The concept of modes of operation in operating system can be extended beyond the dual mode. This is known as the multimode system. In those cases the more than 1 bit is used by the CPU to set and handle the mode. An example of the multimode system can be described by the systems that support virtualisation.
What is dual mode?
Dual mode refers to mobile devices that function on two different bearer technologies, such as GSM and WCDMA, or 1x and WCDMA. Most 3G phones are dual-mode and tri- or quad- band to enable users to roam onto 2G networks when they are outside the 3G coverage area.
What are the different modes of an OS?
A processor in a computer running Windows has two different modes: user mode and kernel mode. The processor switches between the two modes depending on what type of code is running on the processor. Applications run in user mode, and core operating system components run in kernel mode.
What are the two types of operating modes of at *?
Two operating modes of AT are Real mode and protected mode.
What is dual mode execution?
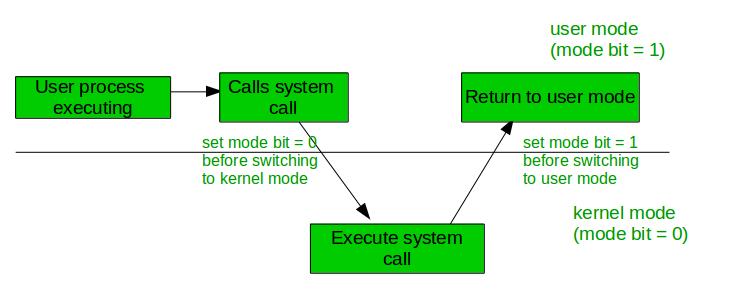
The dual-mode operation is used to provide protection and security to the user program and also to the operating system. Actually, the operating system decides the instruction has to be executed in which particular mode. Mode bit is required to identify in which particular mode the current instruction is executing.
Why is dual-mode needed?
The dual-mode operations in the operating system protect the operating system from illegal users. We accomplish this defense by designating some of the system instructions as privileged instructions that can cause harm. The hardware only allows for the execution of privileged instructions in kernel mode.
Why dual-mode operation can protect system?
The dual mode of operation provides us with the means for protecting the OS from errant users-and errant users from one another. If an attempt is made to execute a privileged instruction in user mode, the hardware does not execute the instruction but rather treats it as illegal and traps it to the OS.
What is difference between kernel mode and user mode?
In kernel mode, the program has direct and unrestricted access to system resources. In user mode, the application program executes and starts. In user mode, a single process fails if an interrupt occurs. Kernel mode is also known as the master mode, privileged mode, or system mode.
What is deadlock OS?
In an operating system, a deadlock occurs when a process or thread enters a waiting state because a requested system resource is held by another waiting process, which in turn is waiting for another resource held by another waiting process.
What is user and kernel mode?
The User mode is normal mode where the process has limited access. While the Kernel mode is the privileged mode where the process has unrestricted access to system resources like hardware, memory, etc.
Why are two modes user and kernel needed?
Why are two modes (user and kernel) needed? User mode prohibits the user from accessing certain areas of memory and executing certain instructions to protect the OS. Kernel mode gives full access to the OS to allow it to do what it needs to do.
What do you mean by multiprogramming?
Multiprogramming is a rudimentary form of parallel processing in which several programs run at the same time on a uniprocessor system. However, because there is only one processor, there is no true simultaneous execution of different programs.
How does CPU support dual mode?
Dual-Mode Operation In user mode, the CPU is restricted to unprivileged instructions and a specified area of memory. User code should always be executed in user mode and the OS design ensures that it is. When responding to system calls, other traps/exceptions, and interrupts, OS code is run.
What are threads in OS?
A thread is the smallest unit of processing that can be performed in an OS. In most modern operating systems, a thread exists within a process – that is, a single process may contain multiple threads.
What are the three main purposes of an OS?
An operating system has three main functions: (1) manage the computer’s resources, such as the central processing unit, memory, disk drives, and printers, (2) establish a user interface, and (3) execute and provide services for applications software.
What does dual mode do on a smartwatch?
Yes, the dual audio feature enables you to connect two audio devices simultaneously. You can also connect two different Bluetooth devices like a smartwatch and headphones at once.
How does dual mode create propulsion?
Dual mode propulsion systems combine the high efficiency of bipropellant rockets with the reliability and simplicity of monopropellant rockets. It is based upon the use of two rocket fuels, liquid hydrogen and more dense hydrocarbon fuels, like RP, which are all burned with liquid oxygen.
What is dual mode in Brocade switch?
Configures a tagged port to accept and transmit both tagged and untagged traffic at the same time.
What is the mode of the system at boot time?
At system boot time, the hardware starts in kernel mode. The operating system is then loaded and starts user applications in user mode. Whenever a trap or interrupt occurs, the hardware switches from user mode to kernel mode (that is, changes the state of the mode bit to 0).
What is CPU protection?
CPU protection protects the CPU of the node that it is configured on from a DOS attack by limiting the amount of traffic coming in from one of its ports and destined to the CPM (to be processed by its CPU) using a combination of the configurable limits.
What is the difference between process and program?
A program is a collection of sequential and ordered operations that should be executed. In contrast, a process is an example of a program being executed. In the process, the resources need is much higher. It may require processing, memory, input/output resources for the successful execution.
What is a timer in OS?
A timer can be set to interrupt the computer after a specified period. The period may be fixed (for example, 1/60 second) or variable (for example, from 1 millisecond to 1 second). A variable timer is generally implemented by a fixed-rate clock and a counter.