As outlined in Syntactic StructuresSyntactic StructuresSyntactic Structures is an influential work in linguistics by American linguist Noam Chomsky, originally published in 1957. It is an elaboration of his teacher Zellig Harris’s model of transformational generative grammar.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Syntactic_StructuresSyntactic Structures – Wikipedia (1957), it comprised three sections, or components: the phrase-structure component, the transformational component, and the morphophonemic component.
What are the elements of syntax?
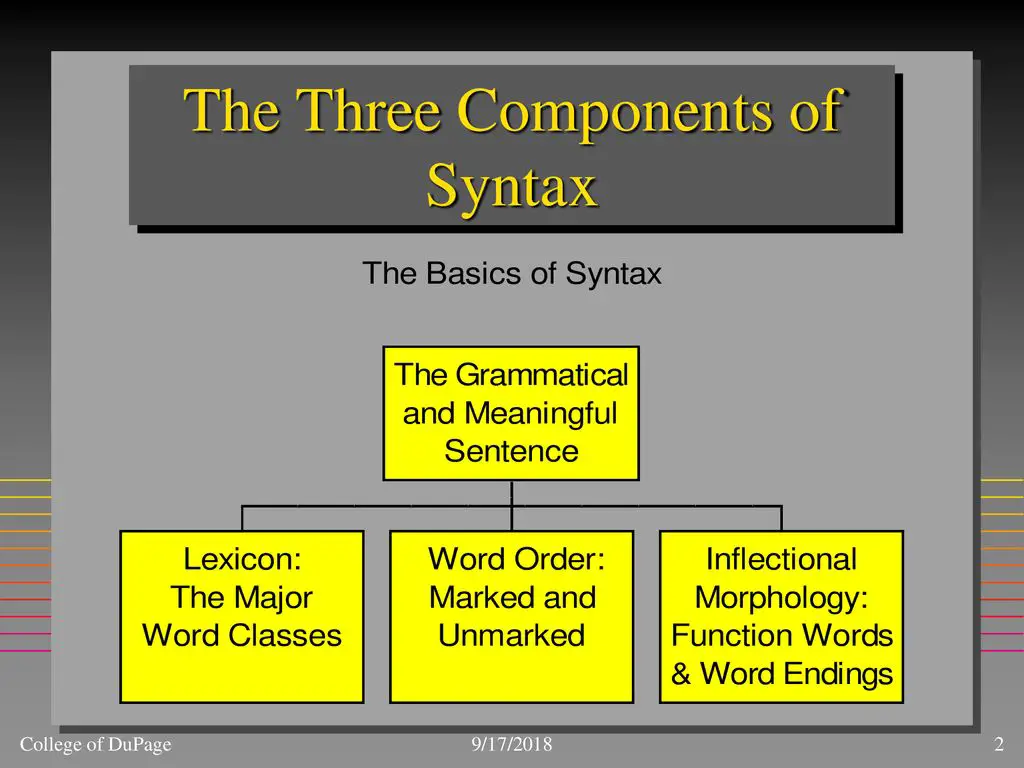
Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituency), agreement, the nature of crosslinguistic variation, and the relationship between form and meaning (semantics).
What are the types of syntax and give examples?
Types of sentences and their syntax modes include simple sentences, compound sentences, complex sentences, and compound-complex sentences. Compound sentences are two simple sentences joined by a conjunction. Complex sentences have dependent clauses, and compound-complex sentences have both types included.
What are the main units of syntax?
Units. The basic units of syntax are words and clitics. A word is the smallest free form in language that can be spoken in isolation or in varying positions within a sentence and retain its semantic and pragmatic content, which we can informally refer to as its meaning.
What are the elements of syntax?
Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituency), agreement, the nature of crosslinguistic variation, and the relationship between form and meaning (semantics).
What are the types of syntax and give examples?
Types of sentences and their syntax modes include simple sentences, compound sentences, complex sentences, and compound-complex sentences. Compound sentences are two simple sentences joined by a conjunction. Complex sentences have dependent clauses, and compound-complex sentences have both types included.
How many types of syntax are there?
Types of syntax: 4 sentence structures with syntax examples There are only four types of sentence structures, which represent different combinations of independent and subordinate clauses. 1 Simple: Includes the minimum requirements for a sentence, with just a single independent clause.
What are the 4 elements of language?
There are four basic aspects of language that have been studied: phonology, syn- tax, semantics, and pragmatics. Phonology is the study of the sounds of a language.
What is basic syntax?
Basic syntax represents the fundamental rules of a programming language. Without these rules, it is impossible to write functioning code. Every language has its own set of rules that make up its basic syntax. Naming conventions are a primary component of basic syntax conventions and vary by language.
What Is syntax explain?
syntax, the arrangement of words in sentences, clauses, and phrases, and the study of the formation of sentences and the relationship of their component parts.
What are the methods of syntax?
Methods are similar to functions: they’re declared with the fn keyword and their name, they can have parameters and a return value, and they contain some code that is run when they’re called from somewhere else.
What Is syntax classified?
Syntax is the part of linguistics that studies the structure and formation of sentences. It explains how words and phrases are arranged to form correct sentences. A sentence could make no sense and still be correct from the syntax point of view as long as words are in their appropriate spots and agree with each other.
What are syntax rules?
Syntax rules are those rules that define or clarify the order in which words or elements are arranged to form larger elements, such as phrases, clauses, or statements. Syntax rules also impose restrictions on individual words or elements.
What are the 7 elements of language?
Language courses include 7 language components that aim at developing learners’ language competency. These are vocabulary, grammar, functions, reading, listening, speaking, and writing.
What are the 5 basic elements of language with definition?
Linguists have identified five basic components (phonology, morphology, syntax, semantics, and pragmatics) found across languages.
What are the elements of syntax?
Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituency), agreement, the nature of crosslinguistic variation, and the relationship between form and meaning (semantics).
What are the types of syntax and give examples?
Types of sentences and their syntax modes include simple sentences, compound sentences, complex sentences, and compound-complex sentences. Compound sentences are two simple sentences joined by a conjunction. Complex sentences have dependent clauses, and compound-complex sentences have both types included.
What are the 3 types of sentences?
Three essential types of sentence are declarative sentences (which are statements), interrogative sentences (which are questions), and imperative sentences (which are orders). Join us as we give examples of each!
What are the 3 key elements of language used by authors?
Many elements of writing contribute to an author’s style, but three of the most important are word choice, sentence fluency, and voice.
What are the five basic elements?
According to some traditions, everything in the universe comes from the five elements: wood, fire, earth, water, and metal.
What is the importance of syntax?
“Syntax skills help us understand how sentences work—the meanings behind word order, structure, and punctuation. By providing support for developing syntax skills, we can help readers understand increasingly complex texts” (Learner Variability Project).
What is a simple sentence syntax?
Simple sentences are sentences containing one independent clause, with a subject and a predicate. Modifiers, compound subjects, and compound verbs/predicates can be used in simple sentences. The standard arrangement of a simple sentence is subject + verb + object, or SVO order.