Collations in SQL Server provide sorting rules, case, and accent sensitivity properties for your data. Collations that are used with character data types, such as char and varchar, dictate the code page and corresponding characters that can be represented for that data type.
What is collation error in SQL?
What is server collation in SQL Server?
Collation in SQL Server is a predefined set of rules that determine how data is saved, accessed, and compared. In other words, it’s a configuration setting that indicates how the database engine should handle character data.
What is collate SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS in SQL Server?
The collate clause is used for case sensitive and case insensitive searches in the columns of the SQL server. There are two types of collate clause present: SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CS_AS for case sensitive. SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS for case insensitive.
How do I get collation in SQL Server?
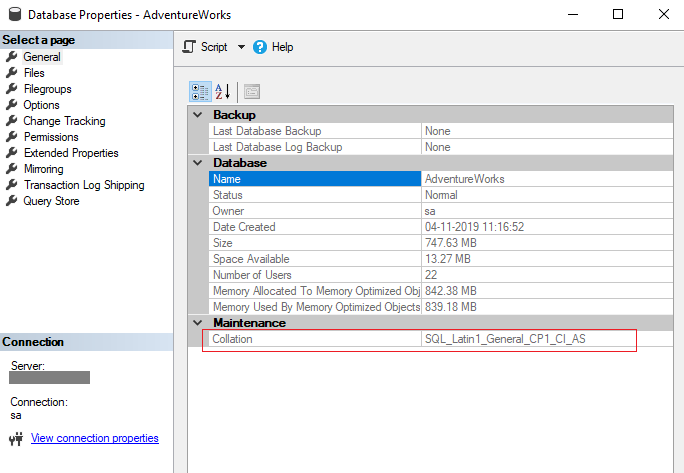
To view the collation setting of a database In Object Explorer, connect to an instance of the Database Engine and on the toolbar, click New Query. In the query window, enter the following statement that uses the sys. databases system catalog view. SELECT name, collation_name FROM sys.
What is collation error in SQL?
How do I change the collation in SQL?
Alternatively, if the database already exists, right-click the database that you want and select Properties. Select the Options page, and select a collation from the Collation drop-down list. After you are finished, select OK.
Does collation affect performance?
If you then specify a COLLATE clause in the query that is different than the collation used for the index, you will have a performance penalty because you won’t be using that index.
What is the difference between Latin1_General_CI_AS and SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS?
The SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS collation is a SQL collation and the rules around sorting data for unicode and non-unicode data are different. The Latin1_General_CI_AS collation is a Windows collation and the rules around sorting unicode and non-unicode data are the same.
What does collation mean in database?
Collation is a set of rules that tell database engine how to compare and sort the character data in SQL Server. Collation can be set at different levels in SQL Server.
What is collation process?
Collation is the assembly of written information into a standard order. Many systems of collation are based on numerical order or alphabetical order, or extensions and combinations thereof. Collation is a fundamental element of most office filing systems, library catalogs, and reference books.
What are %d and %s in SQL?
You must use %d for integer values and %s for string values. You can also use %f for a floating point value, %b for binary data and %% just to insert a percent symbol.
Why is collation used?
Collations in SQL Server provide sorting rules, case, and accent sensitivity properties for your data. Collations that are used with character data types, such as char and varchar, dictate the code page and corresponding characters that can be represented for that data type.
Why do we use collate?
You can use the COLLATE clause to apply a character expression to a certain collation. Character literals and variables are assigned the default collation of the current database. Column references are assigned the definition collation of the column.
What is the difference between Latin1_General_CI_AS and SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS?
The SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS collation is a SQL collation and the rules around sorting data for unicode and non-unicode data are different. The Latin1_General_CI_AS collation is a Windows collation and the rules around sorting unicode and non-unicode data are the same.
How do you fix Cannot resolve the collation conflict between SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS and Latin1_General_CI_AS in the equal to operation?
Issue: Cannot resolve the collation conflict between “SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS” and “Latin1_General_CI_AS” Simply apply the default collation to the fields you are comparing.
What does Norecovery mean in SQL?
NORECOVERY specifies that roll back not occur. This allows roll forward to continue with the next statement in the sequence. In this case, the restore sequence can restore other backups and roll them forward.
What is collation error in SQL?
Which is the best collation for MySQL?
If you elect to use UTF-8 as your collation, always use utf8mb4 (specifically utf8mb4_unicode_ci). You should not use UTF-8 because MySQL’s UTF-8 is different from proper UTF-8 encoding. This is the case because it doesn’t offer full unicode support which can lead to data loss or security issues.
Is SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS case sensitive?
Database collation For example, the default server-level collation in SQL Server for the “English (United States)” machine locale is SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS , which is a case-insensitive, accent-sensitive collation.
How do you fix Cannot resolve the collation conflict between SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS and Latin1_General_CI_AS in the equal to operation?
Issue: Cannot resolve the collation conflict between “SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS” and “Latin1_General_CI_AS” Simply apply the default collation to the fields you are comparing.
What is the difference between Vachar and Nvarchar?
The key difference between varchar and nvarchar is the way they are stored, varchar is stored as regular 8-bit data(1 byte per character) and nvarchar stores data at 2 bytes per character. Due to this reason, nvarchar can hold upto 4000 characters and it takes double the space as SQL varchar.