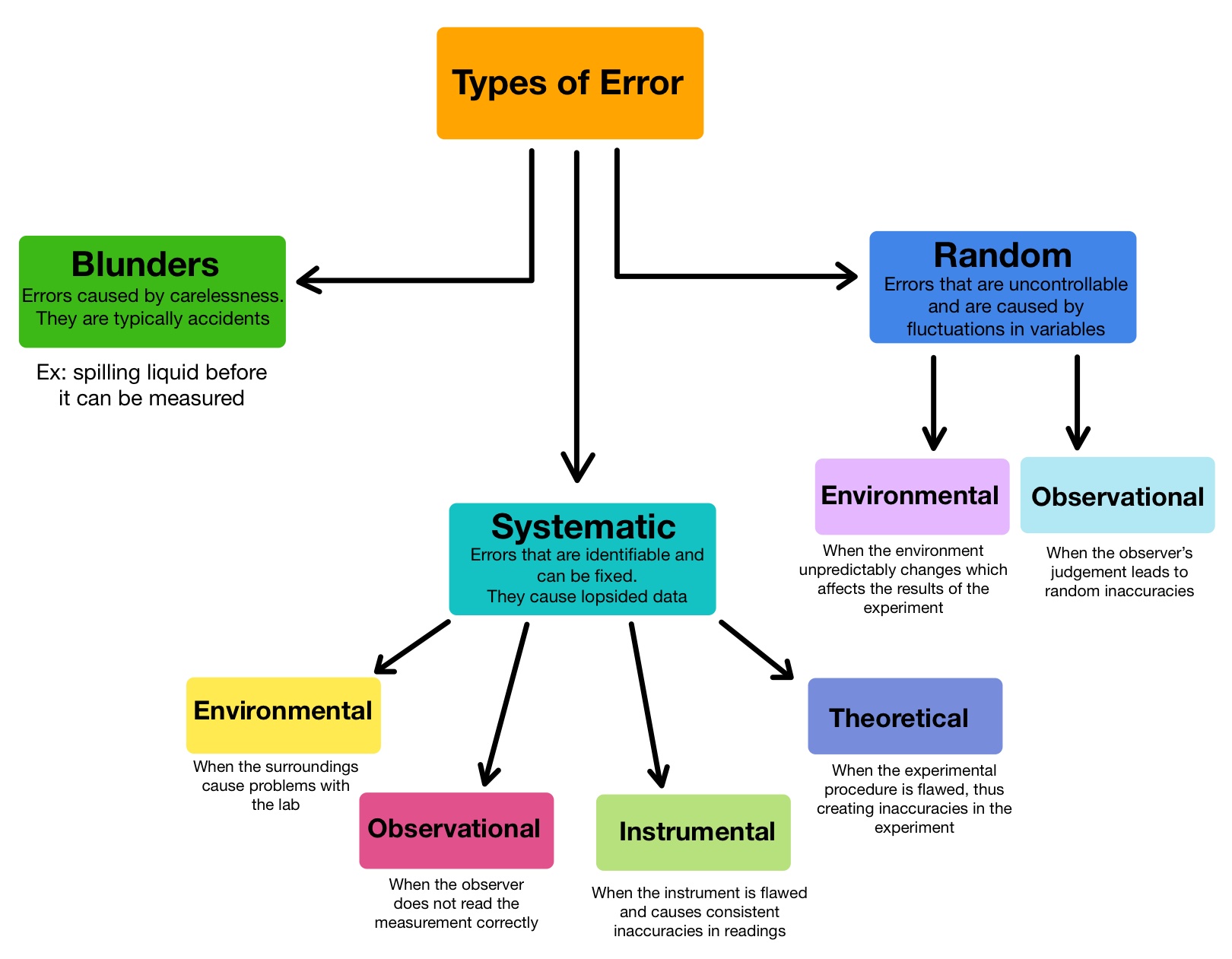
When carrying out experiments, scientists can run into different types of error, including systematic, experimental, human, and random error.
