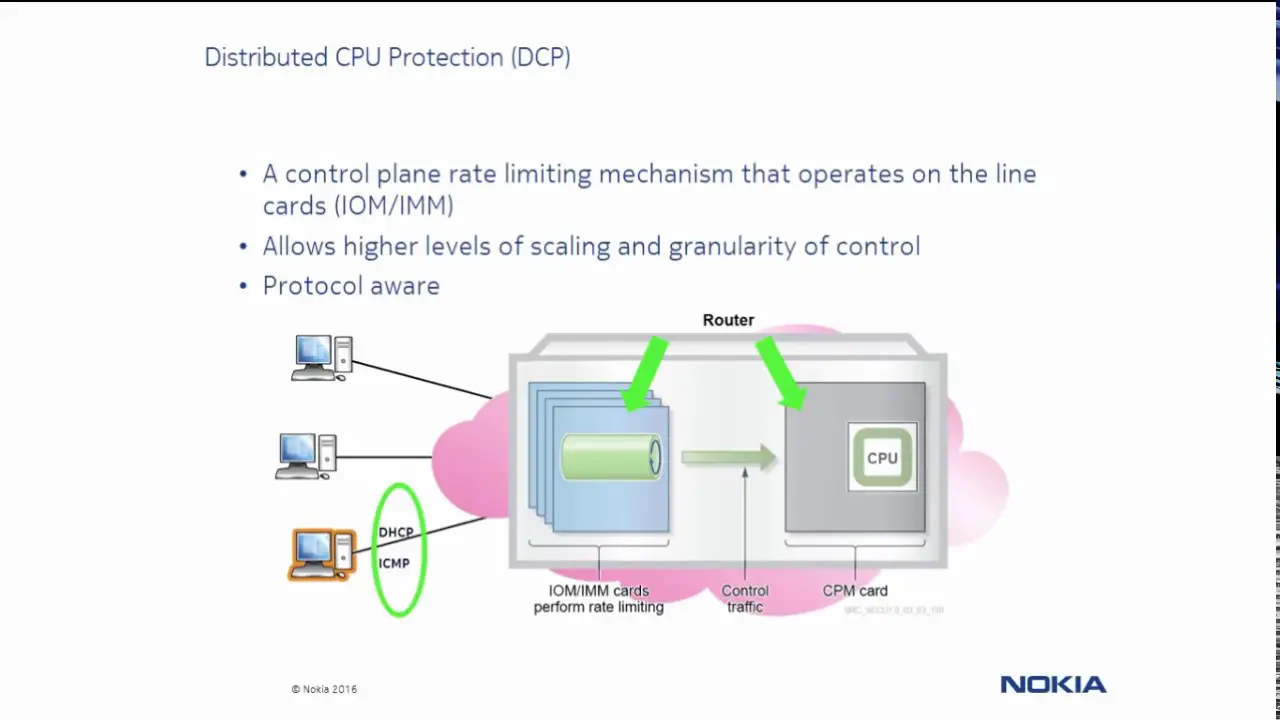
CPU protection protects the CPU of the node that it is configured on from a DOS attack by limiting the amount of traffic coming in from one of its ports and destined to the CPM (to be processed by its CPU) using a combination of the configurable limits.
What protects the CPU in a computer?
CPU protection rings are structural layers that limit interaction between installed applications on a computer and core processes. They typically range from the outermost layer, which is Ring 3, to the innermost layer, which is Ring 0, also referred to as the kernel. Ring 0 is at the core of all system processes.
How CPU and memory are protected by the operating system?
In Memory protection, we have to protect the operating system from user processes and which can be done by using a relocation register with a limit register. Here, the relocation register has the value of the smallest physical address whereas the limit register has the range of the logical addresses.
What is the need of memory protection?
The main purpose of memory protection is to prevent a process from accessing memory that has not been allocated to it. This prevents a bug or malware within a process from affecting other processes, or the operating system itself.
What do you mean by hardware protection?
