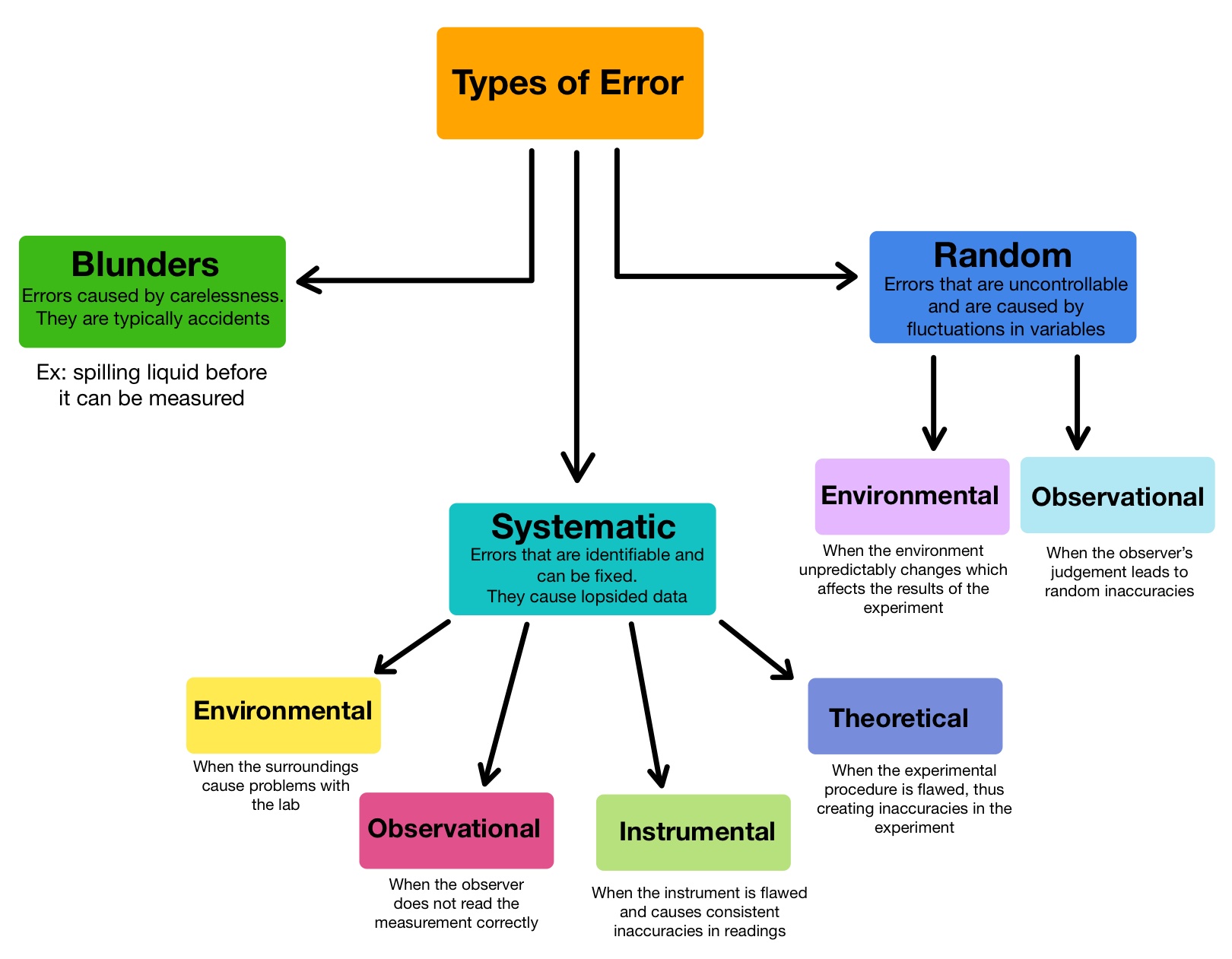
There are four types of systematic error: observational, instrumental, environmental, and theoretical. Observational errors occur when you make an incorrect observation. For example, you might misread an instrument. Instrumental errors happen when an instrument gives the wrong reading.
What are different types of errors explain?
The systematic errors are mainly classified into three categories. Instrumental Errors. Environmental Errors. Observational Errors. Random errors:- the error which is caused by the sudden change in the atmospheric condition, such type of error is called random error.
What are the different types of error class 11?
