A cache hit ratio of 90% and higher means that most of the requests are satisfied by the cache. A value below 80% on static files indicates inefficient caching due to poor configuration.
What is a good hit ratio?
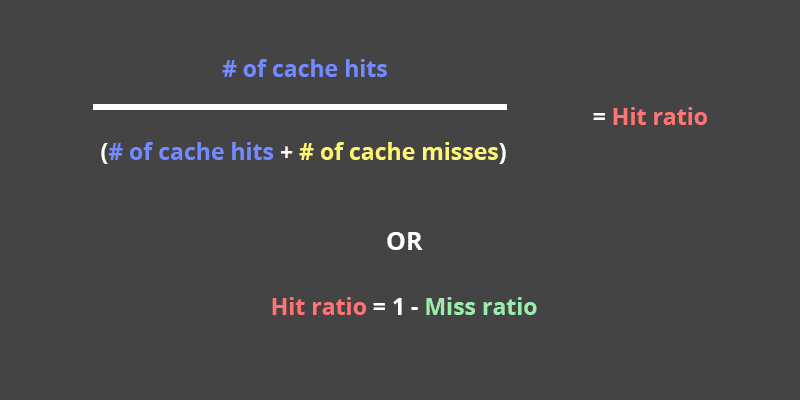
Generally speaking, for most sites, a hit ratio of 95-99%, and a miss ratio of one to five percent is ideal.
What is the cache hit ratio?
Cache hit ratio is a measurement of how many content requests a cache is able to fill successfully, compared to how many requests it receives. A content delivery network (CDN) provides a type of cache, and a high-performing CDN will have a high cache hit ratio.
Can it be possible to have 100% hit in a cache?
That is not mathematically possible.
How do I increase my cache hit rate?
To increase your cache hit ratio, you can configure your origin to add a Cache-Control max-age directive to your objects, and specify the longest practical value for max-age .
What do you mean by cache hit?
A cache hit is a state in which data requested for processing by a component or application is found in the cache memory. It is a faster means of delivering data to the processor, as the cache already contains the requested data.
Is it possible that an L1 cache memory’s hit ratio reaches 100 %? Explain?
The L1 cache has a 1ns access latency and a 100 percent hit rate. It, therefore, takes our CPU 100 nanoseconds to perform this operation.
Why a larger cache can increase the hit rate?
If you access many files and you have a large cache, you will have a larger cache-hit rate because older information still remains in the cache during consistency checks. However, if you have a small cache, there is less room for information to remain.
How is hit rate calculated?
It can be expressed in this simple formula: (number of sales)/(number of prospects) x 100. The hit ratio will vary among sales reps in the same company based on their experience and selling ability, but this is a statistic that helps you plan your selling and prospecting activity.
What is miss penalty in cache?
Miss penalty is defined as the difference between lower level access time and cache access time. Then the above equation becomes effective-access-time = cache-access-time + miss-rate * miss-penalty. Due to locality of reference, many requests are not passed on to the lower level store.
What is average hit rate?
Average hit rate (AVH) = singles + doubles (each base X 2) + triples (each base X 3) + home runs (each base X 4) divided by hits or total bases divided by hits. The goal here is to glance at a player’s average hit rate and home run total to get a feel for a player’s upside in power.
What does hit rate mean in psychology?
in signal detection tasks, the proportion of trials in which a signal is present and the participant correctly responds that it is.
What is the meaning of hit rate?
The percentage of the desired number of outcomes received by a salesperson relative to the total activity level. For example, it is the number of sales as a percentage of the number of calls. It also is called batting average and conversion rate.
What is hit rate Omori?
Hit rate: Hit rate determines wether an attack hits or misses. The default hit rate for most party members is 100%, though this can be changed with items and status effects.
How do you know if a cache is a hit or miss?
If the desired data is in L1, then it’s a cache hit. And if the desired data is in another cache memory level then it’s a cache miss. An access that misses in L1 but hits in L2 wouldn’t usually be called a “cache miss”.
How do the L1 L2 and L3 cache improve CPU performance?
Level 3 (L3) cache is specialized memory developed to improve the performance of L1 and L2. L1 or L2 can be significantly faster than L3, though L3 is usually double the speed of DRAM. With multicore processors, each core can have dedicated L1 and L2 cache, but they can share an L3 cache.
Why L1 cache is faster than L2?
What is the purpose of L1 L2 and L3 cache?
The main difference between L1 L2 and L3 cache is that L1 cache is the fastest cache memory and L3 cache is the slowest cache memory while L2 cache is slower than L1 cache but faster than L3 cache. Cache is a fast memory in the computer. It holds frequently used data by the CPU.
How do I choose a cache size?
Within these hard limits, the factors that determine appropriate cache size include the number of users working on the machine, the size of the files with which they usually work, and (for a memory cache) the number of processes that usually run on the machine.
How cache affects performance?
Cache memory is a large determinant of system performance. The larger the cache, the more instructions can be queued and carried out. Storing instructions in cache reduces the amount of time it takes to access that instruction and pass it to a CPU core.
Is 8 MB cache good?
So, 8MB doesn’t speed up all your data access all the time, but it creates (4 times) larger data “bursts” at high transfer rates. Benchmarking finds that these drives perform faster – regardless of identical specs.” “8mb cache is a slight improvement in a few very special cases.
Is higher or lower cache better?
Always – More the better. A CPU cache is a cache used by the central processing unit of a computer to reduce the average time to access memory. The cache is a smaller, faster memory which stores copies of the data from the most frequently used main memory locations.