Hardware security is vulnerability protection that comes in the form of a physical device rather than software that’s installed on the hardware of a computer system. Hardware security can pertain to a device used to scan a system or monitor network traffic.
What protects the CPU in a computer?
CPU protection rings are structural layers that limit interaction between installed applications on a computer and core processes. They typically range from the outermost layer, which is Ring 3, to the innermost layer, which is Ring 0, also referred to as the kernel. Ring 0 is at the core of all system processes.
What is a function of CPU?
The central processing unit (CPU) guides the computer through the various steps of solving a problem. Data enters the computer through an input unit, is processed by the central processing unit, and is then made available to the user through an output unit.
What protects CPU from malware?
Use Software It offers unparalleled endpoint protection and virus protection. Free BitDefender trial. Malwarebytes – The most effective and widely-adopted anti-malware on the market. The scans are thorough and the program prevents you from executing malicious files and visiting malicious websites.
What controls the CPU operation?
The control unit (CU) is a component of a computer’s central processing unit (CPU) that directs the operation of the processor.
What is the purpose of protection?
Protection refers to keeping something or someone safe. Through protection, we shelter and defend things. Since protecting is to shelter from harm, protection is the act of doing so. Children are under the protection of their parents, who keep them safe.
What are the uses of protection?
Protection is any measure taken to guard a thing against damage caused by outside forces. Protection can be provided to physical objects, including organisms, to systems, and to intangible things like civil and political rights.
Why protection system is required in a computer?
Computer security is important because it keeps your information protected. It’s also important for your computer’s overall health; proper computer security helps prevent viruses and malware, which allows programs to run quicker and smoother.
What is protection example?
Protection is a person or thing that shields from danger, pain or discomfort, or money paid to avoid violence or prosecution. An example of protection is an umbrella to stand under during a rainstorm. An example of protection is money paid by a shopowner to the mob to avoid violence.
How many types of hardware protection are there?
Basically, hardware protection is divided into 3 categories: CPU protection, Memory Protection, and I/O protection.
What protects CPU from malware?
Use Software It offers unparalleled endpoint protection and virus protection. Free BitDefender trial. Malwarebytes – The most effective and widely-adopted anti-malware on the market. The scans are thorough and the program prevents you from executing malicious files and visiting malicious websites.
What is used to protect computer?
Use an anti-malware app – Installing an anti-malware app and keeping it up to date can help defend your PC against viruses and other malware (malicious software). Microsoft Defender is free anti-malware software included with Windows, and it’s kept updated automatically through Windows Update.
What hold the CPU in place?
CPU sockets come in two major types — ball-grid array and pin-grid array. PGA sockets look like a checkerboard with lots of squares. They are designed to hold a CPU chip with an array of pins sticking out of its bottom.
What is the metal that covered the CPU?
Palladium: Palladium is used in cell phones, hard drives, circuit board components and capacitors. Copper: Copper is used in CPU heat sinks, wiring cables, cell phones, printed circuit boards and computer chips. Nickel: Nickel is used in to circuit board components.
What protects the CPU in a computer?
CPU protection rings are structural layers that limit interaction between installed applications on a computer and core processes. They typically range from the outermost layer, which is Ring 3, to the innermost layer, which is Ring 0, also referred to as the kernel. Ring 0 is at the core of all system processes.
How can CPU get damaged?
Overheating can cause damages that may be visible externally. Any burnt marks on and around the CPU socket indicates that the CPU has undergone extreme overheating. In such situations, a replacement may be the only option.
Can touching a CPU damage it?
CPUs are not really fragile, especially LGA ones. Even CPUs without heatspreaders are perfectly safe to handle barehanded. High static environments, or excessive physical force, are the only things that could damage it.
Can a motherboard damage a CPU?
Yes of course it can. The motherboard regulates current and voltage going to the RAM and CPU. If something shorts and you’re either consistently undervolting or overvolting these two things, your wallet will be in trouble as they will get damaged.