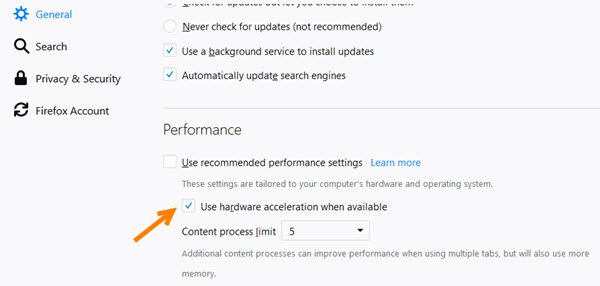
The more the content processes, the better the Firefox performance with multiple tabs, but more memory will be consumed. So you should leave those settings enabled unless you’re an advanced user having a lot of RAM and you know what you’re doing. These Performance settings include the hardware acceleration option also.
Do I need hardware acceleration in Firefox?
Use hardware acceleration when available: This setting allows Firefox to use your computer’s graphics processor, if possible, instead of the main processor, to display graphics-heavy web content such as videos or games. This frees up resources on your computer so it can run other applications, like Firefox, faster.
Should I turn off hardware acceleration in browser?
Faulty hardware acceleration doesn’t help your PC or browser at all, so it’s best to fix it or disable it. You might also run into error messages because of it. For example, when playing a video game, you could get an error warning you about slow performance.
What happens if I turn off hardware acceleration?
For example: If we play a game on a web browser with hardware acceleration turned off, the CPU will handle everything from internet requests to in-game graphics. The CPU will struggle to deliver if the workload is heavy.
Does hardware acceleration improve performance?
Hardware acceleration increases performance of the web browser. When the feature is enabled, some users experience issues that resemble the following when they view various websites: Hardware or software compatibility issues, such as websites that contain streaming or full-screen videos.
Should you turn on hardware acceleration?
In short, enable hardware acceleration wherever you can if you have good hardware and disable it if you have bugs/stability issues.
Does hardware acceleration use more RAM?
Because of the increased resources required to enable hardware acceleration, your app will consume more RAM.
Does turning off hardware acceleration use more CPU?
If you are running off your laptop’s battery, all the more reason to use hardware acceleration. The hardware that handles the offload/acceleration is specialized and uses far less power than the CPU to do the same task. It is always a good idea to let dedicated hardware handle it.
What does hardware acceleration do?
Hardware acceleration invokes a specialized processor to speed up common, complex tasks. One of the most common use cases for hardware acceleration is video encoding and decoding. Graphics cards or other hardware often contain dedicated video encode/decode blocks that can decode and encode videos much more efficiently.
Is hardware acceleration good for streaming?
Hardware-Accelerated Streaming has a number of advantages: More videos can often stream at the same time. Videos can start streaming faster and buffer less often. High-quality videos, especially 4K and HEVC videos, can stream more smoothly.
How can I tell if hardware acceleration is working in Firefox?
You can check hardware acceleration state at about:support page, look at Compositing row. If there’s WebRender, you’re running on hardware. If there’s WebRender (software) you’re on non-accelerated backend.
Where is the hardware acceleration setting in Firefox?
Go to General. Scroll down and go to Performance. Uncheck the box next to Use recommended performance settings. To enable hardware acceleration, tick the box next to Use hardware acceleration when available.
What does hardware acceleration do?
Hardware acceleration invokes a specialized processor to speed up common, complex tasks. One of the most common use cases for hardware acceleration is video encoding and decoding. Graphics cards or other hardware often contain dedicated video encode/decode blocks that can decode and encode videos much more efficiently.
How do I know if I have hardware acceleration in Firefox?
You can check hardware acceleration state at about:support page, look at Compositing row. If there’s WebRender, you’re running on hardware. If there’s WebRender (software) you’re on non-accelerated backend.
What’s better Chrome or Firefox?
Is Firefox Really Better Than Chrome? Firefox is a more private and secure browser than Chrome, but Chrome is faster and contains more features. Is Firefox Safer Than Chrome? Both browsers are safe, but Firefox’s tracking protection is more comprehensive than Chrome’s.
Do I need hardware acceleration in Firefox?
Use hardware acceleration when available: This setting allows Firefox to use your computer’s graphics processor, if possible, instead of the main processor, to display graphics-heavy web content such as videos or games. This frees up resources on your computer so it can run other applications, like Firefox, faster.
What slows down Firefox?
Firefox Uses Too Much CPU or RAM. After using Firefox for some time, it can start to use a lot of your computer’s CPU and/or RAM. To find the cause of the slowdown, first try starting Firefox in Safe Mode. This will make Firefox run without any add-ons or plugins.
Why is my Mozilla Firefox so slow?
The first thing you should do if Firefox is running slow is check for Firefox updates. Keeping your browser up to date will eliminate many sources of slowdown. Select the three bars to open the menu and choose Help > About Firefox.
What’s better Chrome or Firefox?
Is Firefox Really Better Than Chrome? Firefox is a more private and secure browser than Chrome, but Chrome is faster and contains more features. Is Firefox Safer Than Chrome? Both browsers are safe, but Firefox’s tracking protection is more comprehensive than Chrome’s.
What is the fastest browser?
Google Chrome is the fastest web browser you can get on a Windows machine. It surpassed the competition in three out of four tests, outranking even Microsoft’s latest Edge browser—which is now based on Chromium—in all but one test.
Is Firefox multithreaded?
Comparing Chrome and Firefox. Chrome and Firefox now both support multithreading, but they do it in different ways. In Chrome, each and every tab you open gets its own content process.
Should I disable HW overlays?
Disable HW overlays: Using the hardware overlay enables each app that displays something on the screen to use less processing power. Without the overlay, an app shares the video memory and has to constantly check for collision and clipping to render a proper image. The checking uses a lot of processing power.