What is type error with example?
Type I error (false positive): the test result says you have coronavirus, but you actually don’t. Type II error (false negative): the test result says you don’t have coronavirus, but you actually do.
What are the four 4 types of measurement data?
Psychologist Stanley Stevens developed the four common scales of measurement: nominal, ordinal, interval and ratio.
What is error Short answer?
An error is something you have done which is considered to be incorrect or wrong, or which should not have been done.
What are basic errors?
Some common errors are with prepositions most importantly, subject verb agreement, tenses, punctuation, spelling and other parts of speech. Prepositions are tricky, confusing and significant in sentence construction.
What is called error?
An error (from the Latin error, meaning “wandering”) is an action which is inaccurate or incorrect. In some usages, an error is synonymous with a mistake.
What are the different types of error in physics?
There are two types of experimental error: Random error. Systematic error.
What are the different types of errors explain clearly?
The error may arise from the different source and are usually classified into the following types. The gross error occurs because of the human mistakes. For examples consider the person using the instruments takes the wrong reading, or they can record the incorrect data. Such type of error comes under the gross error.
How do you explain type 1 and Type 2 error?
A type I error (false-positive) occurs if an investigator rejects a null hypothesis that is actually true in the population; a type II error (false-negative) occurs if the investigator fails to reject a null hypothesis that is actually false in the population.
What does type 1 and Type 2 error mean?
Type – 1 error is known as false positive, i.e., when we reject the correct null hypothesis, whereas type -2 error is also known as a false negative, i.e., when we fail to reject the false null hypothesis.
What are type 1 2 and 3 errors?
Type I error: “rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true”. Type II error: “failing to reject the null hypothesis when it is false”. Type III error: “correctly rejecting the null hypothesis for the wrong reason”. (1948, p.
What are the 4 level of scales of measurement?
There are four basic levels: nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. A variable measured on a “nominal” scale is a variable that does not really have any evaluative distinction.
What is major error?
Major Error means a substantial deviation from accuracy or correctness.
What type of error is accuracy?
Accuracy and precision are two measures of observational error. Accuracy is how close a given set of measurements (observations or readings) are to their true value, while precision is how close the measurements are to each other.
What is the role of error?
What is the role of error? Making mistakes plays an important and useful part in language learning because it allows learners to experiment with language and measure their success in communicating.
What are the four steps in the measurement process?
Broadly speaking, there are four steps in the measurement process: (a) conceptually defining the construct, (b) operationally defining the construct, (c) implementing the measure, and (d) evaluating the measure. In this section, we will look at each of these steps in turn.
What are single errors?
During data transmission, when the sender sends data, the receiver receives the altered form of that data, which means an error has occurred in the pathway of data transmission. If this error occurred in only a single bit among all the data bits, then it is called a Single bit error.
What causes error?
Common sources of error include instrumental, environmental, procedural, and human. All of these errors can be either random or systematic depending on how they affect the results.
What is a 0 error?
zero error Any indication that a measuring system gives a false reading when the true value of a measured quantity is zero, eg the needle on an ammeter failing to return to zero when no current flows. A zero error may result in a systematic uncertainty.
What is the full form of an error?
An error (from the Latin error, meaning “wandering”) is an action which is inaccurate or incorrect. In some usages, an error is synonymous with a mistake. The etymology derives from the Latin term ‘errare’, meaning ‘to stray’.
What are the 4 most serious writing errors?
The article “Four Most Serious Errors” illustrated four most common errors in english writing, including fragments, run-ons,problem with subject-verb agreement and problems with verb form and tense. The author first demonstrated elements of a sentence such as subjects and verbs.
What are examples of human error?
Human error is a generic term that involves all those instances where a planned activity fails to achieve its intended outcome. For example, forgetting to set your park brake in your car or misapplying your vehicle brakes in wet and slippery road conditions.