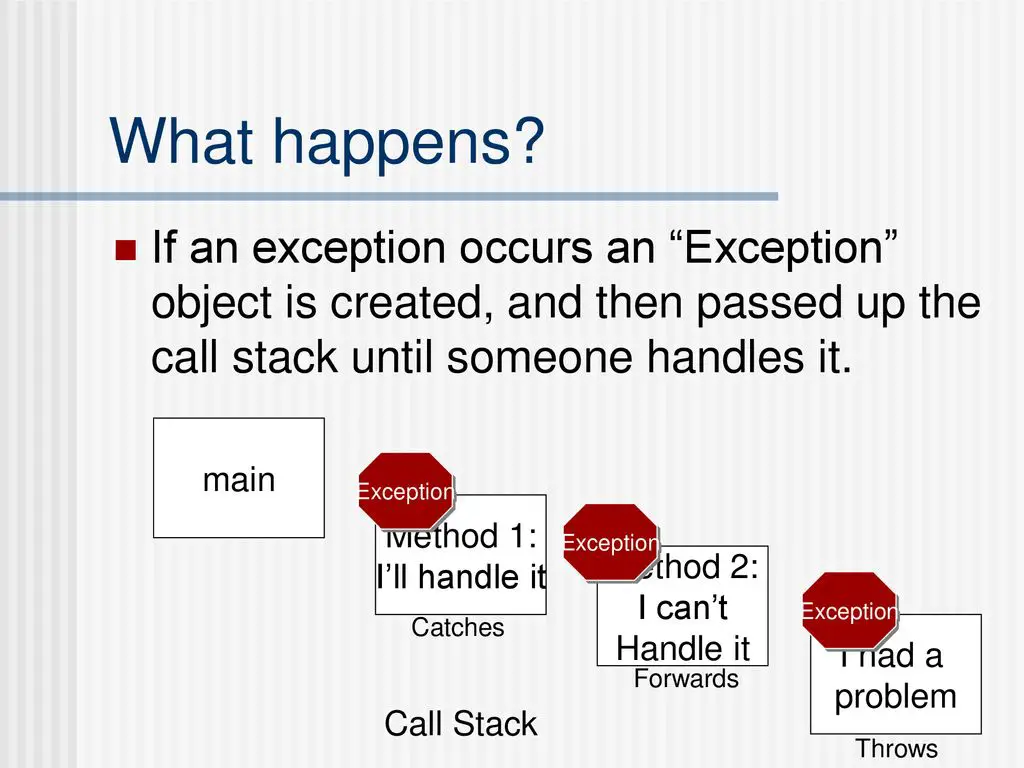
Definition: An exception is an event, which occurs during the execution of a program, that disrupts the normal flow of the program’s instructions. When an error occurs within a method, the method creates an object and hands it off to the runtime system.
What happens when exception occurs in Java?
When an exception occurs inside a Java method, the method creates an Exception object and passes the Exception object to the JVM (in Java term, the method ” throw ” an Exception ). The Exception object contains the type of the exception, and the state of the program when the exception occurs.
What happens when an exception occurs in a thread?
An uncaught exception will cause the thread to exit. When it bubbles to the top of Thread. run() it will be handled by the Thread’s UncaughtExceptionHandler. By default, this will merely print the stack trace to the console.
What happens when an exception is triggered?
This is what normally happens when an exception is triggered: The current code state is saved. The code execution will switch to a predefined (custom) exception handler function.
What happens when exception occurs in C++?
When an exception occurs within the try block, control is transferred to the exception handler. If no exception is thrown, the code continues normally and the handlers are ignored. An exception in C++ is thrown by using the throw keyword from inside the try block.
What happens when exception is not caught?
What happens if an exception is not caught? If an exception is not caught (with a catch block), the runtime system will abort the program (i.e. crash) and an exception message will print to the console. The message typically includes: name of exception type.
How do exceptions work in Java?
An exception object is an instance of an exception class. It gets created and handed to the Java runtime when an exceptional event occurred that disrupted the normal flow of the application. This is called “to throw an exception” because in Java you use the keyword “throw” to hand the exception to the runtime.
What happens if an exception is thrown in runnable?
You can catch your checked exception in the run() method, and throw an unchekced exception (i.e., RuntimeException ) in its place. This will terminate the thread with a stack trace; perhaps that’s what you’re after.
How do you handle exceptions in run?
So even if run() throws exception the program cannot catch it. You should put thread execution result to some class level variable and then read it from there. Or alternatively use new API: executors and interface Callable that declares method call() that returns future result of the thread execution.
How do you handle exceptions in multithreading?
The current exception-handling implementation is safe for multithreading; exceptions in one thread do not interfere with exceptions in other threads. However, you cannot use exceptions to communicate across threads; an exception thrown from one thread cannot be caught in another.
What is difference between error and exception?
The error indicates trouble that primarily occurs due to the scarcity of system resources. The exceptions are the issues that can appear at runtime and compile time. 2. It is not possible to recover from an error.
Can we use exception in trigger?
A trigger exception (also known as a “blocking trigger”) is a kind of trigger that can be used to block another trigger’s ability to fire under certain conditions. For example, if a tag has a trigger to fire on all pages and a trigger exception that is set to “Page URL equals thankyou.
What is exception handling in OOP?
Exception handling is a mechanism that separates code that detects and handles exceptional circumstances from the rest of your program. Note that an exceptional circumstance is not necessarily an error. When a function detects an exceptional situation, you represent this with an object.
What is an exception in C++ Mcq?
Explanation:- An exception is defined as the problem in C++ program that arises during the execution of the program for example divide by zero error. 3. In nested try-catch block, if the inner catch block gets executed, then_____________ A. Program stops immediately.
What are exceptions in Java?
Definition: An exception is an event, which occurs during the execution of a program, that disrupts the normal flow of the program’s instructions. When an error occurs within a method, the method creates an object and hands it off to the runtime system.
What happens when exception is thrown in finally block in Java?
The finally block executes whether exception rise or not and whether exception handled or not. A finally contains all the crucial statements regardless of the exception occurs or not. In this case, the program runs fine without throwing any exception and finally block execute after the try block.
What if exception occurs in Finalize method?
If an uncaught exception is thrown during the finalization, the exception is ignored and finalization of that object terminates. So, in this case the “GC will halt the process for that object” and in which case it may be that some its resources are not have been correctly released.
What happens when exception occurs in Java?
When an exception occurs inside a Java method, the method creates an Exception object and passes the Exception object to the JVM (in Java term, the method ” throw ” an Exception ). The Exception object contains the type of the exception, and the state of the program when the exception occurs.
Can we handle exception without catch block?
Yes, it is possible. You can use an uncaught exception handler. Its responsibility is to catch the exceptions that your program didn’t catch, and do something with it.
Can we throw exception in catch block?
When an exception is cached in a catch block, you can re-throw it using the throw keyword (which is used to throw the exception objects). Or, wrap it within a new exception and throw it.
Why exception handling is needed?
Exception handling is the process of responding to unwanted or unexpected events when a computer program runs. Exception handling deals with these events to avoid the program or system crashing, and without this process, exceptions would disrupt the normal operation of a program.
How do you handle an exception thrown in Java?
Throwing an exception is as simple as using the “throw” statement. You then specify the Exception object you wish to throw. Every Exception includes a message which is a human-readable error description. It can often be related to problems with user input, server, backend, etc.