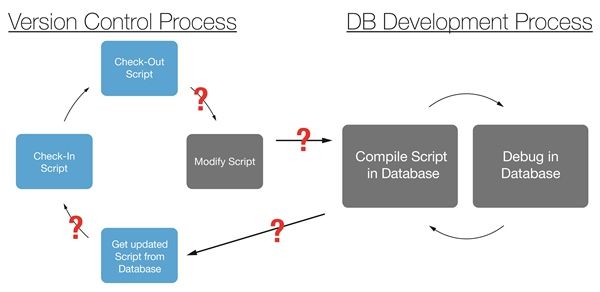
Versioning a database means sharing all changes of a database that are neccessary for other team members in order to get the project running properly. Database versioning starts with a settled database schema (skeleton) and optionally with some data.
What is database version control?
Database version control is the practice of tracking every change made to the database by every team member. Like application version control, database version control acts as a single source of truth. It empowers you with complete visibility, traceability, and continuous monitoring of the changes in your database.
What is database schema version?
Schema versioning deals with the need to retain current data, and the ability to query and update it, through alternate database structures. (The structure of a database is held in a schema (pl. schemata or schemas).
How do you store a version number in a database?
There is no generally-accepted place to store a version number in a database schema. Databases don’t have version numbers by convention. There is no standard way of putting in this or any other information about an application into the database.
What is version control in SQL Server?
What does SQL Source Control do? SQL Source Control plugs into SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) and links your databases to an existing version control system, such as Git, TFS or Subversion. This allows you to manage changes to database schema and static data alongside application code.
What DB version is 19c?
Oracle Database 19c is the current long term release, and it provides the highest level of release stability and longest time-frame for support and bug fixes. Oracle Database 21c, also available for production use today as an innovation release, provides an early insight into the many enhancements and new capabilities.
What are the three types of version control?
The types of VCS are: Local Version Control System. Centralized Version Control System. Distributed Version Control System.
What are the 3 types of database schema?
Schema is of three types: Logical Schema, Physical Schema and view Schema. Logical Schema – It describes the database designed at logical level. Physical Schema – It describes the database designed at physical level. View Schema – It defines the design of the database at the view level.
What is version and examples?
: a form of something (such as a product) that is different in some way from other forms. A new version of the word processing program should be available soon. I have an older version of the software. This new design is better than the first version. A film version of the novel is being made.
What means version number?
What Does Version Number Mean? A version number is a unique sequence of numbers which identifies the state of development of computer software.
What is the use of version option?
You can use versioning to: Track history of a version When versioning is enabled, you can see when an item or file was changed and who changed it. You can also see when properties (information about the file) were changed.
Why do we need a version control?
Version control systems are software tools that help software teams manage changes to source code over time. As development environments have accelerated, version control systems help software teams work faster and smarter.
What is version control and why is it important?
Version control — also known as source control or revision control — is an important software development practice for tracking and managing changes made to code and other files. It is closely related to source code management.
What is version control give an example?
Version control is a component of software configuration management. Changes are usually identified by a number or letter code, termed the “revision number”, “revision level”, or simply “revision”. For example, an initial set of files is “revision 1”.
Why do we need data version control?
A good data version control tool will allow you to have unified data sets with a strong repository of all your experiments. It will also enable smooth collaboration between all team members so everyone can follow changes in real-time and always know what’s happening.
What is database version control?
Database version control is the practice of tracking every change made to the database by every team member. Like application version control, database version control acts as a single source of truth. It empowers you with complete visibility, traceability, and continuous monitoring of the changes in your database.
Is Oracle 19c same as 21c?
Oracle Database 19c is the current long term release, and it provides the highest level of release stability and longest time-frame for support and bug fixes. Oracle Database 21c, also available for production use today as an innovation release, provides an early insight into the many enhancements and new capabilities.
Is Oracle 12c and 19c same?
Oracle Database 19c is the final, and therefore ‘long term support’ release of the Oracle Database 12c family of products (which includes Oracle Database 18c). ‘Long term support’ means that Oracle Database 19c comes with 4 years of premium support and a minimum of 3 years extended support.
What is 12c database?
Oracle Database 12c is a relational database management system (RDBMS) designed for both on-premises and cloud uses and deployable on a choice of clustered or single servers. It provides comprehensive features for managing data in transaction processing, business intelligence and content management applications.
How many types of versions are there?
There are two types of version control: centralized and distributed.
What is version control Example?
Version control is a system that records changes to a file or set of files over time so that you can recall specific versions later. For the examples in this book, you will use software source code as the files being version controlled, though in reality you can do this with nearly any type of file on a computer.
What are 3 examples of a database?
MySQL, SQL Server, MongoDB, Oracle Database, PostgreSQL, Informix, Sybase, etc. are all examples of different databases. These modern databases are managed by DBMS.