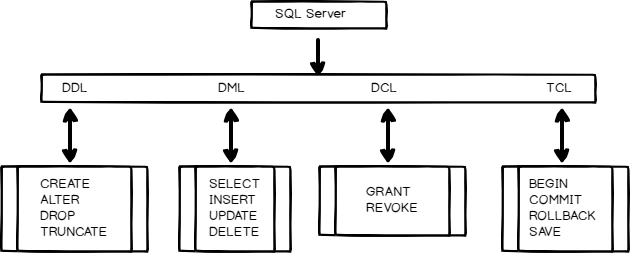
The second part of a SQL query is the name of the column you want to retrieve for each record you are getting. You can obviously retrieve multiple columns for each record, and (only if you want to retrieve all the columns) you can replace the list of them with * , which means “all columns”.
Should you use * in SQL?
That’s all about why you should not use SELECT * in the SQL query anymore. It’s always better to use the explicit column list in the SELECT query than a * wildcard. It not only improves the performance but also makes your code more explicit.
What does the asterisk (*) symbol mean in SQL?
The asterisk or star symbol ( * ) means all columns. The semi-colon ( ; ) terminates the statement like a period in sentence or question mark in a question.
What does * do in a search string?
A search string is a combination of keywords, truncation symbols, and boolean operators you enter into the search box of a library database or search engine. Example: educat* AND student* gives results that include “education, educator, educating” and “student, students”.
What does the asterisk (*) symbol mean in SQL?
The asterisk or star symbol ( * ) means all columns. The semi-colon ( ; ) terminates the statement like a period in sentence or question mark in a question.
What does the * wildcard represent access?
The asterisk “*” and the question mark “?” are the two main wildcard characters in Access you need to know. The asterisk represents multiple unknown characters. For example, the criteria “N*” would find all “N” words like “Nebraska,” “Ned,” “Not,” “Never Ever,” etc. The question mark represents one unknown character.
What does the wildcard operator * do?
In software, a wildcard character is a kind of placeholder represented by a single character, such as an asterisk ( * ), which can be interpreted as a number of literal characters or an empty string. It is often used in file searches so the full name need not be typed.
Should you use select * in code?
Avoid using SELECT * When writing queries, it would be better to set the columns you need in the select statement rather than SELECT *. There are many reasons for that recommendation, like: SELECT * Retrieves unnecessary data besides that it may increase the network traffic used for your queries.
Why should you not use select * in SQL?
When you use select * you’re make it impossible to profile, therefore you’re not writing clear & straightforward code and you are going against the spirit of the quote. select * is an anti-pattern. So selecting columns is not a premature optimization.
What is select * in Oracle SQL?
A SELECT statement consists of a query with an optional ORDER BY clause, an optional result offset clause, an optional fetch first clause, an optional FOR UPDATE clause and optionally isolation level. The SELECT statement is so named because the typical first word of the query construct is SELECT.
Why is an asterisk (*) used here?
It is most commonly used to signal a footnote, but it is sometimes also used to clarify a statement or to censor inappropriate language.
What does * mean after a set?
Apparently, if one adds an asterisk to the right side of a set definition, it means the set to the left can be built out of elements in the set to the right.
What is the difference between select * and select 1?
There is no difference between EXISTS with SELECT * and SELECT 1. SQL Server generates similar execution plans in both scenarios. EXISTS returns true if the subquery returns one or more records. Even if it returns NULL or 1/0.
What is * in a search?
The asterisk is a wildcard that matches zero or more characters. For example, a search on ‘Sam*’ will bring back results that include ‘Sam’, ‘Samantha’, ‘Samuel’, etc. You can also search alternate spellings with the asterisk (*), which represents 0 to 5 unknown characters.
What is the function of * operator?
Multiplication * (Asterisk) Basic arithmetic operator used for multiplication; the result of an arithmetic operator is usually a numeric value.
What does * mean in Boolean search?
The asterisk serves as the truncation (or wildcard) operator. Unlike the other operators, it should be appended to the word to be affected. Words match if they begin with the word preceding the * operator.
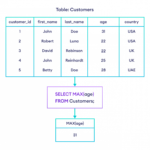
Can we use max with * in SQL?
Try using this SQL SELECT statement: SELECT * FROM employees WHERE department_id=30 AND salary = (SELECT MAX(salary) FROM employees WHERE department_id=30); This will return the employee information for only the employee in department 30 that has the highest salary.
What does DEL * * do?
This command will delete every file (*. *) from every folder (/s) inside the Adobe folder in the user’s Documents directory. The folders will remain, but every file will get removed.
Which is an SQL*Plus command?
SQL*Plus is a command-line tool that provides access to the Oracle RDBMS. SQL*Plus enables you to: Enter SQL*Plus commands to configure the SQL*Plus environment. Startup and shutdown an Oracle database.
What are SQL*Plus variables?
If a double ampersand reference causes SQL*Plus to prompt you for a value, then SQL*Plus defines the variable as that value (i.e. the value is stored until you exit). Any subsequent reference to the variable (even in the same command) using either “&” or “&&” substitutes the newly defined value.
What does distinct mean *?
Meaning: Clearly or sharply defined to the mind. Synonyms: clear-cut; distinct; trenchant.
How do I remove duplicates in SQL?
According to Delete Duplicate Rows in SQL, you can also use the SQL RANK feature to get rid of the duplicate rows. Regardless of duplicate rows, the SQL RANK function returns a unique row ID for each row. You need to use aggregate functions like Max, Min, and AVG to perform calculations on data.