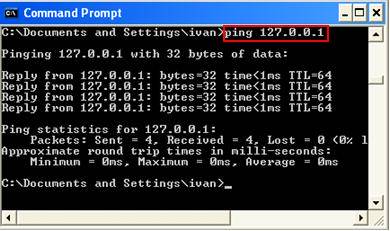
The IP address 127.0. 0.1 is a special-purpose IPv4 address and is called the localhost or loopback address. All computers use this address as their own, but it doesn’t let computers communicate with other devices as a real IP address does.
What does a 127 IP address mean?
… The class A network number 127 is assigned the “loopback” function, that is, a datagram sent by a higher level protocol to a network 127 address should loop back inside the host. No datagram “sent” to a network 127 address should ever appear on any network anywhere.
Is 127 a valid IP address?
All the addresses starting with 127 are dedicated to testing the connectivity but all zeros(127.0. 0.0) and all ones(127.255. 255.255) in address 127 is not allowed. All zeros represent the subnet id and all ones are generally used for BroadCasting.
What is the IP 127.0 0.1 used for?
Localhost is the default name of the computer you are working on. The term is a pseudo name for 127.0. 0.1, the IP address of the local computer. This IP address allows the machine to connect to and communicate with itself.
What class is IP address starting with 127?
Class B Network The number 127 is reserved for loopback, which is used for internal testing on the local machine.
Should I use 127.0 0.1 for DNS?
127.0. 0.1 should not be seen on the local network. It’s a special internal IP address for the loopback adapter. The IP of the server on the other hand is assigned to the network adapter.
Why is 127 not an IP address?
Why not some other IP address like 121.9. 1.1 or anything else? The answer to this question lies in the fact that by 1981, 0 and 127 were the only reserved Class A networks. As 0 was used for pointing to a specific host, 127, the last network number, was left for loopback IP address or localhost.
What is the difference between 127.0 0.1 and localhost?
Hence, the address for localhost has to be looked up or resolved, whereas using 127.0. 0.1 goes directly to that IP address. Another significant difference between localhost and 127.0. 0.1 is how the request is sent.
What is localhost on my wifi?
“The localhost is the default name describing the local computer address also known as the loopback address. For example, typing: ping localhost would ping the local IP address of 127.0. 0.1 (the loopback address). When setting up a web server or software on a web server, 127.0.
What is a local host IP?
Localhost is a hostname that refers to the local machine currently making the request. On many computers, localhost is an alias for the IP address 127.0. 0.1. When a computer pings this IP address, it is communicating with itself.
What are the 4 types of IP address?
How an IP Address Works. An IP address allows computers to send and receive data over the internet. Most IP addresses are purely numerical, but as internet usage grows, letters have been added to some addresses. There are four different types of IP addresses: public, private, static, and dynamic.
What is an example of a private IP address?
Private addresses include IP addresses from the following subnets: Range from 10.0. 0.0 to 10.255. 255.255 — a 10.0.
What is the difference between 127.0 0.1 and localhost?
Hence, the address for localhost has to be looked up or resolved, whereas using 127.0. 0.1 goes directly to that IP address. Another significant difference between localhost and 127.0. 0.1 is how the request is sent.
What is the loopback address used for?
The IP address 127.0. 0.1 is called a loopback address. Packets sent to this address never reach the network but are looped through the network interface card only. This can be used for diagnostic purposes to verify that the internal path through the TCP/IP protocols is working.
What is an example of a private IP address?
Private addresses include IP addresses from the following subnets: Range from 10.0. 0.0 to 10.255. 255.255 — a 10.0.
What does a 127 IP address mean?
… The class A network number 127 is assigned the “loopback” function, that is, a datagram sent by a higher level protocol to a network 127 address should loop back inside the host. No datagram “sent” to a network 127 address should ever appear on any network anywhere.
What is the equivalent of 127.0 0.1 in IPv6?
The name localhost normally resolves to the IPv4 loopback address 127.0. 0.1, and to the IPv6 loopback address ::1.
What do the IP address 127.0 0.1 and the URL http localhost have in common?
127.0. 0.1 is the loopback Internet protocol (IP) address also referred to as the localhost. The address is used to establish an IP connection to the same machine or computer being used by the end-user. The same convention is defined for computers that support IPv6 addressing using the connotation of ::1.
How do I find my local DNS server?
Open your Command Prompt from the Start menu (or type “Cmd” into the search in your Windows task bar). Next, type ipconfig/all into your command prompt and press Enter. Look for the field labeled “DNS Servers.” The first address is the primary DNS server, and the next address is the secondary DNS server.
What is the loopback address used for?
The IP address 127.0. 0.1 is called a loopback address. Packets sent to this address never reach the network but are looped through the network interface card only. This can be used for diagnostic purposes to verify that the internal path through the TCP/IP protocols is working.
How do I find my loopback IP address?
At the command line, type NETSTAT . Select option 1 (Work with TCP/IP interface status) for IPv4 interfaces, or select option 4 (Work with IPv6 interface status) for IPv6 interfaces. Scroll down to find the loopback interface (127.0.
What is the difference between localhost and IP address?
When you access localhost , your /etc/hosts file will tell your computer not to look any further and redirects you to your own computer. When you access the local IP adress, your computer will ask the router to fetch the data, and your router will then point back to your computer.
Why is localhost’s IP address 127?
As 0 was used for pointing to a specific host, 127, the last network number, was left for loopback IP address or localhost. Y ou might have definitely heard of 127.0.0.1. You also might be knowing that 127.0.0.1 points to localhost. But, why is localhost ‘s IP address 127.0 .0.1–why not something else?
What is the difference between 0 and 127 network numbers?
The answer to this question lies in the fact that by 1981, 0 and 127 were the only reserved Class A networks. As 0 was used for pointing to a specific host, 127, the last network number, was left for loopback IP address or localhost. Y ou might have definitely heard of 127.0.0.1. You also might be knowing that 127.0.0.1 points to localhost.
What is the purpose of the Class A network number 127?
The class A network number 127 is assigned the “loopback” function, that is, a datagram sent by a higher level protocol to a network 127 address should loop back inside the host. No datagram “sent” to a network 127 address should ever appear on any network anywhere.
How secure is 127.0.0.1?
TCP/IP checks all the messages send or received through this IP and block the messages that contain the loopback addresses. It helps in improving the security of the data shared through this address. Someone can not retrieve your data by disguising as a traffic signal.