Typically, DNS errors are caused by problems on the user end, whether that’s with a network or internet connection, misconfigured DNS settings, or an outdated browser. They can also be attributed to a temporary server outage that renders the DNS unavailable.DNS problems usually stem from improper configuration of DNS records during most times. If you fail to put down the right values and IP addresses of your records, then there is a high likelihood that you will be bogged down by DNS resolution issues. Some records such as MX, SPF and DKIM are essential for email delivery.
What are common DNS issues?
High DNS latency equals high loading times. High DNS latency can be as a result of the DNS name servers not being in close geographic proximity to a large percentage of users who visit your site. Another reason might be network congestion.
What happens if DNS server is down?
What Does “DNS Server Not Responding“ Mean? DNS Server Not Responding error means that your browser was unable to connect to the internet or the DNS of the domain you’re trying to reach are unavailable. In order to resolve it, restart your router or modem, check for network issues and update your browser.
How do I reset my router DNS?
This is the procedure to use: Turn off both your router & ONT. While they are off, clear your internet cache from all browsers, and close all browsers. Go to command prompt (cmd) run ipconfig /flushdns.
Is DNS and IP address the same?
An IP address is an address assigned to any computer (including servers) to identify it on a given network. A DNS address is a Domain Name Service which is used to convert alphabetic references into a server’s IP address generally for hosting services.
How can I test if my DNS server is working?
Here’s how to check DNS settings in Windows and see if your DNS is working: Open the Command Prompt. Type ipconfig /all and press Enter. Look for the DNS Servers entry to check your DNS settings and verify that they are correct.
What is DNS server in Wi-Fi?
The Domain Name System (DNS) Server is a server that is specifically used for matching website hostnames (like example.com)to their corresponding Internet Protocol or IP addresses. The DNS server contains a database of public IP addresses and their corresponding domain names.
What DNS server should I use?
Answer: Public DNS systems such as OpenDNS, Cloudflare, or Google DNS are better than the servers maintained by internet service providers. You should use public DNS servers as they offer maximum uptime, faster speeds, and increased security.
Is it safe to flush DNS?
Clearing the DNS server will remove any invalid addresses, whether because they’re outdated or because they’ve been manipulated. It’s also important to note flushing the cache doesn’t have any negative side effects.
Does Flushing DNS speed up internet?
It’s possible that flushing DNS can have some improvement, but it won’t be much. If anything, it’ll clear out obsolete entries if it hasn’t been done in a while and caching is interfering with something, but clearing the cache can actually lower overall speeds (slightly) by requiring new DNS lookups for every resource.
Does restarting router clear cache?
This is sometimes called a “power-cycle.” Rebooting your router cleans out the device’s short-term memory (also called “cache”) to keep it running more smoothly.
What DNS server should I use on my router?
Can my router be infected?
Can a Wi-Fi router get a virus? Yes, a Wi-Fi router can get a virus. Wi-Fi routers are a bridge from your computer or phone to the internet, and they’re lucrative targets for cybercriminals. Malware on a router can spread to any device connected to the router.
Who is responsible for DNS server?
ICANN is the global non-profit organization responsible for coordinating the Internet’s core systems of unique identifiers, most notably the Domain Name System (DNS).
What does a DNS do?
2.1 that computers use to connect to each other. The Internet’s DNS system works much like a phone book by managing the mapping between names and numbers. DNS servers translate requests for names into IP addresses, controlling which server an end user will reach when they type a domain name into their web browser.
What is DNS Example?
For example, when a Web address (URL) is typed into a browser, a DNS query is made to learn an IP address of a Web server associated with that name. Using the www.example.com URL, example.com is the domain name, and www is the hostname. DNS resolution maps www.example.com into an IP address (such as 192.0. 2.1).
Will changing my DNS affect anything?
Although DNS is not directly related to your Internet speed, it can influence how fast an individual webpage appears on your computer. Once a connection has been established though, it should not affect download speeds. If you want to amend your router’s DNS servers however, this can help improve your overall speed.
Why is 8.8 8.8 a popular DNS server?
It is just another DNS server option. Actually, it is the DNS server of Google, it means that Google provides the DNS and maintenance of this service, which means it is “more reliable” than some another DNS servers due to the fact that is maintained by one of the biggest IT companies of the world.
What does changing your DNS to 8.8 8.8 do?
By changing your 8.8. 8.8 DNS, you are switching your operator from your ISP to Google Public DNS. It protects users from DDOS and malware attacks. However, by doing this, Google can see all your DNS queries and collect even more data.
Should I change DNS on router?
