Put simply, syntax refers to grammar, while semantics refers to meaning. Syntax is the set of rules needed to ensure a sentence is grammatically correct; semantics is how one’s lexicon, grammatical structure, tone, and other elements of a sentence coalesce to communicate its meaning.
Is grammar a part of syntax?
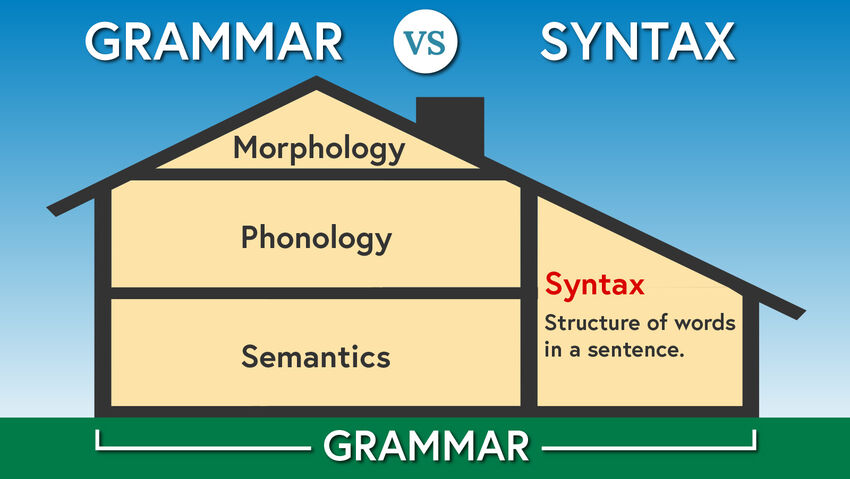
Syntax is a part of grammar, the overarching rules dictating the structure of a language. All syntax rules are grammar rules, but not all grammar rules are syntax rules.
Is grammar part of semantics?
Grammar refers to the structure of language: how words are used in speech and how groups of words are put together in patterns. Semantics refers to the literal meaning of the words we use. Both concepts are connected to the use of language, but are different aspects of language function.
Is grammar a syntax or morphology?
Grammar is made up of morphology and syntax. Morphology refers to the rules that govern word structure and construction, whereas syntax refers to the rules that govern word sequence and sentence structure.
Is grammar a subset of syntax?
Because syntax is a part of grammar, all syntactical rules are also grammar rules. Here are some elements of syntax: Parts of a sentence: Subject, predicate, object, direct object. Phrases: A group of words without a subject or predicate.
Whats the difference between syntax and grammar?
Grammar and syntax are two different concepts under linguistics and grammar rules. Syntax dictates rules on word arrangement, while grammar indicates overall language laws. Grammar is also the entire system of language rules that includes syntax.
What part of language is grammar?
grammar, rules of a language governing the sounds, words, sentences, and other elements, as well as their combination and interpretation. The word grammar also denotes the study of these abstract features or a book presenting these rules.
What concepts fall under grammar?
Topics include grammatical categories (nouns, verbs, adjectives, prepositions, etc.), syntactic roles (subject, object, head, complement), phrase structure (noun phrases, verb phrases, etc.), and inflection (e.g. case and number for nouns; tense, aspect and modality for verbs; grade and comparison for adjectives).
Is grammar an example of syntax?
Syntax is a subdivision of grammar. Grammar comprises the entire system of rules for a language, including syntax. Syntax deals with the way that words are put together to form phrases, clauses, and sentences.
What is grammar in linguistics?
For linguists, grammar is simply the collection of principles defining how to put together a sentence. One sometimes hears people say that such-and-such a language ‘has no grammar’, but that is not true of any language. Every language has restrictions on how words must be arranged to construct a sentence.
Does morphology include grammar?
Morphology includes the grammatical processes of inflection (q.v.) and derivation. Inflection marks categories such as person, tense, and case; e.g., “sings” contains a final -s, marker of the 3rd person singular, and the German Mannes consists of the stem Mann and the genitive singular inflection -es.
Why is syntax important in grammar?
“Syntax skills help us understand how sentences work—the meanings behind word order, structure, and punctuation. By providing support for developing syntax skills, we can help readers understand increasingly complex texts” (Learner Variability Project).
What are the three elements of syntax?
As outlined in Syntactic Structures (1957), it comprised three sections, or components: the phrase-structure component, the transformational component, and the morphophonemic component.
What is grammatical subject in syntax?
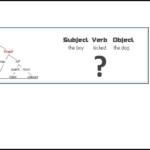
The subject is a grammatical term used to describe the nouns, pronouns, and noun phrases that occur before the verb in a sentence. Thus, the subject describes a position in the sentence. When the verb is in the active form, the subject of the sentence is the “do-er” or agent—who or what—that causes the action.
What are the parts of syntax?
Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituency), agreement, the nature of crosslinguistic variation, and the relationship between form and meaning (semantics).
What is included in syntax?
Syntax covers topics like word order and grammar rules, such as subject-verb agreement or the correct placement of direct and indirect objects. Syntax is essential to understanding constituency, the term for multiple words acting as a single unit.
What are the three parts of syntax?
As outlined in Syntactic Structures (1957), it comprised three sections, or components: the phrase-structure component, the transformational component, and the morphophonemic component.
Is syntax the same as semantics?
Syntax refers to the set of rules that create sentence structure. Writers can also call these the grammar rules. Semantics refers to the study of the meaning of sentences. Sometimes, grammatically correct words do not make sense, even when they are correct grammatically.
What are the types of grammar?
In English, there are two kinds of grammar: prescriptive grammar & descriptive grammar.
What is an example of syntax in language?
Syntax in English sets forth a specific order for grammatical elements like subjects, verbs, direct and indirect objects, etc. For example, if a sentence has a verb, direct object, and subject, the proper order is subject → verb → direct object.
What are examples of semantics?
Semantics is the study of meaning in language. It can be applied to entire texts or to single words. For example, “destination” and “last stop” technically mean the same thing, but students of semantics analyze their subtle shades of meaning.
What category is the in grammar?
A determiner is a word that determines the kind of reference a noun or noun phrase has, for example a, an, the, every, some. It distinguishes between referents/entities that are identifiable in a given context (definite noun phrases) and entities which are not (indefinite noun phrases).