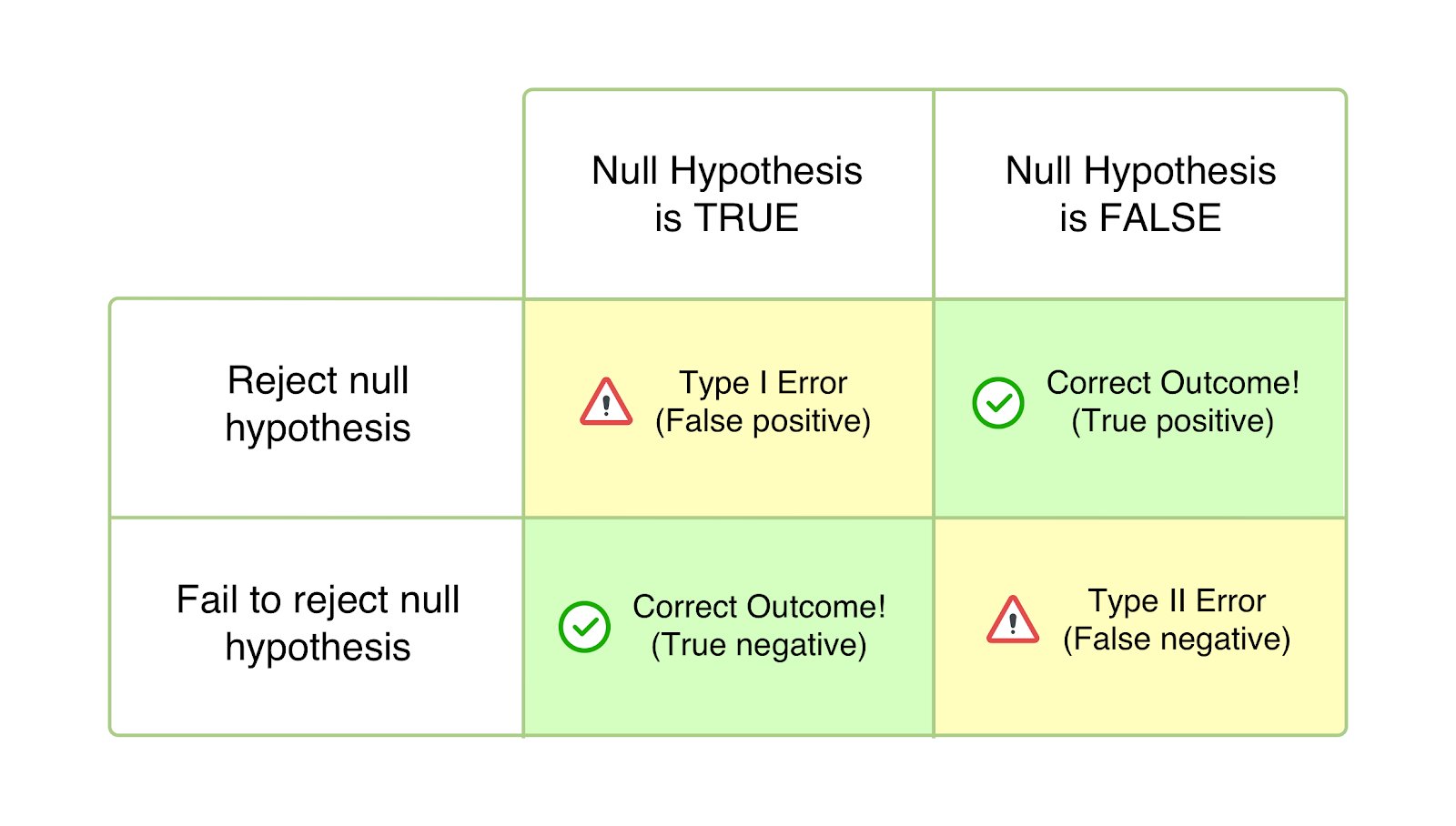
What are Type I and Type II errors? In statistics, a Type I error means rejecting the null hypothesis when it’s actually true, while a Type II error means failing to reject the null hypothesis when it’s actually false.
What are the two types of errors in research?
A type I error (false-positive) occurs if an investigator rejects a null hypothesis that is actually true in the population; a type II error (false-negative) occurs if the investigator fails to reject a null hypothesis that is actually false in the population.
