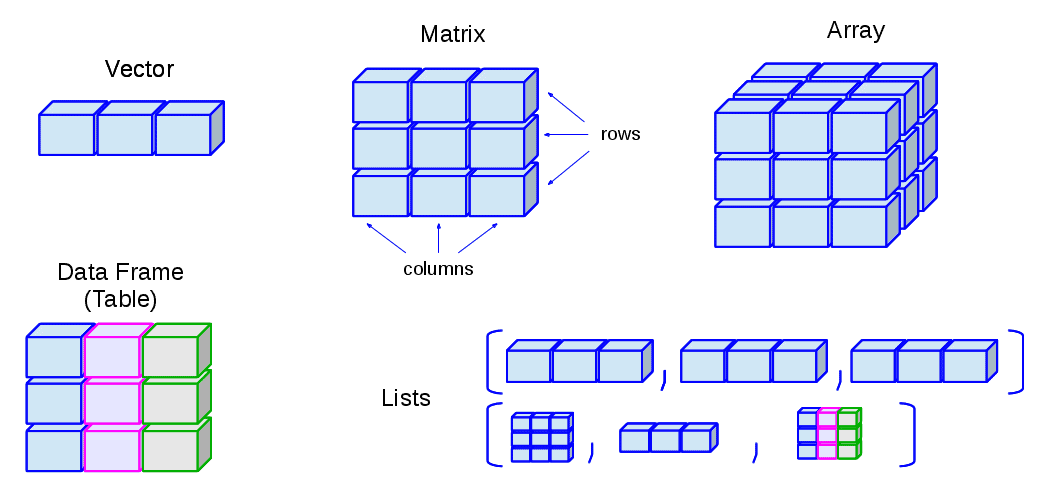
A vector is a one-dimensional data structure and all of its elements are of the same data type. A factor is one-dimensional and every element must be one of a fixed set of values, called the levels of the factor.
Is vector a data structure in C++?
In C++, vectors are used to store elements of similar data types. However, unlike arrays, the size of a vector can grow dynamically. That is, we can change the size of the vector during the execution of a program as per our requirements. Vectors are part of the C++ Standard Template Library.
What data structures do vectors use?
A vector, in computing, is generally a one-dimensional array, typically storing numbers. Vectors typically have fixed sizes, unlike lists and queues. The vector data structure can be used to represent the mathematical vector used in linear algebra.
Is vector a data type?
Vector data types and operations. Vector data types are defined by the type name (char, uchar, ushort, int, uint, float, long, and ulong) followed by a literal value n which corresponds to the number of elements in the vector. These data types work with standard C operators, such as +, -, and *.
Is vector linear data structure?
Atomic vectors and lists are both linear data structures insofar as they only have one dimension (1D) and are characterized by their length.
What data structures do vectors use?
A vector, in computing, is generally a one-dimensional array, typically storing numbers. Vectors typically have fixed sizes, unlike lists and queues. The vector data structure can be used to represent the mathematical vector used in linear algebra.
Is vector a data structure in C?
A vector is a one-dimensional data structure and all of its elements are of the same data type.
Is a vector an array?
We can think of a vector as a list that has one dimension. It is a row of data. An array is a list that is arranged in multiple dimensions. A two-dimensional array is a vector of vectors that are all of the same length.
Is Factor a data type or data structure?
Also, you will learn about levels of a factor. Factor is a data structure used for fields that takes only predefined, finite number of values (categorical data). For example: a data field such as marital status may contain only values from single, married, separated, divorced, or widowed.
What is vector data structure in Java?
Vector is like the dynamic array which can grow or shrink its size. Unlike array, we can store n-number of elements in it as there is no size limit. It is a part of Java Collection framework since Java 1.2. It is found in the java.
What are the types of vector data?
Vector data is split into three types: point, line (or arc), and polygon data.
What is a list in data structures?
What is a List? A list is an ordered data structure with elements separated by a comma and enclosed within square brackets. For example, list1 and list2 shown below contains a single type of data.
What is raster data structure?
In its simplest form, a raster consists of a matrix of cells (or pixels) organized into rows and columns (or a grid) where each cell contains a value representing information, such as temperature. Rasters are digital aerial photographs, imagery from satellites, digital pictures, or even scanned maps.
What is the stack in data structure?
Stacks in Data Structures is a linear type of data structure that follows the LIFO (Last-In-First-Out) principle and allows insertion and deletion operations from one end of the stack data structure, that is top.
Which is not a linear data structure?
Explanation: Tree and graphs are not linear.
What is the difference between a vector and an array C++?
A Vector is a sequential-based container whereas an array is a data structure that stores a fixed number of elements (elements should of the same type) in sequential order. Vectors are sometimes also known as dynamic arrays.
What is a vector in programming?
A vector, in programming, is a type of array that is one dimensional. Vectors are a logical element in programming languages that are used for storing a sequence of data elements of the same basic type. Members of a vector are called components.
What data structures do vectors use?
A vector, in computing, is generally a one-dimensional array, typically storing numbers. Vectors typically have fixed sizes, unlike lists and queues. The vector data structure can be used to represent the mathematical vector used in linear algebra.
What is a vector in programming?
A vector, in programming, is a type of array that is one dimensional. Vectors are a logical element in programming languages that are used for storing a sequence of data elements of the same basic type. Members of a vector are called components.
Can we use vector in C language?
Vectors are a modern programming concept, which, unfortunately, aren’t built into the standard C library. Vectors are same as dynamic arrays with the ability to resize itself automatically when an element is inserted or deleted, with their storage being handled automatically by the container.
Can we use vector in C?
You can’t. By definition, C knows nothing of any of the required components of a std::vector , including, but not limited to: C does not have namespaces, so it can’t understand the std namespace. C does not have templates, so it can’t understand the std::vector
What is vector vs array?
Vector is a sequential container to store elements and not index based. Array stores a fixed-size sequential collection of elements of the same type and it is index based. Vector is dynamic in nature so, size increases with insertion of elements. As array is fixed size, once initialized can’t be resized.
Does a vector data structure need to have a starting point?
The vector data structure (say, the design of a vector class) DOES need to store the size, so at a minimum, there would be a starting point (the base of an array, or some address in memory) and a distance from that point indicating size.
What is a vector in R data structure?
A vector in R contains values that are all of the same type. Vectors correspond to a single variable in a data set. Most data sets consist of more than just one variable, so to store a complete data set we need a different data structure. In R, several variables can be stored together in an object called a data frame.
What is the difference between a variable and a vector?
Vectors correspond to a single variable in a data set. Most data sets consist of more than just one variable, so to store a complete data set we need a different data structure. In R, several variables can be stored together in an object called a data frame.
What is the difference between a vector and a data frame?
A vector can be used to represent a single variable in a data set. A factor can be used to represent a categorical variable in a data set. There is also an array data structure that extends this idea to more than two dimensions. A data frame can be used to represent an entire data set.