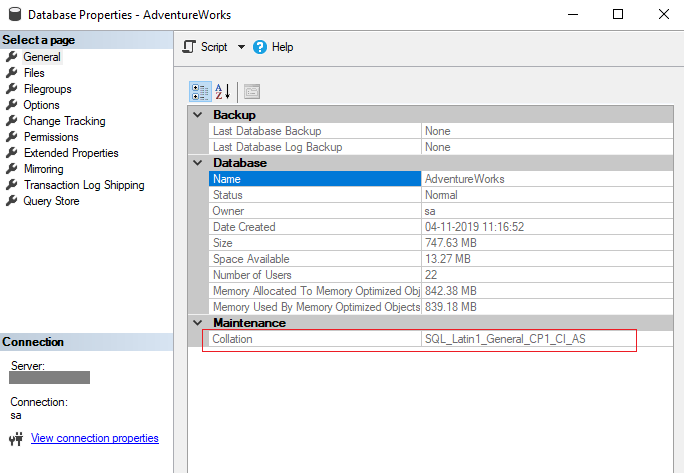
Server-level collation for Microsoft SQL Server If you don’t choose a different collation, the server-level collation defaults to SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS. The server collation is applied by default to all databases and database objects. You can’t change the collation when you restore from a DB snapshot.
What is the default SQL Server collation?
Server-level collation for Microsoft SQL Server If you don’t choose a different collation, the server-level collation defaults to SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS. The server collation is applied by default to all databases and database objects. You can’t change the collation when you restore from a DB snapshot.
What is the difference between SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS and Latin1_General_CI_AS?
The SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS collation is a SQL collation and the rules around sorting data for unicode and non-unicode data are different. The Latin1_General_CI_AS collation is a Windows collation and the rules around sorting unicode and non-unicode data are the same.
Does collation matter in SQL?
Data always follows collation constraint rules, which are configured when creating an object. When retrieving data using a T-SQL query, collation plays a fundamental role in the execution. It matters which collation is associated with a column when ordering clause is applied to that column.
What is SQL Server collation settings?
Collations in SQL Server provide sorting rules, case, and accent sensitivity properties for your data. Collations that are used with character data types, such as char and varchar, dictate the code page and corresponding characters that can be represented for that data type.
What is the default SQL Server collation?
Server-level collation for Microsoft SQL Server If you don’t choose a different collation, the server-level collation defaults to SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS. The server collation is applied by default to all databases and database objects. You can’t change the collation when you restore from a DB snapshot.
Does collation matter in SQL?
Data always follows collation constraint rules, which are configured when creating an object. When retrieving data using a T-SQL query, collation plays a fundamental role in the execution. It matters which collation is associated with a column when ordering clause is applied to that column.
What is SQL Server collation settings?
Collations in SQL Server provide sorting rules, case, and accent sensitivity properties for your data. Collations that are used with character data types, such as char and varchar, dictate the code page and corresponding characters that can be represented for that data type.
Does collation affect performance?
If you then specify a COLLATE clause in the query that is different than the collation used for the index, you will have a performance penalty because you won’t be using that index.
What does SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS mean?
The collate clause is used for case sensitive and case insensitive searches in the columns of the SQL server. There are two types of collate clause present: SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CS_AS for case sensitive. SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS for case insensitive.
Is SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS deprecated?
Is SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS case sensitive?
Database collation For example, the default server-level collation in SQL Server for the “English (United States)” machine locale is SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS , which is a case-insensitive, accent-sensitive collation.
Why do we need collation?
A collation allows character data for a given language to be sorted using rules that define the correct character sequence, with options for specifying case-sensitivity, accent marks, kana character types, use of symbols or punctuation, character width, and word sorting.
Why do we use collation?
Collections are used to store, retrieve, manipulate, and communicate aggregate data. Typically, they represent data items that form a natural group, such as a poker hand (a collection of cards), a mail folder (a collection of letters), or a telephone directory (a mapping of names to phone numbers).
What is DB collation?
Collation is a set of rules that tell database engine how to compare and sort the character data in SQL Server. Collation can be set at different levels in SQL Server. Below are the three levels: SQL Server level. Database level.
What is set Read_committed_snapshot on?
Setting the READ_COMMITTED_SNAPSHOT ON option allows access to versioned rows under the default READ COMMITTED isolation level. If the READ_COMMITTED_SNAPSHOT option is set to OFF, you must explicitly set the Snapshot isolation level for each session in order to access versioned rows.
What is collation sensitivity?
Collation refers to a set of rules that determine how data is sorted and compared. Character data is sorted using rules that define the correct character sequence, with options for specifying case-sensitivity, accent marks, kana character types and character width. Case sensitivity: If A and a, C and c, etc.
What is default SQL format?
The default date format in SQL is DD-MON-YY.
What is default data format in SQL?
The default string literal format, which is used for down-level clients, complies with the SQL standard form that is defined as YYYY-MM-DD. This format is the same as the ISO 8601 definition for DATE.
Is SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS deprecated?
What is the default collation for utf8mb4?
From MySQL 8.0, utf8mb4 is the default character set, and the default collation for utf8mb4 is utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci.
What is the default SQL Server collation?
Server-level collation for Microsoft SQL Server If you don’t choose a different collation, the server-level collation defaults to SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS. The server collation is applied by default to all databases and database objects. You can’t change the collation when you restore from a DB snapshot.