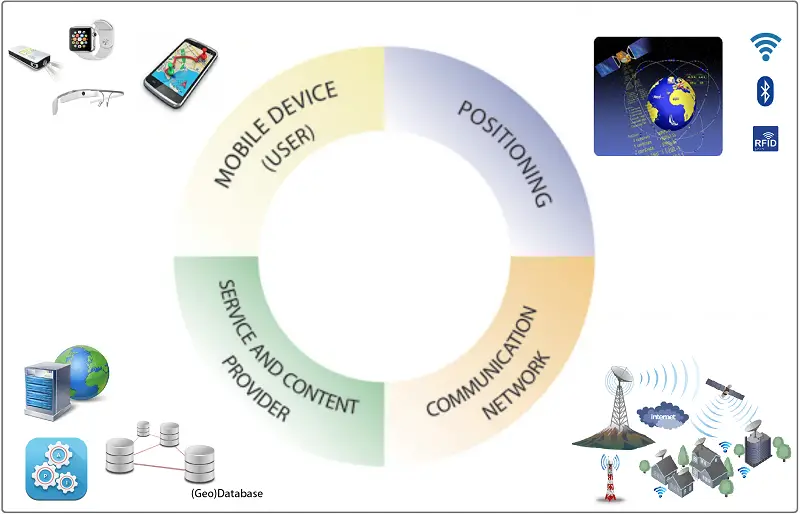
What exactly is location-based data? Location-based analytics provides a feed of data from multiple sources such as Wi-Fi and GPS to provide collaborative reports on the behaviors of consumers, while they are in a shopping mall, a restaurant, an airport, etc.
What is a location database?
In other words, it is information collected by a network or service about where the user’s phone or other device is or was located – for example, tracing the location of a mobile phone from data collected by base stations on a mobile phone network.
What is the meaning of location based services?
A location-based service (LBS) is a software service for mobile device applications that requires knowledge about where the mobile device is geographically located. The application collects geodata, which is data gathered in real time using one or more location tracking technologies.
What is the purpose of location-based computing?
Location-based computing (LBC) services are applications that use the position of a device and its user in the provision of a value-added service. Examples of these applications include services such as Tinder, Meetup or Windy, which use the geographic location of their users to provide or augment an activity.
How is location-based data used?
Location-based analytics provides a feed of data from multiple sources such as Wi-Fi and GPS to provide collaborative reports on the behaviors of consumers, while they are in a shopping mall, a restaurant, an airport, etc. All of the data is consent-based and anonymized to protect the privacy of consumers.
What are advantages of location-based services?
Location-based services offer real-time execution Furthermore, businesses can connect with a targeted set of audiences and gain benefits of localization. With communication features on location-based apps, businesses can collect data about their customer behavior to create a strategic marketing plan.
How do location-based systems work?
Location-based services can use a smartphone’s GPS technology to track a person’s location if the user has allowed access. After a smartphone user opts in, the service is able to identify their location down to the street address without manual data entry.
Why is location data important in business?
Location data can also improve retail operations and customer experience (CX). Beyond using location data to provide directions to stores or identify nearby inventory, retailers can also use it to alert workers when customers arrive for curbside pickup, or to allocate workers in anticipation of a surge of shoppers.
What is location-based algorithm?
Location-based recommendation is a recommender system that incorporates location information, such as that from a mobile device, into algorithms to attempt to provide more-relevant recommendations to users.
What is location example?
A place’s absolute location is its exact place on Earth, often given in terms of latitude and longitude. For example, the Empire State Building is located at 40.7 degrees north (latitude), 74 degrees west (longitude). It sits at the intersection of 33rd Street and Fifth Avenue in New York City, New York.
What are the two different types of location?
Geographers can describe the location of a place in one of two ways: absolute and relative.
What are the methods of location?
Crash location can be documented using five primary methods: Intersection, Off-Intersection, Address, Mile Marker or Exit. Additionally, landmarks may be used to supplement the primary methods.
What is location and examples?
A place’s absolute location is its exact place on Earth, often given in terms of latitude and longitude. For example, the Empire State Building is located at 40.7 degrees north (latitude), 74 degrees west (longitude). It sits at the intersection of 33rd Street and Fifth Avenue in New York City, New York.
What is location data platform?
Location Data Platforms collect geospatial data from multiple providers and work as an inventory for companies that need data for their operations. Through this aggregation buyers can access various sources of real time location data through the same platform.
What is location data management?
A location is the level at which a data load is executed in Data Management. You define locations to specify where to load the data. Additionally, Locations enable you to use the same import format for more than one target application where the dimensionality of the target applications is the same.
What is a location data domain?
With a Multi-Domain MDMMDMMaster data management (MDM) is a technology-enabled discipline in which business and information technology work together to ensure the uniformity, accuracy, stewardship, semantic consistency and accountability of the enterprise’s official shared master data assets.https://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Master_data_managementMaster data management – Wikipedia solution, organizations can centralize and connect Location data to other domains like Product, Customer, Supplier, and Asset. Location data adds the context of “Where” to these domains, helping organizations improve analytics and forecasting, as well as formulate big-picture initiatives.
Who uses location data?
74% of logistics and transport services use location data for this purpose, with 53% of retailers, 33% of real estate companies, 30% of financial services and just 10% of travel and tourism companies also citing this as a use for location data.
What are the source of location data?
Global Positioning System (GPS) Your device receives signals from the satellites and it can calculate where it is by measuring the time it takes for the signal to arrive. This produces very accurate and precise data under the right conditions.
What is location data platform?
Location Data Platforms collect geospatial data from multiple providers and work as an inventory for companies that need data for their operations. Through this aggregation buyers can access various sources of real time location data through the same platform.
What is location based analysis?
Location analytics is the practice of adding a layer of geographical data to a business’s data assets in order to extract more valuable insights.
What are the four components of location?
Four components characterize location problems: (1) customers, who are presumed to be already located; (2) facilities that will be located; (3) a space in which customers and facilities are located; and (4) a metric that indicates distances or times between customers and facilities.
Is Google maps a location based service?
Google Maps, previously referred to as Google Local, is a global online map service, which includes landmarks, path lines, area shapes, vector maps, satellite maps, topographic maps, etc.