Error Detecting Techniques: Single parity check. Two-dimensional parity check. Checksum. Cyclic redundancy check.
What are different types error detection techniques?
There are three main techniques for detecting errors in frames: Parity Check, Checksum and Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC).
What is the most common method of error detection?
One of the most common techniques for detecting transmission errors is a technique known as the cyclic redundancy check (CRC).
How many types of error detection are there?
Error Detecting Techniques: Single parity check. Two-dimensional parity check. Checksum. Cyclic redundancy check.
What are the 5 sources of error?
Common sources of error include instrumental, environmental, procedural, and human. All of these errors can be either random or systematic depending on how they affect the results. Instrumental error happens when the instruments being used are inaccurate, such as a balance that does not work (SF Fig. 1.4).
What are the 3 major types of error in error analysis?
Researchers have identified three broad types of error analysis according to the size of the sample. These types are: massive, specific and incidental samples.
What are the 3 types of error analysis?
Researchers have identified three broad types of error analysis according to the size of the sample. These types are: massive, specific and incidental samples.
What are the 3 types of errors in science?
In science, errors are often categorized as systematic, random, or blunders.
What are the three main error types?
Fatal Error There are three (3) types of fatal errors: Startup fatal error (when the system can’t run the code at installation) Compile time fatal error (when a programmer tries to use nonexistent data) Runtime fatal error (happens while the program is running, causing the code to stop working completely)
What is an example of error detection?
To avoid this, we use error-detecting codes which are additional data added to a given digital message to help us detect if an error occurred during transmission of the message. A simple example of error-detecting code is parity check.
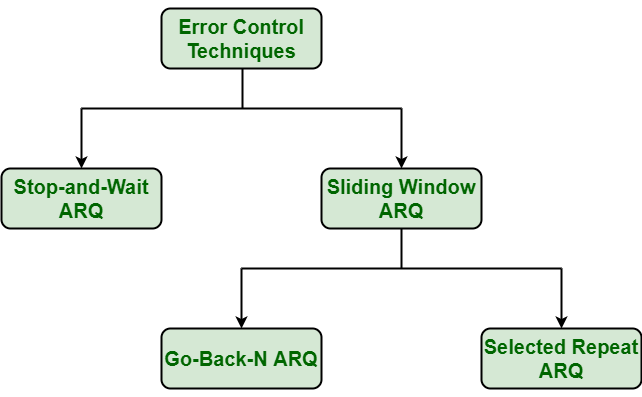
What are the error correction techniques?
Error Correction can be handled in two ways: Backward error correction: Once the error is discovered, the receiver requests the sender to retransmit the entire data unit. Forward error correction: In this case, the receiver uses the error-correcting code which automatically corrects the errors.
What are the main types of data error?
Data can be affected by two types of error: sampling error and non-sampling error.
What are the sources and type of error?
Personal errors – There are two main types of errors: personal and methodological. These errors are completely due to the analyst’s human error and have nothing to do with the prescribed procedure or methodology. Instrumental errors – Quite often, instruments need calibration and are not accurate and accurate.
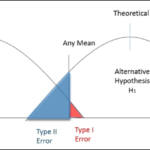
What are the 2 types of errors?
What are Type I and Type II errors? In statistics, a Type I error means rejecting the null hypothesis when it’s actually true, while a Type II error means failing to reject the null hypothesis when it’s actually false.
What are the 3 measurement errors?
There are three major sources of measurement error: gross, systematic, and random. Gross error is people-caused error.
What are Type 1 2 and 3 errors?
Type I error: “rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true”. Type II error: “failing to reject the null hypothesis when it is false”. Type III error: “correctly rejecting the null hypothesis for the wrong reason”. (1948, p.
What are the 5 sources of error?
Common sources of error include instrumental, environmental, procedural, and human. All of these errors can be either random or systematic depending on how they affect the results. Instrumental error happens when the instruments being used are inaccurate, such as a balance that does not work (SF Fig. 1.4).
What are the 2 types of errors?
What are Type I and Type II errors? In statistics, a Type I error means rejecting the null hypothesis when it’s actually true, while a Type II error means failing to reject the null hypothesis when it’s actually false.
What are the two main type of error?
Personal errors – There are two main types of errors: personal and methodological. These errors are completely due to the analyst’s human error and have nothing to do with the prescribed procedure or methodology. Instrumental errors – Quite often, instruments need calibration and are not accurate and accurate.
What are the main types of data error?
Data can be affected by two types of error: sampling error and non-sampling error.
What error detection means?
Error detection means to decide whether the received data is correct or not without having a copy of the original message. Error detection uses the concept of redundancy, which means adding extra bits for detecting errors at the destination.
How does error detection technique work?
For error detection, the sender needs to send some additional bits along with the data bits. The receiver performs necessary checks based upon the additional redundant bits. If it finds that the data is free from errors, it removes the redundant bits before passing the message to the upper layers.