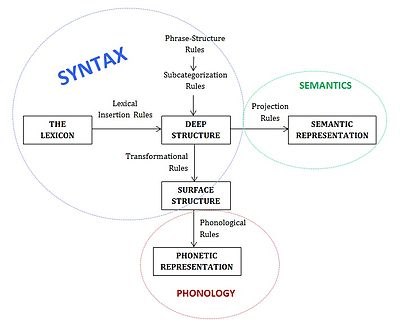
Syntactic features are formal properties of syntactic objects which determine how they behave with respect to syntactic constraints and operations (such as selection, licensing, agreement, and movement).
What are formal features in syntax?
There are formal features, which are those features that are relevant to the operation of the syntax, and then there are semantic features, which are those features that are relevant to the interpretation of the meaning.
What are the three elements of syntax?
As outlined in Syntactic Structures (1957), it comprised three sections, or components: the phrase-structure component, the transformational component, and the morphophonemic component.
What is syntactic feature analysis?
Syntactic analysis is an analysis that focuses on understanding the logical meaning of sentences or of parts of sentences. While lemmatization focuses purely on feature extraction and data cleaning, syntactic analysis analyzes the relationship between words and the grammatical structure of sentences.
What are the main features of sentence?
The subject and predicate make up the two basic structural parts of any complete sentence. In addition, there are other elements, contained within the subject or predicate, that add meaning or detail. These elements include the direct object, indirect object, and subject complement.
What are types of syntax?
Types of sentences and their syntax modes include simple sentences, compound sentences, complex sentences, and compound-complex sentences. Compound sentences are two simple sentences joined by a conjunction. Complex sentences have dependent clauses, and compound-complex sentences have both types included.
What is the importance of syntax?
“Syntax skills help us understand how sentences work—the meanings behind word order, structure, and punctuation. By providing support for developing syntax skills, we can help readers understand increasingly complex texts” (Learner Variability Project).
What are the 7 language features?
Language can have scores of characteristics but the following are the most important ones: language is arbitrary, productive, creative, systematic, vocalic, social, non-instinctive and conventional. These characteristics of language set human language apart from animal communication.
Is syntax a linguistic feature?
Syntax is the part of linguistics that studies the structure and formation of sentences. It explains how words and phrases are arranged to form correct sentences. A sentence could make no sense and still be correct from the syntax point of view as long as words are in their appropriate spots and agree with each other.
What are syntactic functions?
Definition: A syntactic function is the grammatical relationship of one constituent to another within a syntactic construction. Kinds: Adjunct.
Is tense a syntactic feature?
Tense is often assumed to be and frequently referred to as a ‘morphosyntactic category’ or ‘morphosyntactic feature’. As summarised in Mithun (1999:23), tense is “one of the most frequently cited examples of a prototypical inflectional category”, seen as having “relevance to syntax”.
What are formal features?
1. Structural and/or stylistic aspects of an utterance, text, or artwork in any medium. See also form; structure; style; textual analysis; textual features. 2. The structural and stylistic conventions of a genre: see also iconography.
What are 5 main formal elements?
The Formal Elements are the parts used to make a piece of artwork. The art elements are line, shape, form, tone, texture, pattern, colour and composition. They are often used together, and how they are organised in a piece of art determines what the finished piece will look like.
What Is syntax in formal language?
Syntax is usually associated with the rules (or grammar) governing the composition of texts in a formal language that constitute the well-formed formulas of a formal system. In computer science, the term syntax refers to the rules governing the composition of well-formed expressions in a programming language.
What is formal syntax and semantics?
•Syntax: the form or structure of the. expressions, statements, and program units. •Semantics: the meaning of the expressions, statements, and program units. •Syntax and semantics provide a language’s.
What Is syntax with example?
Syntax is the order or arrangement of words and phrases to form proper sentences. The most basic syntax follows a subject + verb + direct object formula. That is, “Jillian hit the ball.” Syntax allows us to understand that we wouldn’t write, “Hit Jillian the ball.”
What is basic syntax?
What Is Basic Syntax? Basic syntax represents the fundamental rules of a programming language. Without these rules, it is impossible to write functioning code. Every language has its own set of rules that make up its basic syntax.
What are the 4 features of a paragraph?
There are four essential elements that an effective paragraph should consistently contain: unity, coherence, a topic sentence, and sufficient development. In order for a paragraph to maintain a sense of unity, the paragraph must focus solely on a single idea, point, or argument that is being discussed.
What are the features of phrases?
Phrases are a combination of two or more words that can take the role of a noun, a verb, or a modifier in a sentence. Phrases are different from clauses because while dependent and independent clauses both contain a subject and a verb, phrases do not.
What is called syntax?
syntax, the arrangement of words in sentences, clauses, and phrases, and the study of the formation of sentences and the relationship of their component parts.
What is a syntax in language?
Syntax is a term used by linguists to describe a set of principles and rules that govern sentence structure and word order in a particular language. In English, the general rule of syntax follows the subject-verb-object rule.
What is short syntax called?
Parataxis (from Greek: παράταξις, “act of placing side by side”; from παρα, para “beside” + τάξις, táxis “arrangement”) is a literary technique, in writing or speaking, that favors short, simple sentences, without conjunctions or with the use of coordinating, but not with subordinating conjunctions.