By default, your router uses your Internet service provider’s DNS servers. If you change the DNS server on your router, every other device on your network will use it. Really, if you want to use a third-party DNS server on your devices, we recommend you just change it on your router.
How long is DNS cache stored?
A. By default, Windows stores positive responses in the DNS cache for 86,400 seconds (i.e., 1 day) and stores negative responses for 300 seconds (5 minutes).
How often should I flush my DNS?
If you need clear DNS cache from client side for every 15 minutes, it is OK. After these caches were cleared, if needed, the client will re-query these records from DNS server. TTL times are always represented in seconds.
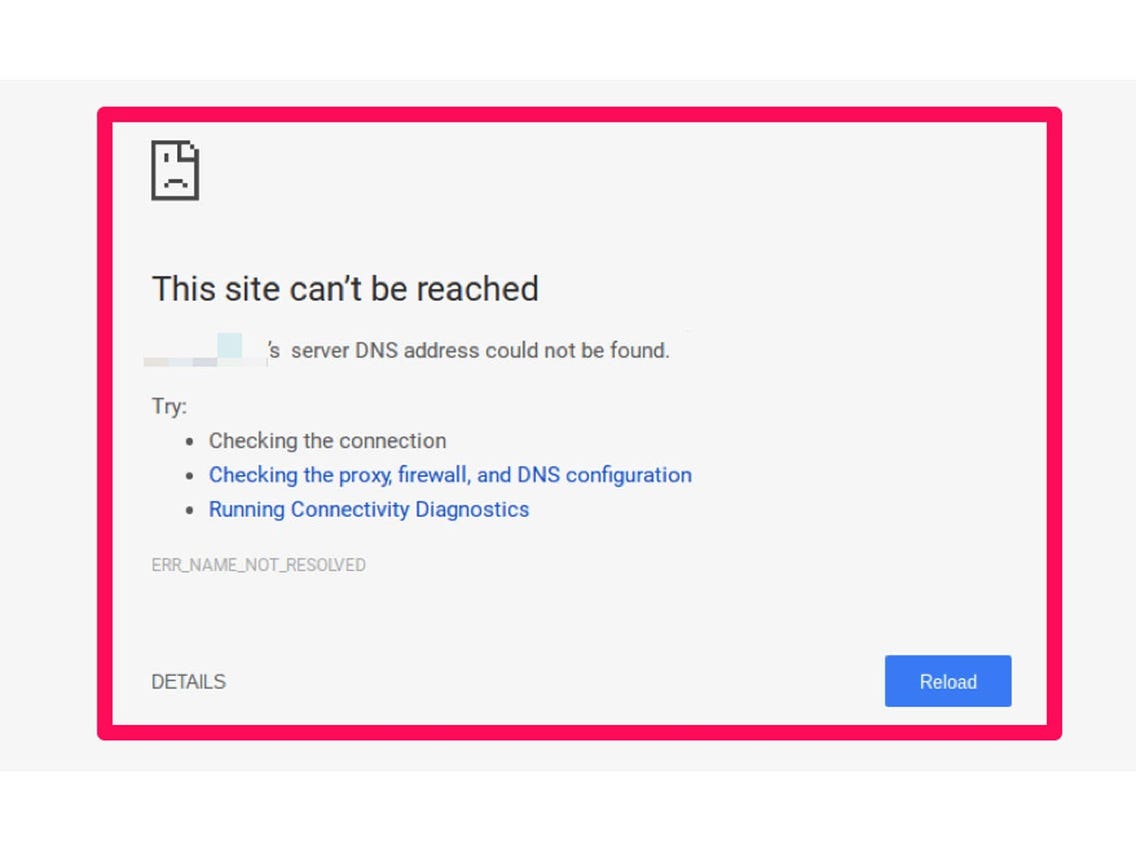
What happens when DNS server fails?
The DNS server returns the IP address, and the browser connects to the webpage that then appears on your screen. End users are unaware of the background tasks required to make the system work. If the DNS server is unavailable, the browser has no way of acquiring the website’s IP address, so it returns an error.
Who is to blame for a DNS error?
In some cases, a DNS error is the fault of the ISP, (Internet Service Provider), and you can spend hours trying to solve it locally only to realize it’s not within your control!
What is a DNS server?
Common DNS Errors and How to Fix Them Your DNS server is what translates the words that you type into a URL bar into the IP address necessary to connect you to the internet. DNS stands for Domain Name System, and when it’s working properly, it’s part of what allows you to use internet-connected services, such as email or your web browser.
Why am I getting DNS resolution issues?
If you fail to put down the right values and IP addresses of your records, then there is a high likelihood that you will be bogged down by DNS resolution issues. Some records such as MX, SPF and DKIM are essential for email delivery.