1) Instrumental error: This error occurs due to poor calibration of the measuring device or the measuring apparatus. 2) Observational error: This error occurs due to poor observation by the observer, while taking measurements. Observational error is also called gross error or personal error.
How many types of error are there?
Generally errors are classified into three types: systematic errors, random errors and blunders.
What are different types of errors explain?
The systematic errors are mainly classified into three categories. Instrumental Errors. Environmental Errors. Observational Errors. Random errors:- the error which is caused by the sudden change in the atmospheric condition, such type of error is called random error.
What is called error?
An error is something you have done which is considered to be incorrect or wrong, or which should not have been done.
What are different types of errors in accounting?
Data entry errors Entering items in the wrong account. Transposing numbers. Leaving out or adding a digit or a decimal place. Omitting or duplicating an entry.
What are different types of errors explain?
The systematic errors are mainly classified into three categories. Instrumental Errors. Environmental Errors. Observational Errors. Random errors:- the error which is caused by the sudden change in the atmospheric condition, such type of error is called random error.
What are different types of errors in data link layer?
Errors can be of three types, namely single bit errors, multiple bit errors, and burst errors. Single bit error − In the received frame, only one bit has been corrupted, i.e. either changed from 0 to 1 or from 1 to 0. Multiple bits error − In the received frame, more than one bits are corrupted.
What is error and example?
The definition of an error is a mistake or the state of being wrong. An example of an error is when you add 2+2 and get 5. An example of error is when a mistake leads you to come to the wrong collusion and you continue to believe this incorrect conclusion. noun.
What is error explain types of error in auditing?
Types of Errors: Clerical Errors: Such an error arises on account of wrong posting. Errors of Commission : When amount of transaction or entry is incorrectly recorded in accounting books/ledger. Errors of Omission : When the transactions are not recorded in the books of original entry or posted to the ledger.
How many types of errors are there in Trial Balance explain with example?
Here we detail about the four types of errors in preparation of trial balance, i.e., (i) Errors of Omission, (ii) Errors of Commission, (iii) Errors of Principle, and (iv) Compensating Errors.
What are different types of errors explain?
The systematic errors are mainly classified into three categories. Instrumental Errors. Environmental Errors. Observational Errors. Random errors:- the error which is caused by the sudden change in the atmospheric condition, such type of error is called random error.
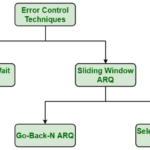
What is error control explain it briefly?
Error control is the technique of detecting and correcting blocks of data during communication. In other words, it checks the reliability of characters both at the bit level and packet level.
What is single bit and burst error?
In a single-bit error, a 0 is changed to a 1 or a 1 to a 0. In a burst error, multiple bits are changed. Single-Bit Error: The term single-bit error means that only 1 bit of a given data unit (such as a byte, character, or packet) is changed from 1 to 0 or from 0 to 1.
What are different types of errors in data link layer?
Errors can be of three types, namely single bit errors, multiple bit errors, and burst errors. Single bit error − In the received frame, only one bit has been corrupted, i.e. either changed from 0 to 1 or from 1 to 0. Multiple bits error − In the received frame, more than one bits are corrupted.
What do u mean by error?
error, mistake, and blunder mean an act or statement that is not right or true or proper. error is used for failure to follow a model correctly. There was an error in the addition. mistake is used when someone misunderstands something or does not intend to do wrong.
What are the different types of errors describe the errors which are not disclosed by a trial?
Errors of complete omission, error of principle, compensating error, a wrong entry in the subsidiary books are not disclosed by the trial balance.
What are the different types of errors describe the errors which are not disclosed by a trial balance?
Errors of complete omission, error of principle, compensating error, wrong entry in the subsidiary books are not disclosed by the trial balance.
What are different types of errors explain?
The systematic errors are mainly classified into three categories. Instrumental Errors. Environmental Errors. Observational Errors. Random errors:- the error which is caused by the sudden change in the atmospheric condition, such type of error is called random error.
What is error flow?
The error flow acts as a catch-all for messages that are propagated from any unwired fail terminal on any primitive or node, in either a request or a response flow. By default, an error flow consists of: An Error Input node, which has a catchAll terminal, with the type set to anyType.
Why is error control important?
Purpose of Error Control : The function of the error control function of the data link layer helps in dealing with data frames that are damaged in transit, data frames lost in transit, and the acknowledgement frames that are lost in transmission.