What is a Type 2 error also known as?
A type II error, also known as an error of the second kind or a beta error, confirms an idea that should have been rejected, such as, for instance, claiming that two observances are the same, despite them being different.
What is Type 2 error in statistics?
Type 2 errors happen when you inaccurately assume that no winner has been declared between a control version and a variation although there actually is a winner. In more statistically accurate terms, type 2 errors happen when the null hypothesis is false and you subsequently fail to reject it.
What are Type 1 2 and 3 errors?
Type I error: “rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true”. Type II error: “failing to reject the null hypothesis when it is false”. Type III error: “correctly rejecting the null hypothesis for the wrong reason”. (1948, p.
What are the two types of errors in research?
A type I error (false-positive) occurs if an investigator rejects a null hypothesis that is actually true in the population; a type II error (false-negative) occurs if the investigator fails to reject a null hypothesis that is actually false in the population.
What is a Type 2 error also known as?
A type II error, also known as an error of the second kind or a beta error, confirms an idea that should have been rejected, such as, for instance, claiming that two observances are the same, despite them being different.
What are the types of error?
Generally errors are classified into three types: systematic errors, random errors and blunders.
Why do Type 2 errors occur?
Type II error is mainly caused by the statistical power of a test being low. A Type II error will occur if the statistical test is not powerful enough. The size of the sample can also lead to a Type I error because the outcome of the test will be affected.
Is a Type 2 error a random error?
A Type II error occurs when there really is a difference (association, correlation) overall, but random sampling caused your data to not show a statistically significant difference.
What is Type 2 error quizlet?
type II error. An error that occurs when a researcher concludes that the independent variable had no effect on the dependent variable, when in truth it did; a “false negative” type II error. occurs when researchers fail to reject a false null hypotheses.
What are Type 1 and Type 2 errors examples?
Type I error (false positive): the test result says you have coronavirus, but you actually don’t. Type II error (false negative): the test result says you don’t have coronavirus, but you actually do.
What is Type 2 error formula?
What is the probability of a Type II error? Step 1: Based on the above question, Power = 0.85. This means that the probability of correctly rejecting the null hypothesis is 0.85 or 85%. Step 2: We can use the formula 1 – Power = P(Type II Error) to find our probability.
Which is bad Type 1 or Type 2 error?
Hence, many textbooks and instructors will say that the Type 1 (false positive) is worse than a Type 2 (false negative) error. The rationale boils down to the idea that if you stick to the status quo or default assumption, at least you’re not making things worse. And in many cases, that’s true.
What is a Type 3 error example?
You can also think of a Type III error as giving the right answer (i.e. correctly rejecting the null) to the wrong question. Either way, you’re still arriving at the correct conclusion for the wrong reason. When we say the “wrong question”, that normally means you’ve formulated your hypotheses incorrectly.
What are Type 1 errors called?
A type 1 error is also known as a false positive and occurs when a researcher incorrectly rejects a true null hypothesis. This means that your report that your findings are significant when in fact they have occurred by chance.
What causes Type 2 error in research?
Type II error is mainly caused by the statistical power of a test being low. A Type II error will occur if the statistical test is not powerful enough. The size of the sample can also lead to a Type I error because the outcome of the test will be affected.
What are the two types of errors in research?
A type I error (false-positive) occurs if an investigator rejects a null hypothesis that is actually true in the population; a type II error (false-negative) occurs if the investigator fails to reject a null hypothesis that is actually false in the population.
What is a Type 2 error also known as?
A type II error, also known as an error of the second kind or a beta error, confirms an idea that should have been rejected, such as, for instance, claiming that two observances are the same, despite them being different.
What is Type 2 error in statistics?
Type 2 errors happen when you inaccurately assume that no winner has been declared between a control version and a variation although there actually is a winner. In more statistically accurate terms, type 2 errors happen when the null hypothesis is false and you subsequently fail to reject it.
What are basic errors?
Some common errors are with prepositions most importantly, subject verb agreement, tenses, punctuation, spelling and other parts of speech. Prepositions are tricky, confusing and significant in sentence construction.
What is called error?
An error is something you have done which is considered to be incorrect or wrong, or which should not have been done.