Gpresult is a command-line tool that shows the Resultant Set of Policy (RSoP) for a user or computer based on applied Group Policy settings.
How do you read Gpresult?
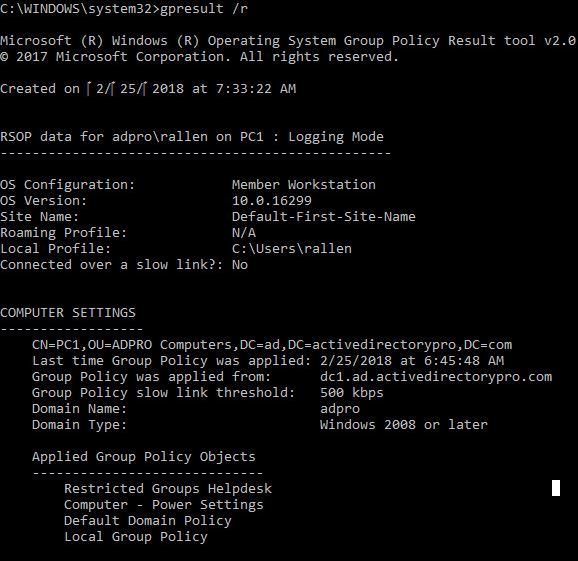
gpresult Command: To see the Gpresult commands, go to the command prompt and type the command: “gpresult /?” The output shown below displays the description and parameter list of the resultant set of policies (RSoP) for a target user and the computer.
Where is the Gpresult file saved?
This generates an html report of the applied group policy objects. If you don’t specify a path it will save it to the system32 folder.
What is the difference between Rsop and Gpresult?
RSOP is a great way to discover the result of the policy assigned to a computer. GPResult displays RSOP data in logging mode which includes policy settings like user and computer OU path, domain name, AD group memberships, security settings, and applied GPOs for both users and computers.
How do I get Gpresult in a text file?
Click Start, Run, and enter cmd to open a command window. 2. Type gpresult and redirect the output to a text file as shown in Figure 1 below: All I get is a list of options, redirected or not.
Where is the Gpresult file saved?
This generates an html report of the applied group policy objects. If you don’t specify a path it will save it to the system32 folder.
What is the difference between Rsop and Gpresult?
RSOP is a great way to discover the result of the policy assigned to a computer. GPResult displays RSOP data in logging mode which includes policy settings like user and computer OU path, domain name, AD group memberships, security settings, and applied GPOs for both users and computers.
What is the use of Group Policy?
Group Policy is an infrastructure that allows you to specify managed configurations for users and computers through Group Policy settings and Group Policy Preferences. To configure Group Policy settings that affect only a local computer or user, you can use the Local Group Policy Editor.
What is the difference between the Gpupdate and Gpresult commands?
– gpupdate [/target: {computer/user}] [/force] [ /wait: value] [/logoff] [/boot]. The gpresult command displays Group Policy settings and Resultant Set of Policy (RSOP) for a user or a computer. – /s computer specifies the name or IP address of a remote computer.
How do I check Group Policy?
To search for Group Policy settings in the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC), use the Group Policy Search tool. To find the Group Policy settings, click Windows Components, and then click Internet Explorer.
How do I check my Group Policy?
On the Contents tab in the details pane, click a tab to display GPOs. Double-click the GPO to display its history. Right-click the GPO version for which to review the settings, click Settings, and then click HTML Report or XML Report to display a summary of the GPO’s settings.
How do I get Group Policy reports?
Open the Group Policy Management Console (Start->Administrative Tools->Group Policy Management or by running gpmc. msc from Run or a command prompt). 2. Right-click on Group Policy Results at the bottom of that screen, and choose ‘Group Policy Results Wizard…’.
How do I run GPResult remotely?
System Administrators can run GPResult on any remote computer within their scope of management. By default, GPResult returns settings in effect on the computer on which GPResult is run. To run GPResult, select any computer on the same net work, Click Start, Run, and enter cmd to open a command window.
What is RSoP report?
Resultant Set of Policy (RSoP) is an addition to Group Policy to assist in policy implementation and troubleshooting. RSoP is a query engine that polls existing policies and planned policies, and then reports the results of those queries.
What is Gpupdate command?
The gpupdate command refreshes a computer’s local Group Policy, and any Active Directory-based group policies.
What different ways you can view GPO results?
The easiest way to see which Group Policy settings have been applied to your machine or user account is to use the Resultant Set of Policy Management Console. To open it, press the Win + R keyboard combination to bring up a run box. Type rsop. msc into the run box and then hit enter.
How can you tell if a Group Policy has been applied?
You can use the GPResult command with /scope: user or /scope: computer option to display the applied group policy settings on the user or computer. You can also view the applied group policy settings of the specific user.
How do I view Group Policy?
To search for Group Policy settings in the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC), use the Group Policy Search tool. To find the Group Policy settings, click Windows Components, and then click Internet Explorer.
How do you read Gpresult?
gpresult Command: To see the Gpresult commands, go to the command prompt and type the command: “gpresult /?” The output shown below displays the description and parameter list of the resultant set of policies (RSoP) for a target user and the computer.
Where is the Gpresult file saved?
This generates an html report of the applied group policy objects. If you don’t specify a path it will save it to the system32 folder.
What is an example of a GPO?
Examples of group policies include configuring operating system security, adding firewall rules, or managing applications like Microsoft Office or a browser. Group Policies also install software and run startup and login scripts.
What is Group Policy in simple words?
Group Policy is a hierarchical infrastructure that allows a network administrator in charge of Microsoft’s Active Directory to implement specific configurations for users and computers. Group Policy is primarily a security tool, and can be used to apply security settings to users and computers.