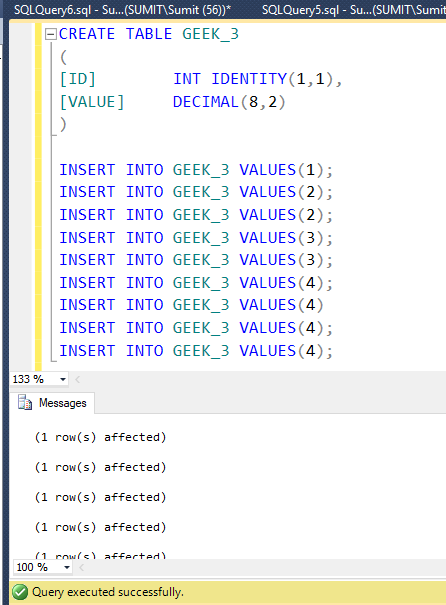
WHERE id =* means in SQL?
The asterisk in the where condition is actually part of a non-ANSI outer join operator , it is used to define an implicit outer join.
Should you use * in SQL?
That’s all about why you should not use SELECT * in the SQL query anymore. It’s always better to use the explicit column list in the SELECT query than a * wildcard. It not only improves the performance but also makes your code more explicit.
What does the * asterisk represent in a SQL statement?
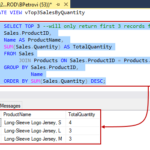
The asterisk or star symbol ( * ) means all columns. The semi-colon ( ; ) terminates the statement like a period in sentence or question mark in a question.
What does the * wildcard represent access?
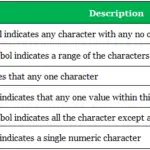
The asterisk “*” and the question mark “?” are the two main wildcard characters in Access you need to know. The asterisk represents multiple unknown characters. For example, the criteria “N*” would find all “N” words like “Nebraska,” “Ned,” “Not,” “Never Ever,” etc. The question mark represents one unknown character.
What is the difference between * and wildcard characters?
Difference between wildcards (*) and (?) A wildcard character is a kind of placeholder represented by a single character, such as an asterisk (*) and question mark (?), which can be interpreted as a number of literal characters or an empty string. It is often used in file searches so the full name need not be typed.
What do the asterisks * * indicate?
The asterisk is used to call out a footnote, especially when there is only one on the page. Less commonly, multiple asterisks are used to denote different footnotes on a page (i.e., *, **, ***).
Why is an asterisk (*) used here?
It is most commonly used to signal a footnote, but it is sometimes also used to clarify a statement or to censor inappropriate language.
When would you use the asterisk (*) wildcard instead of the question mark (?) wildcard?
Wildcards take the place of one or more characters in a search term. A question mark (?) is used for single character searching. An asterisk (*) is used for multiple character searching.
What does DEL * * do?
This command will delete every file (*. *) from every folder (/s) inside the Adobe folder in the user’s Documents directory. The folders will remain, but every file will get removed.
Does COUNT (*) ignore NULL values?
The notation COUNT(*) includes NULL values in the total. The notation COUNT( column_name ) only considers rows where the column contains a non- NULL value.
What does the * mean in search?
The asterisk is a commonly used wildcard symbol that broadens a search by finding words that start with the same letters. Use it with distinctive word stems to retrieve variations of a term with less typing.
Why using select * in an SQL query is a bad practice?
By using SELECT *, you can be returning unnecessary data that will just be ignored, but fetching that data is not free of cost. This results in some wasteful IO cycles at the database end since you will be reading all of that data off the pages when perhaps you could have read the data from index pages.
Is select * faster than select column?
Selecting distinct and less than all columns will always be faster than selecting *.
Does COUNT (*) ignore NULL values?
The notation COUNT(*) includes NULL values in the total. The notation COUNT( column_name ) only considers rows where the column contains a non- NULL value.
Which is an SQL*Plus command?
SQL*Plus is a command-line tool that provides access to the Oracle RDBMS. SQL*Plus enables you to: Enter SQL*Plus commands to configure the SQL*Plus environment. Startup and shutdown an Oracle database.
What is a unique key in SQL?
The UNIQUE constraint ensures that all values in a column are different. Both the UNIQUE and PRIMARY KEY constraints provide a guarantee for uniqueness for a column or set of columns. A PRIMARY KEY constraint automatically has a UNIQUE constraint.
How many characters does the * wildcard replace?
Asterisk (*): It is used for replacing 1 or more characters from a selector attribute.
What does the * wildcard mean in SQL?
A wildcard character is used to substitute one or more characters in a string. Wildcard characters are used with the LIKE operator. The LIKE operator is used in a WHERE clause to search for a specified pattern in a column.
What is an * asterisk symbol in Linux?
The asterisk ( * ) The asterisk represents any number of unknown characters. Use it when searching for documents or files for which you have only partial names.
How many character does * Replace?
Wildcards are symbols that enable you to replace zero or multiple characters in a string. These can be quite useful when dealing with dynamically-changing attributes in a selector. Asterisk (*) – replaces zero or more charactersQuestion mark (?)
Can we combine wildcard characters and * give an example?
You could. But remember, the * wildcard represents *any* string of characters–including spaces. It’s not limited to characters within a word (and neither are other wildcards).