gaming. It largely depends on the game, but more importantly, when the game was made.
Which cache level is on the motherboard?
A Level 3 (L3) cache is a specialized cache that that is used by the CPU and is usually built onto the motherboard and, in certain special processors, within the CPU module itself.
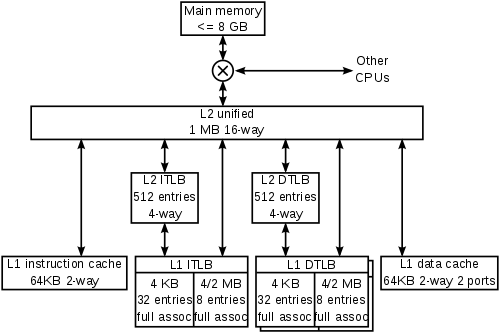
Where is L1 L2 and L3 cache located?
L1 is located on CPU chip, L2 is located between processor and main memory, but there is a point to know that in some system L2 is located on CPU chip while in some other system L2 is located on mother board itself, and L3 is constantly located on main board chip.
Is 12 MB cache good for gaming?
If you are a gamer, then you might want to increase the cache to 12MB at least. The newly released processors have small L2 caches, but this does not mean that they are slow when it comes to processing programs. The processor cores are smaller, but there are a lot more of them.
Which cache on the CPU is used first?
At the highest level, the most frequently used information – say, the instructions in a loop which execute repeatedly – is stored directly on a special section of the processor chip, called Level 1 (L1) cache. This is the fastest memory of all.
Is cache on the CPU or motherboard?
Some systems also have a third layer of cache L3 which again could be located on either the CPU or the motherboard. Older 486 systems, for example, had L1 in the CPU and an optional L2 on the motherboard. Most modern systems have all the cache on the CPU. Around that time all cache on the motherboard was also common.
What is CPU cache used for?
Memory Caches A memory cache, also called a “CPU cache,” is a memory bank that bridges main memory and the processor. Comprising faster static RAM (SRAM) chips than the dynamic RAM (DRAM) used for main memory, the cache allows instructions to be executed and data to be read and written at higher speed.
Does CPU have memory?
No, the CPU doesn’t contain Main Memory. A central processing unit (CPU) is the electronic circuitry within a computer that carries out the instructions of a computer program by performing the basic arithmetic, logical, control and input/output (I/O) operations specified by the instructions.