Definition of a vector. A vector is an object that has both a magnitude and a direction. Geometrically, we can picture a vector as a directed line segment, whose length is the magnitude of the vector and with an arrow indicating the direction. The direction of the vector is from its tail to its head.
How do you write a vector?
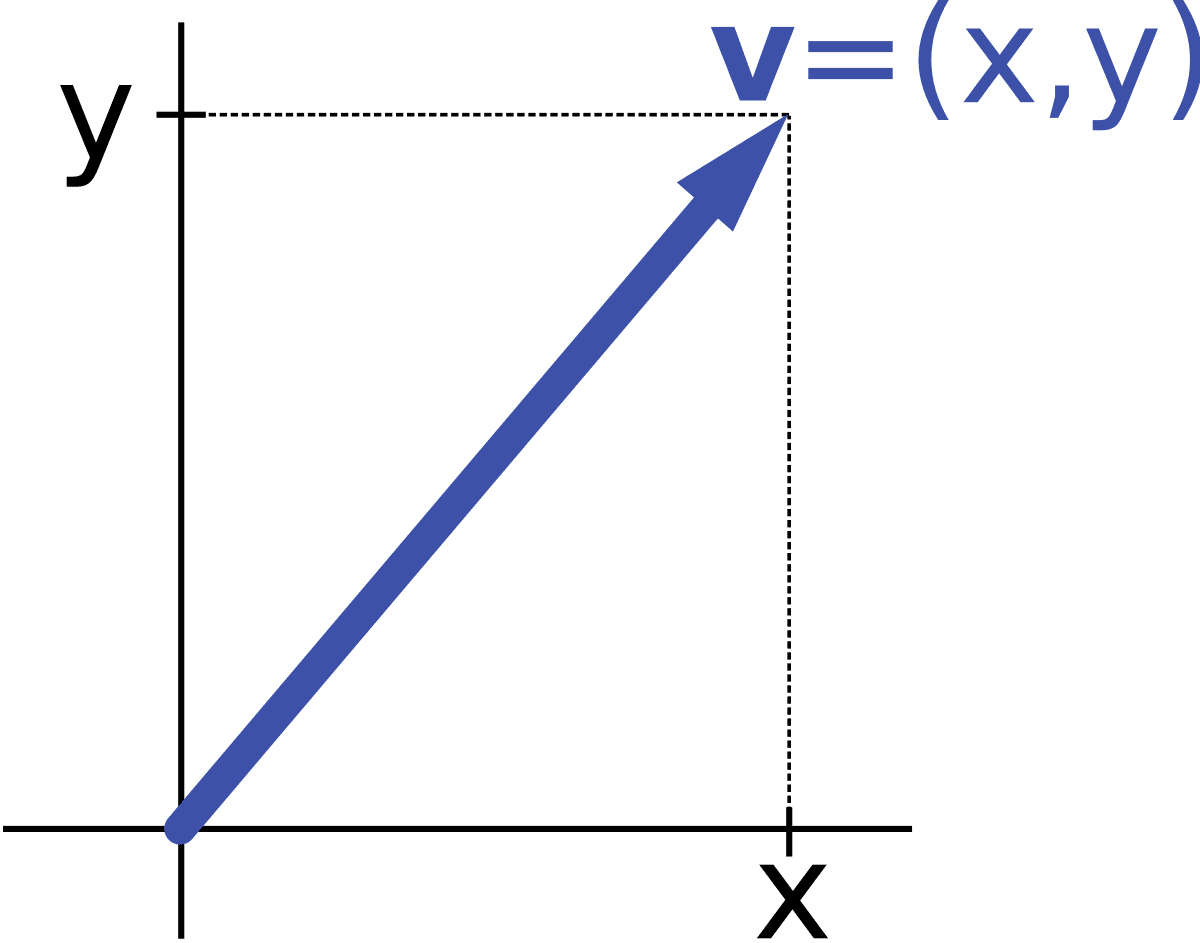
When a vector is just a list of numbers, we can visualize it as an arrow in space. For example, we visualize the vector (4,2)left parenthesis, 4, comma, 2, right parenthesis as an arrow whose tail is at the origin and whose tip is at the point ( 4 , 2 ) (4, 2) (4,2)left parenthesis, 4, comma, 2, right parenthesis.
What is vector with example?
A vector is a quantity or phenomenon that has two independent properties: magnitude and direction. The term also denotes the mathematical or geometrical representation of such a quantity. Examples of vectors in nature are velocity, momentum, force, electromagnetic fields, and weight.
