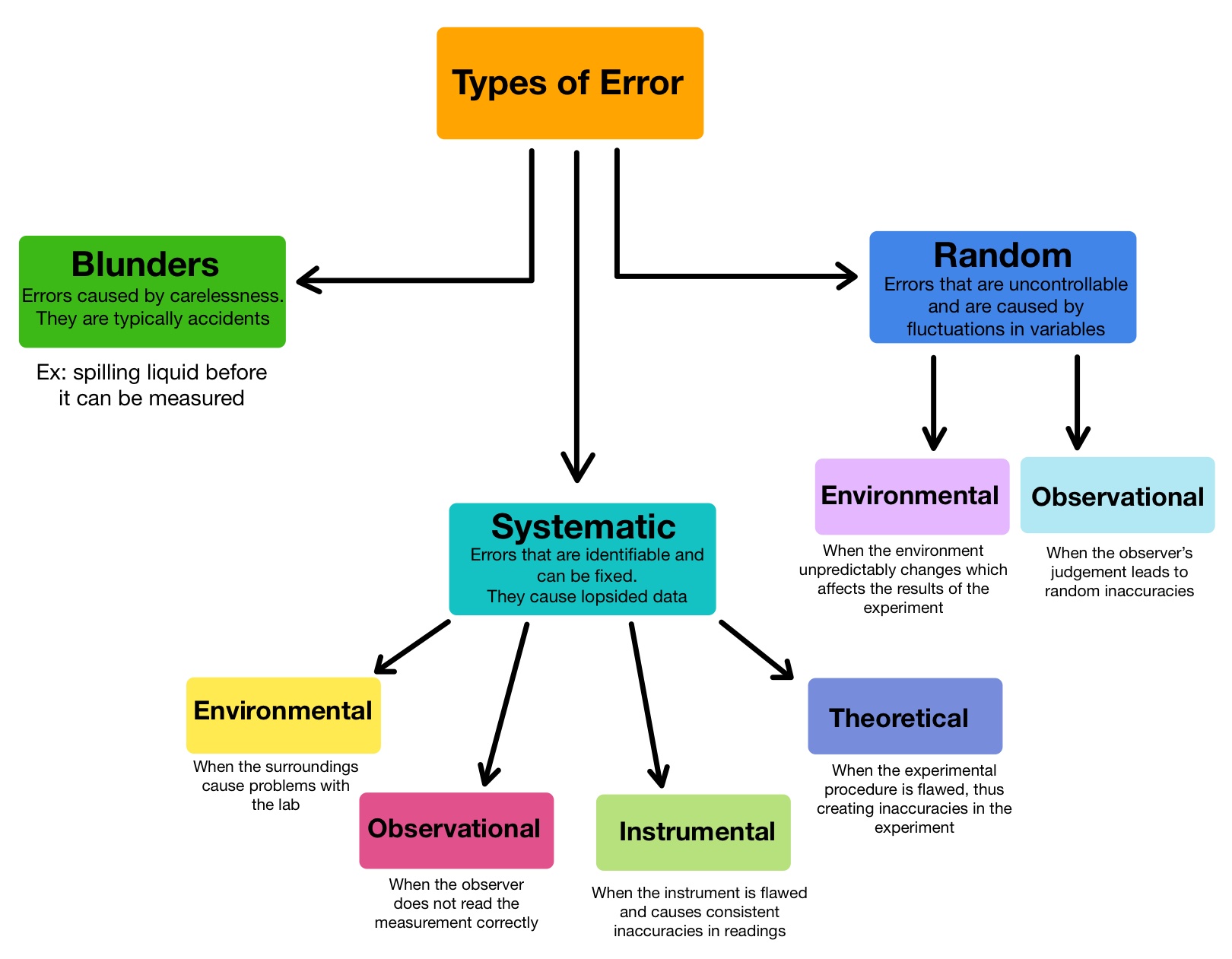
Common sources of error include instrumental, environmental, procedural, and human. All of these errors can be either random or systematic depending on how they affect the results. Instrumental error happens when the instruments being used are inaccurate, such as a balance that does not work (SF Fig.
