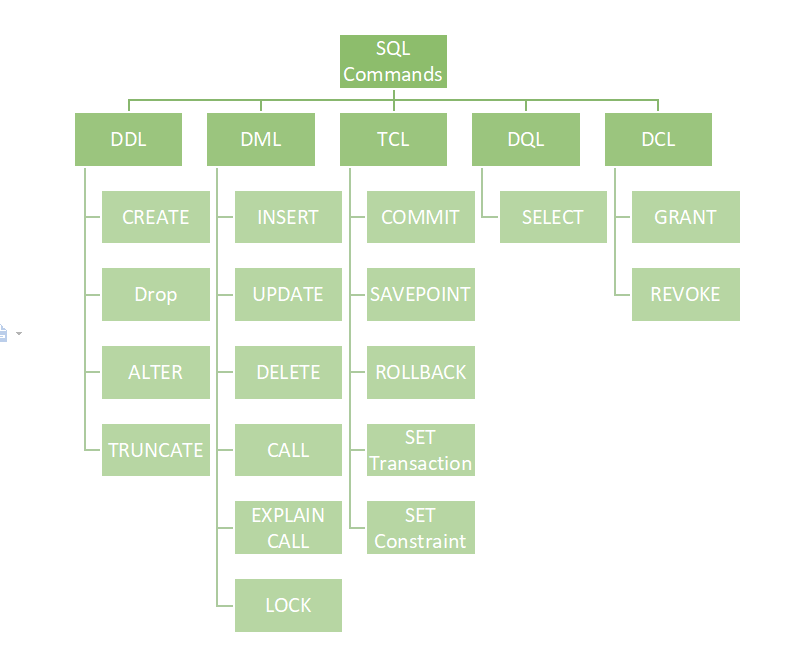
The full form of DQL is Data Query Language. DQL is a part of the grouping involved in SQL (Structures Query Language) sub-languages. The SQL sub languages have four major categories, DQL, DDL, DCL, and DML.
What is DQL used for?
SQL is used to communicate with a database. According to ANSI (American National Standards Institute), it is the standard language for relational database management systems. SQL statements are used to perform tasks such as update data on a database, or retrieve data from a database.
What is DQL in SQL with examples?
DQL statements are used for performing queries on the data within schema objects. The purpose of DQL commands is to get the schema relation based on the query passed to it. Although often considered part of DML, the SQL SELECT statement is strictly speaking an example of DQL.
Is DQL and DML same?
The Data Manipulation Language (DML) is the domain of INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE, which you use to manipulate data. Some bundle the Data Query Language (DQL) into DML, arguing that it also manipulates data.
What is DQL in SQL with examples?
DQL statements are used for performing queries on the data within schema objects. The purpose of DQL commands is to get the schema relation based on the query passed to it. Although often considered part of DML, the SQL SELECT statement is strictly speaking an example of DQL.
Is SELECT DQL or DML?
if you refer to 11g Documentation as in HERE – Types of SQL Statements, you will find that Select is a DML statement, which is a limited form of DML, which can query the data and not manipulate it.
What is difference between DQL and SQL?
Doctrine Query Language (DQL) is like an abstraction of your queries. This makes queries independent of the version or type of (SQL) database that your project is built on. From the documentation: You need to think about DQL as a query language for your object model, not for your relational schema.
What are the 5 types of SQL commands?
Types of SQL Commands. There are five types of SQL commands: DDL, DML, DCL, TCL, and DQL.
What is index in DQL?
An index is a schema object. It is used by the server to speed up the retrieval of rows by using a pointer. It can reduce disk I/O(input/output) by using a rapid path access method to locate data quickly.
What is DQL full form?
The full form of DQL is Data Query Language. DQL is a part of the grouping involved in SQL (Structures Query Language) sub-languages. The SQL sub languages have four major categories, DQL, DDL, DCL, and DML.
Is DDL and DQL same?
DDL – Data Definition Language. DQL – Data Query Language. DML – Data Manipulation Language.vor 3 Tagen
What is DQL and its commands?
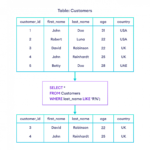
DQL is a portion of a SQL statement that allows you to get and organise data from a database. You can use the SELECT command to extract data from a database in order to perform actions on it. It is the same as the projection operation in relational algebra.
Is DQL a part of SQL?
We can define DQL as follows it is a component of SQL statement that allows getting data from the database and imposing order upon it. It includes the SELECT statement. This command allows getting the data out of the database to perform operations with it.
Which commands come under DQL?
Data Query Language DQL is used to fetch the data from the database. It uses only one command: SELECT.
Which DQL statement is used to process a search query?
SQLSELECT statements are used to retrieve data from the database and also, they populate the result of the query into the result-sets.
What is DQL in SQL with examples?
DQL statements are used for performing queries on the data within schema objects. The purpose of DQL commands is to get the schema relation based on the query passed to it. Although often considered part of DML, the SQL SELECT statement is strictly speaking an example of DQL.
What is schema in SQL?
What is DML command?
DML is an abbreviation for Data Manipulation Language. Data Manipulation Language or DML represents a collection of programming languages explicitly used to make changes in the database, such as: CRUD operations to create, read, update, and delete data. Using the INSERT, SELECT, UPDATE and Delete commands.
What is DCL and TCL in SQL?
DCL – Data Control Language. TCL – Transaction Control Language.
Which are the two categories of DQL statements?
SQL statements are divided into two major categories: data definition language (DDL) and data manipulation language (DML).
What are the 3 types of SQL?
Data Definition Language (DDL) Statements. Data Manipulation Language (DML) Statements. Transaction Control Statements.
What are 3 SQL languages?
SQL has three main components: the Data Manipulation Language (DML), the Data Definition Language (DDL), and the Data Control Language (DCL).