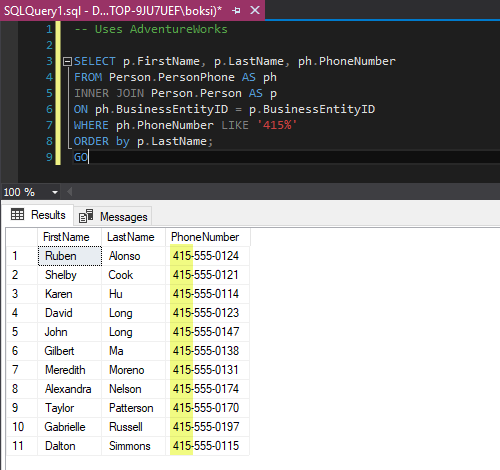
The LIKE operator is used in a WHERE clause to search for a specified pattern in a column. There are two wildcards often used in conjunction with the LIKE operator: The percent sign (%) represents zero, one, or multiple characters. The underscore sign (_) represents one, single character.
What is %s in SQL statement?
Placeholders. pixel13 commented 16 years ago. They’re just placeholders for the values that follow in the command (e.g. in db_query). You must use %d for integer values and %s for string values. You can also use %f for a floating point value, %b for binary data and %% just to insert a percent symbol.
What are %d and %s in SQL?
%d – the argument is treated as an integer, and presented as a (signed) decimal number. %s – the argument is treated as and presented as a string. in your examples, $slug is a string and $this->id is an integer. look at http://www.php.net/manual/en/function.sprintf.php for more info.
Is like filter in SQL?
You can use the LIKE operator in the WHERE condition to do a pattern matching comparison, like to find a string somewhere in a text value. The “%” character will match any sequence of 0 or more characters in the value, the “_” character will match a single character.
Is * a wildcard in SQL?
To broaden the selections of a structured query language (SQL-SELECT) statement, two wildcard characters, the percent sign (%) and the underscore (_), can be used. The percent sign is analogous to the asterisk (*) wildcard character used with MS-DOS.
How do I use multiple wildcards in SQL?
There are two wildcards used in conjunction with the LIKE operator. The percent sign represents zero, one or multiple characters. The underscore represents a single number or character. These symbols can be used in combinations.
What are the 5 types of SQL operators?
There are six types of SQL operators that we are going to cover: Arithmetic, Bitwise, Comparison, Compound, Logical and String.
What are the 3 types of SQL commands?
There are 3 main types of commands. DDL (Data Definition Language) commands, DML (Data Manipulation Language) commands, and DCL (Data Control Language) commands.
Can I use like in select SQL?
The SQL LIKE condition allows you to use wildcards to perform pattern matching in a query. The LIKE condition is used in the WHERE clause of a SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statement.
What is like filter?
The LIKE clause is a filtering condition designed to search attribute-label string values to match a specified pattern. The LIKE clause can be used with the following criteria: LIKE – filters for the string pattern and is case sensitive. ILIKE – filters for the string pattern and is case insensitive.
How do you use like variables?
Using the CONCAT() function, we can work with user variables in LIKE clause. The syntax is as follows. set @anyVariableName=’anyValue’; select yourColumnName1,yourColumnName2,yourColumnName3,…
What is difference between * and & wildcard character?
Difference between wildcards (*) and (?) A wildcard character is a kind of placeholder represented by a single character, such as an asterisk (*) and question mark (?), which can be interpreted as a number of literal characters or an empty string.
Is != And <> same in SQL?
If != and <> both are the same, which one should be used in SQL queries? Here is the answer – You can use either != or <> both in your queries as both technically same but I prefer to use <> as that is SQL-92 standard.
Is wildcard a character?
Wildcards are special characters that can stand in for unknown characters in a text value and are handy for locating multiple items with similar, but not identical data. Wildcards can also help with getting data based on a specified pattern match. For example, finding everyone named John on Park Street.
What are the two types of wildcards?
The most common wildcards are the asterisk (*), which represents one or more characters, and question mark (?), which represents a single character.
Why are wildcards useful?
Wildcards are symbols used in database searchs to represent a letter or letters in a word. Wildcards can be useful when searching for information because they enable different forms or spelling of a word to be searched similtaneously.
What does <> mean in MySQL?
The symbol <> in MySQL is same as not equal to operator (!=). Both gives the result in boolean or tinyint(1). If the condition becomes true, then the result will be 1 otherwise 0. Case 1 − Using !=
What does <> mean in DBMS?
It means ‘not equal to’.
What are the seven 7 types of operator?
In Python, there are seven different types of operators: arithmetic operators, assignment operators, comparison operators, logical operators, identity operators, membership operators, and boolean operators.
What are the 4 parts of SQL?
The scope of SQL includes data query, data manipulation (insert, update, and delete), data definition (schema creation and modification), and data access control.
Should we use like in SQL?
The SQL Like is used when we want to return the row if specific character string matches a specified pattern. The pattern can be a combination of regular characters and wildcard characters. To return a row back, regular characters must exactly match the characters specified in the character string.
What is difference between Rlike and like in SQL?
RLIKE edit Description: This operator is similar to LIKE , but the user is not limited to search for a string based on a fixed pattern with the percent sign ( % ) and underscore ( _ ); the pattern in this case is a regular expression which allows the construction of more flexible patterns.