What are the 3 types of experimental errors?
Three general types of errors occur in lab measurements: random error, systematic error, and gross errors. Random (or indeterminate) errors are caused by uncontrollable fluctuations in variables that affect experimental results.
Which are the two kinds of experimental errors?
Systematic and random errors are the two main types of experimental error.
What are examples of random errors?
An example of random error is putting the same weight on an electronic scales several times and obtaining readings that vary in random fashion from one reading to the next. The differences between these readings and the actual weight correspond to the random error of the scale measurements.
How many types of errors are there?
Generally errors are classified into three types: systematic errors, random errors and blunders.
What are errors in a chemistry experiment?
To a scientist, the definition of “error” is, in some cases, different from the normal use of this term. An error in chemistry still often means a mistake, such as reading a scale incorrectly, but it is also the normal, unavoidable inaccuracies associated with measurements in a lab.
What are examples of random errors?
An example of random error is putting the same weight on an electronic scales several times and obtaining readings that vary in random fashion from one reading to the next. The differences between these readings and the actual weight correspond to the random error of the scale measurements.
What is the most common lab error?
The most common lab errors in the collection of the samples and reporting are: Wrong labeling of the sample. The technique of the blood sample: This is very important to follow an excellent technique to collect good quality blood.
What is human error in a lab?
Human error in chemical analysis is any action or lack thereof that leads to exceeding the tolerances of the conditions required for the normative work of the measuring/testing (chemical analytical) system with which the human interacts.
What are the common causes of error in laboratory testing?
The two major causes of analytical errors are instrument malfunction and operator error. Some examples of analytical errors include equipment malfunction, procedures (i.e., standard operating procedures and assay instructions) not followed, undetected failure of quality control, sample mixups, and test interference.
What is research error in research?
Random error. error introduced by a lack of precision in conducting the study. defined in terms of the null hypothesis, which is no difference between the intervention group and the control group. reduced by meticulous technique and by large sample size.
What are sources of error?
“Sources of Error” are factors (causes) that may limit the accuracy and/or the precision of experimental results. Sources of error are factors inherent within the experimental set-up and procedures that cannot be “fixed”, no matter how hard you try.
Is human error a random error?
I would say neither. Random errors are natural errors. Systematic errors are due to imprecision or problems with instruments. Human error means you screwed something up, you made a mistake.
What are the different types of errors explain with example?
The error may arise from the different source and are usually classified into the following types. The gross error occurs because of the human mistakes. For examples consider the person using the instruments takes the wrong reading, or they can record the incorrect data. Such type of error comes under the gross error.
What are errors and explain its types?
The uncertainty in a measurement is called an error. There are 3 types of errors namely – Random error. Systematic error. Gross error.
What are the two major errors that researchers can make?
There are two main types of experimental error that scientists and non-scientists alike must be aware of: systematic errors and random errors.
How many types of errors are there?
Generally errors are classified into three types: systematic errors, random errors and blunders.
Is human error a random error?
I would say neither. Random errors are natural errors. Systematic errors are due to imprecision or problems with instruments. Human error means you screwed something up, you made a mistake.
What are sources of error?
“Sources of Error” are factors (causes) that may limit the accuracy and/or the precision of experimental results. Sources of error are factors inherent within the experimental set-up and procedures that cannot be “fixed”, no matter how hard you try.
What type of error affects accuracy?
Precision vs accuracy Random error mainly affects precision, which is how reproducible the same measurement is under equivalent circumstances. In contrast, systematic error affects the accuracy of a measurement, or how close the observed value is to the true value.
What is an example of human error?
Human Error is an action or inaction Human error is a generic term that involves all those instances where a planned activity fails to achieve its intended outcome. For example, forgetting to set your park brake in your car or misapplying your vehicle brakes in wet and slippery road conditions.
What types of errors can cause invalid test results?
Three main reasons that incorrect data is provided as a result of lab testing is that the specimen is associated with the wrong person, possibly because a patient is misidentified, a specimen is mislabeled, or information is entered incorrectly into the computer.