What does a vector look like in physics?
vector, in physics, a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. It is typically represented by an arrow whose direction is the same as that of the quantity and whose length is proportional to the quantity’s magnitude.
What is a vector in math?
vector, in mathematics, a quantity that has both magnitude and direction but not position. Examples of such quantities are velocity and acceleration.
Is vector just an arrow?
Definition of a Vector A vector is a quantity with both magnitude and direction. We will frequently represent a vector quantity with an arrow, where the direction of the vector is the direction that the arrow points, and the magnitude of the vector is represented by the length of the arrow.
What is a vector structure?
A vector, in computing, is generally a one-dimensional array, typically storing numbers. Vectors typically have fixed sizes, unlike lists and queues. The vector data structure can be used to represent the mathematical vector used in linear algebra.
Does vector mean direction?
Definition of a vector. A vector is an object that has both a magnitude and a direction. Geometrically, we can picture a vector as a directed line segment, whose length is the magnitude of the vector and with an arrow indicating the direction. The direction of the vector is from its tail to its head.
Why are vectors represented as arrows?
Scalar quantities have a magnitude (size) only, whereas vector quantities have a magnitude and a direction. Vectors can be represented graphically as arrows. The length of the arrow indicates the magnitude of the vector. The direction of the arrow indicates the direction of the vector.
Is a vector a line?
Vectors are not lines and they have a very different function than lines. A vector is a direction and a magnitude, that’s it. It can also be made “magnitudeless” by being unitized (see Vicente’s response to your other question). A line, of course, has direction and magnitude, but it also has LOCATION.
How do you find a vector?
Explanation: To find the directional vector, subtract the coordinates of the initial point from the coordinates of the terminal point.
How do you write a vector in i and J?
A vector can be described using i,j notation. A unit vector is a vector of length 1, in Cartesian co-ordinates the unit vectors along the axis are denoted by i and j respectively. Any two-dimensional vector can be written in the form ai+bj a i + b j .
How do you write a vector in component form?
Component Form: The component form of a vector →v is written as →v=⟨vx,vy⟩ v → = ⟨ v x , v y ⟩ , where vx represents the horizontal displacement between the initial and terminal points, and vy represents the vertical displacement between the initial and terminal points.
How do you write a vector in terms of unit vectors?
A unit vector is a vector whose magnitude is 1, or in mathematical terms, a unit. In vector geometry, the notation of a unit vector is slightly different. Unit vectors are denoted by placing a hat (^) on top of the vectors. The vector v shown in the figure below is a unit vector and can be represented by v^.
How do you write a vector?
When a vector is just a list of numbers, we can visualize it as an arrow in space. For example, we visualize the vector (4,2)left parenthesis, 4, comma, 2, right parenthesis as an arrow whose tail is at the origin and whose tip is at the point ( 4 , 2 ) (4, 2) (4,2)left parenthesis, 4, comma, 2, right parenthesis.
What is a vector in simple English?
A vector is a mathematical object that has a size, called the magnitude, and a direction. It is often represented by boldface letters (such as , , ), or as a line segment from one point to another (as in ).
Are all arrows vectors?
It’s not. Mathematicians generally think of vectors as abstract objects, which live in what is called a vector space.
What is a synonym for vector?
In this page you can discover 21 synonyms, antonyms, idiomatic expressions, and related words for vector, like: transmitter, raster, binary, course, heading, linear, matrix, parameter, orthogonal, four-element and sequence.
What is the symbol of unit vector?
Unit Vector is represented by the symbol ‘^’, which is called a cap or hat, such as ^a a ^ . It is given by ^a a ^ = a/|a| Where |a| is for norm or magnitude of vector a. It can be calculated using a unit vector formula or by using a calculator.
What does V mean in vectors?
Vectors. A vector is an object with magnitude and direction (velocity, force, acceleration, etc). A scalar is an object with just magnitude (temperature, pressure, age, length). A vector, denoted v or v, has no initial point and is often best thought of as at the origin.
What is a proper vector?
A vector whose magnitude is zero, is called a null vector or zero vector. It is represented by 0 and its starting and end points are the same. The direction of null vector is not known. (vii) Proper vector. All the non-zero vectors are called proper vectors.
What is the opposite vector?
The vector −a is the opposite of the vector a. The vector −a has the same magnitude as a but points in the opposite direction.