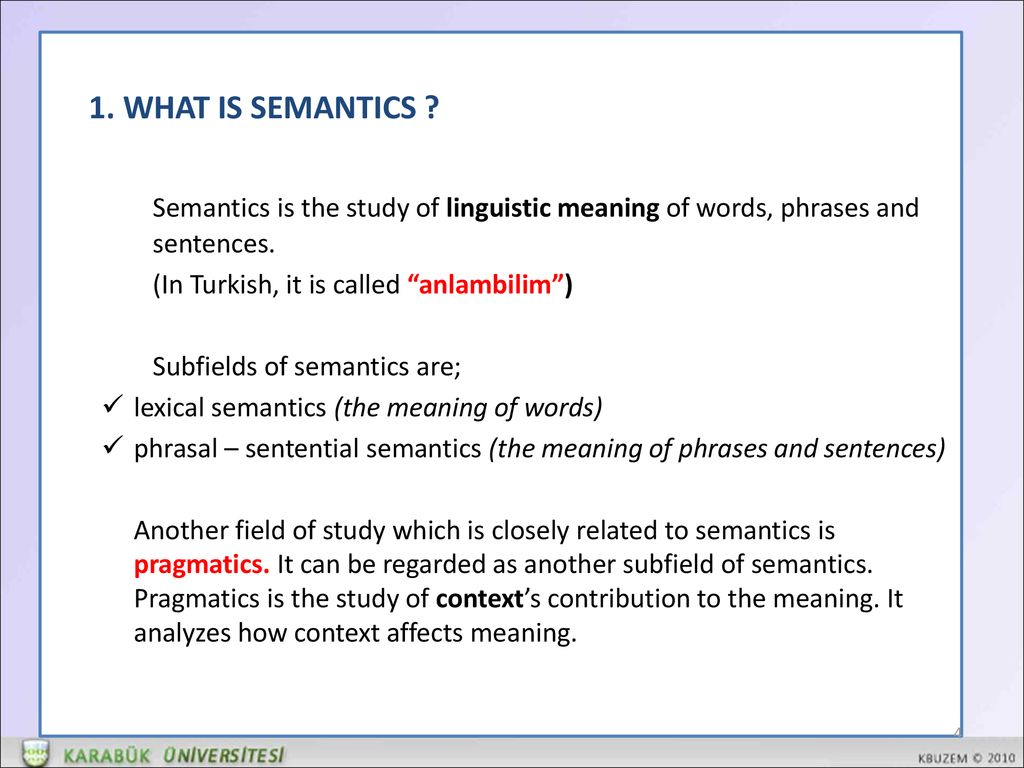
Semantics is the study of meaning in language. It can be applied to entire texts or to single words. For example, “destination” and “last stop” technically mean the same thing, but students of semantics analyze their subtle shades of meaning.
What is an example of semantics in a sentence?
For example, in everyday use, a child might make use of semantics to understand a mom’s directive to “do your chores” as, “do your chores whenever you feel like it.” However, the mother was probably saying, “do your chores right now.”
What does it mean to say something is semantic?
If something is semantic, it has to do with the meaning of a word.
What are the two types of semantics?
Semantics is the study of meaning. There are two types of meaning: conceptual meaning and associative meaning.
What is an example of semantics in a sentence?
For example, in everyday use, a child might make use of semantics to understand a mom’s directive to “do your chores” as, “do your chores whenever you feel like it.” However, the mother was probably saying, “do your chores right now.”
What are semantic features examples?
An element of a word’s denotation or denotative meaning. For example, young, male, and human are semantic features of the word boy. Also called a semantic component.
What is an example of semantic problem?
For example, when people say or use the word gay. One person might think its related to the sexuality of someone. There are others that say “that’s gay” to them, it might mean that’s sucks, or others might use the word gay as happy.
What are the main types of semantics?
The three major types of semantics are formal, lexical, and conceptual semantics.
What are the basic concepts of semantics?
Definition 1.1 (expanded) Semantics is the study of meaning in human languages. More precisely, it is the study and representation of the meaning Page 6 6 Natural Language Semantics of every kind of constituent and expression in language, and also of the meaning relationships between them.
What is an example of semantics in psychology?
Some examples of semantic memories might include: Recalling that Washington, D.C., is the U.S. capital and Washington is a state. Recalling that April 1564 is the date on which Shakespeare was born. Recalling the type of food people in ancient Egypt used to eat. Knowing that elephants and giraffes are both mammals.
What are the 7 types of semantics?
Geoffrey Leech (1981) studied the meaning in a very broad way and breaks it down into seven types [1] logical or conceptual meaning, [2] connotative meaning, [3] social meaning, [4] affective meaning, [5] reflected meaning, [6] collective meaning and [7] thematic meaning.
Why is semantics important?
Semantics is the study of the meaning of words. Many words have very similar meanings and it is important to be able to distinguish subtle differences between them. For example, ‘anger’ and ‘rage’ are similar in meaning (synonyms) but ‘rage’ implies a stronger human reaction to a situation than ‘anger.
What are the four types of semantics?
Types of Semantics There are seven types of linguistic semantics: cognitive, computation, conceptual, cross-cultural, formal, lexical, and truth-conditional.
What is words and sentences in semantics?
A “word” is a string of characters that can have different meanings (jaguar: car or animal?; driver: one who drives a vehicle or the part of a computer?; rows, the plural noun or the third singular person of the verb to row?). A “sentence” is a group of words that express a complete thought.
What is sentence structure in semantics?
Syntax puts our meaning (“semantics”) into sentences, and phonology puts the sentences into the sounds that we hear and there must, surely, be a structure in the meaning that is expressed in the syntax and phonology.
What are some examples of semantic change?
Examples in English. Awful — Literally “full of awe”, originally meant “inspiring wonder (or fear)”, hence “impressive”. In contemporary usage, the word means “extremely bad”. Awesome — Literally “awe-inducing”, originally meant “inspiring wonder (or fear)”, hence “impressive”.
What is an example of semantics in a sentence?
For example, in everyday use, a child might make use of semantics to understand a mom’s directive to “do your chores” as, “do your chores whenever you feel like it.” However, the mother was probably saying, “do your chores right now.”
What is a real life example of semantic memory?
Some examples of semantic memory: Knowing that grass is green. Recalling that Washington, D.C., is the U.S. capital and Washington is a state. Knowing how to use scissors.
What are some examples of semantic change?
Examples in English. Awful — Literally “full of awe”, originally meant “inspiring wonder (or fear)”, hence “impressive”. In contemporary usage, the word means “extremely bad”. Awesome — Literally “awe-inducing”, originally meant “inspiring wonder (or fear)”, hence “impressive”.
What is a semantics in communication?
Semantics is the study of meaning, signs and symbols used for communication. The word is actually derived from the Greek word “sema” which means “signs”. Semantic barriers, then, are obstacles in communication that distort the meaning of a message being sent.
What are the two main areas of semantics?
“Based on the distinction between the meanings of words and the meanings of sentences, we can recognize two main divisions in the study of semantics: lexical semantics and phrasal semantics.
What are semantics skills?
Semantic skills refers to the ability to understand meaning in different types of words, phrases, narratives, signs and symbols and the meaning they give to the speaker and listener. Difficulties with semantic skills can lead to children not fully understanding what has been said.