If the DNS server is unavailable, the browser has no way of acquiring the website’s IP address, so it returns an error. Now everyone knows the server is down because it only takes seconds for the news to spread.As soon as a server goes down, the DNS server should automatically switch the DNS A record to list the IP address for the working server first. When DNS resolvers come back to request the IP address for the site, they receive the updated IP address, and route the user to the redundant server.
What happens when DNS fail?
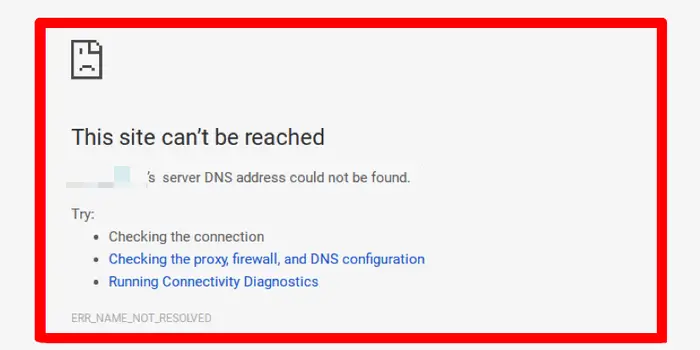
If DNS isn’t working properly, you won’t be able to use web-connected services, such as your browser or email, despite your computer or router showing a working internet connection. The webpage may timeout, give you an error message, or even bring up a specific “DNS error” message.
Can a DNS server go down?
DNS name servers are very important; they are the primary source that directs to the actual hostnames, which is what a client is looking for. These name servers can go down at times due to an issue (i.e. DDoS attacks, network issues with the server, etc.).
What is the consequence if the DNS servers are down or not reachable?
This server then dissolves the domain name into a numeric sequence and returns a corresponding IP address. Should the DNS server fail to produce an answer because it’s down, then it won’t be possible to access the desired website; the result is the error message “DNS server not responding”.
What is DNS server in WIFI?
The Domain Name System (DNS) Server is a server that is specifically used for matching website hostnames (like example.com)to their corresponding Internet Protocol or IP addresses. The DNS server contains a database of public IP addresses and their corresponding domain names.
What are common DNS issues?
High DNS latency equals high loading times. High DNS latency can be as a result of the DNS name servers not being in close geographic proximity to a large percentage of users who visit your site. Another reason might be network congestion.
What does a DNS do?
2.1 that computers use to connect to each other. The Internet’s DNS system works much like a phone book by managing the mapping between names and numbers. DNS servers translate requests for names into IP addresses, controlling which server an end user will reach when they type a domain name into their web browser.
How long do DNS outages last?
You might need to way up to 24 hours, so the changes are well propagated. Check if you have paid for your domain name. If you have forgotten to pay your domain name, it won’t answer queries anymore when it expires. Set reminders for domain renovation and don’t miss the time.
How many DNS servers are there?
Right now there are over 600 different DNS root servers distributed across every populated continent on earth.
Does DNS affect Internet speed?
Although DNS is not directly related to your Internet speed, it can influence how fast an individual webpage appears on your computer. Once a connection has been established though, it should not affect download speeds. If you want to amend your router’s DNS servers however, this can help improve your overall speed.
What is DNS failure mean?
(Domain Name System failure) The inability of a DNS server to convert a domain name to an IP address in a TCP/IP network. A DNS failure may occur within a company’s private network or within the Internet.
Does restarting computer flush DNS?
A DNS Server’s cache is cleared at reboot. Other than that you can manually clear the cache at any time by using the DNS Admin console.
How do you diagnose DNS problems?
Run ipconfig /all at a command prompt, and verify the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway. Check whether the DNS server is authoritative for the name that is being looked up. If so, see Checking for problems with authoritative data.
Does DNS change your IP address?
No. Switching DNS servers will not change your IP address. DNS servers translate domain names to IP addresses. By default, all the web browsers come with the option to automatically detect the DNS settings of their current network.
What is difference between DNS and IP address?
An IP address is an address assigned to any computer (including servers) to identify it on a given network. A DNS address is a Domain Name Service which is used to convert alphabetic references into a server’s IP address generally for hosting services.
Who is the owner of DNS server?
ICANN is the global non-profit organization responsible for coordinating the Internet’s core systems of unique identifiers, most notably the Domain Name System (DNS).
Who owns domain server?
The Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) is the non-profit organization that oversees the assignment of both IP addresses and domain names.
Who is in charge of DNS servers?
Management of TLD nameservers is handled by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA), which is a branch of ICANN. The IANA breaks up the TLD servers into two main groups: Generic top-level domains: These are domains that are not country specific, some of the best-known generic TLDs include .com, . org, .
How do I find the DNS on my router?
The easiest way to find out your dns server IP address is to go through the router’s admin interface status page. All routers have a built-in web-based setup page that allows the user to customize settings and set view properties such as IP address and dns settings.
What does changing your DNS to 8.8 8.8 do?
By changing your 8.8. 8.8 DNS, you are switching your operator from your ISP to Google Public DNS. It protects users from DDOS and malware attacks. However, by doing this, Google can see all your DNS queries and collect even more data.
Should I use 8.8 8.8 DNS?
That is not recommended and may even be a violation of your security policies, depending on the level of security required in your organization or by any governing agency. DNS forwarders that only point to 8.8. 8.8 are using your ISP connection to hop to 8.8.
What DNS server should I use?
Answer: Public DNS systems such as OpenDNS, Cloudflare, or Google DNS are better than the servers maintained by internet service providers. You should use public DNS servers as they offer maximum uptime, faster speeds, and increased security.
What happens when DNS server fails?
The DNS server returns the IP address, and the browser connects to the webpage that then appears on your screen. End users are unaware of the background tasks required to make the system work. If the DNS server is unavailable, the browser has no way of acquiring the website’s IP address, so it returns an error.
What to do when DNS server is down?
Troubleshooting. The root of such irritating messages can often be traced back to the server outage. In such cases, the DNS server is temporarily unavailable. Most of the time, these problems can be corrected by changing browsers, switching a few of your firewall settings, or restarting your router.
What happens if a DNS server goes down for 24 hours?
What will happen if a root DNS server goes down for 24 hours? A “single” root DNS server consists of several hundred servers all responding to the same IP address. Having one of them go down is a non-event; BGP or OSPF Anycasting takes care of the details.
Is my ISP’s DNS server down?
An ISP’s DNS server may be down. To check, ping the IP addresses of the DNS servers. Remove any addresses that do not respond. To find the IP addresses, select the “Obtain DNS server address automatically.”