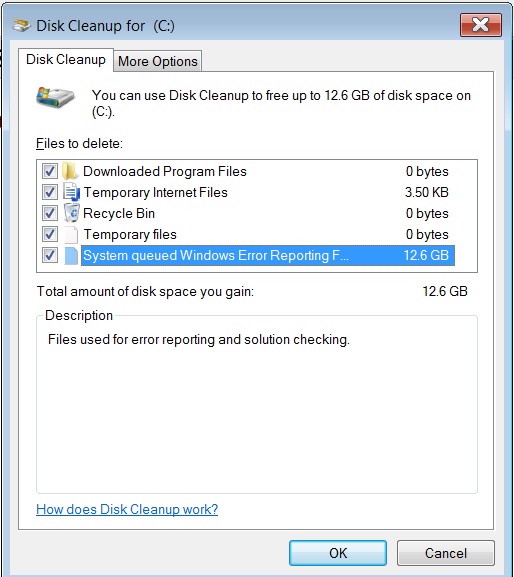
The system queued Windows Error Reporting Files are used by Microsoft Windows for error reporting and solution checking. These files contain the error reports related to the software and hardware problems and are stored temporarily in the system.
Can I delete Windows Error Reporting files?
Windows Error Reporting runs as a Windows service and can optionally be entirely disabled. If Windows Error Reporting itself crashes, then an error reports that the original crashed process cannot be sent. You can delete the files from “C:\Users\username\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\WER”.
What are Windows Error Reporting files?
Windows Error Reporting (WER) is a Windows function that captures the data of software crashes and can report this information to software vendors via Microsoft’s Winqual service.
Is it safe to delete system queued Windows Error Reporting files?
‘Queued’ just means that it contains error reports that haven’t been sent yet for whatever reason, and as such have been stored locally on your hard disk, waiting to be sent. They are both safe to remove.
Can I delete files used for error reporting and solution checking?
Note: You can delete the files used for error reporting and solution checking only if you do not have any issues with computer. If you have issues with computer then we can use these error reporting and solution checking files for troubleshooting purpose.
What files are safe to delete in Disk Cleanup?
Overall, you can safely delete almost everything in Disk Cleanup as long as you don’t plan on rolling back a device driver, uninstalling an update, or troubleshooting a system problem. But you should probably steer clear of those “Windows ESD Installation files” unless you’re really hurting for space.
How do I get rid of error reporting files?
To clear all these errors and logs using the built-in tools, open the Control Panel and go to System and Security -> Security and Maintenance -> Maintenance -> View reliability history -> View all problem reports, then click Clear all problem reports.
Can I disable Windows Error Reporting Service?
The Disable-WindowsErrorReporting cmdlet disables Windows Error Reporting (WER) on the server. Windows Error Reporting is a flexible feedback infrastructure that gathers information about hardware and software problems, reports the information to Microsoft, and gives users any available solutions.
Where are Windows error reports stored?
WER settings are located in one of the following registry subkeys: HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\Windows Error Reporting. HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\Windows Error Reporting.
How do I check Windows Error Reporting?
To open the Problem Reports log, type problem reports in the search box and then click View All Problem Reports. Figure 17-3 shows a portion of the error history for a computer that was upgraded to Windows 10 in the first month after it was available.
Is it OK to delete Windows update cleanup files?
It is safe to delete those filed with cleanup, however you may not be able to reverse any Windows updates if desired after you use Windows Update Cleanup.
Does Disk Cleanup improve performance?
Disk Cleanup helps free up space on your hard disk, creating improved system performance. Disk Cleanup searches your disk and then shows you temporary files, Internet cache files, and unnecessary program files that you can safely delete.
Is it safe to delete system error memory dump files?
Well, deleting the files will not affect the normal use of your computer. So it is safe to delete system error memory dump files. By deleting system error memory dump files, you can get some free space on your system disk. However, dump files can be recreated automatically every time when there is a system crash.
Is it OK to delete previous Windows installations?
Ten days after you upgrade to Windows, your previous version of Windows will be automatically deleted from your PC. However, if you need to free up drive space, and you’re confident that your files and settings are where you want them to be in Windows, you can safely delete it yourself.
How do I clean up Windows Update files?
On the Disk Cleanup tab, select Windows Update Cleanup, and then click OK. Note By default, the Windows Update Cleanup option is already selected. When a dialog box appears, click Delete Files.
What happens if I delete delivery optimization files?
Delivery Optimization in Windows 10 clears its cache automatically. Files are removed from the cache after a short time period or when their contents take up too much disk space. However, If you need more disk space on your PC, you can clear the cache manually.
Is it safe to delete DirectX shader cache?
Is it OK to delete DirectX Shader Cache? It depends on the situation, hardware configuration, game or software, etc. At times, deleting the DirectX Shader Cache can improve the performance of your game. However, if there were no issue with the cache, you would not find any improvement at all.
Where are Windows error reports stored?
WER settings are located in one of the following registry subkeys: HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\Windows Error Reporting. HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\Windows Error Reporting.
How do I get rid of Windows errors?
Repair hard-drive errors. Select the Start button, then in the search box on the taskbar, type command prompt. Choose Command Prompt from the list of results. In the window that pops up, type chkdsk/f C: and press the Enter key. Repairs automatically start on your hard drive, and you’ll be asked to restart your device.
How do I remove the Windows 10 error message?
From the Home screen, click on System. Next, on the following screen, click on the Storage option from the list on the left. Then on the right panel, click on the Temporary files options. When the next screen comes up, check the box labeled “System error memory dump files” and then click the Remove Files button.
What files can I delete from Windows 10 to free up space?
Windows suggests different types of files you can remove, including recycle bin files, Windows Update Cleanup files, upgrade log files, device driver packages, temporary internet files, and temporary files.
Why am I getting a Windows send error?
Misconfigured settings, interaction with third-party software, and limitations of Outlook are the common reasons why you encountered this issue.