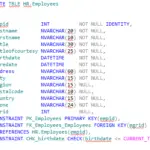
Type 1 dimension mapping (SCD1): This keeps only current data and does not maintain historical data. Note : Use SCD1 mapping when you do not want history of previous data. Type 2 dimension/version number mapping (SCD2): This keeps current as well as historical data in the table.
What is SCD type1?
Type 1 SCDs – Overwriting. In a Type 1 SCD the new data overwrites the existing data. Thus the existing data is lost as it is not stored anywhere else. This is the default type of dimension you create. You do not need to specify any additional information to create a Type 1 SCD.
What is the difference between SCD Type 2 and SCD Type 3?
Difference : SCD2 is unlimited history and SCD3 is limited history. Explanation: 1- Using SCD2 you can save unlimited history with the help of the Surrogate Key .
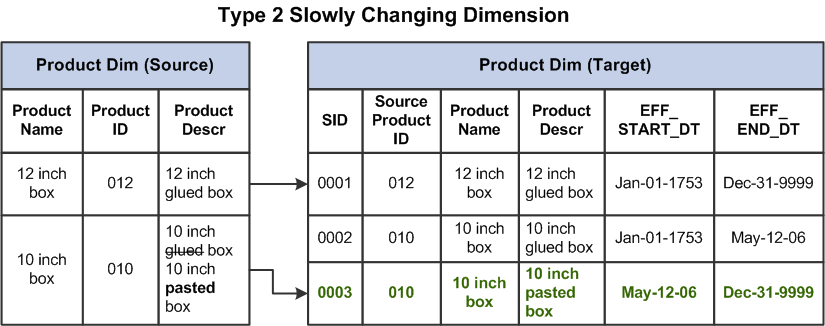
What is SCD type2?
As we discussed in SCD type 2, we maintain the history by adding a different version of the row to the dimension. However, if the changes are rapid in nature Type 2 SCD will not be scalable. For example, let us assume we want to keep the customer risk type depending on his previous payment.
What is SCD and explain all types?
A slowly changing dimension (SCD) is a dimension that is able to handle data attributes which change over time. For example: A customer dimension may hold attributes such as name, address, and phone number. Over time, a customer’s details may change (e.g. move addresses, change phone number, etc).
What is SCD type1?
Type 1 SCDs – Overwriting. In a Type 1 SCD the new data overwrites the existing data. Thus the existing data is lost as it is not stored anywhere else. This is the default type of dimension you create. You do not need to specify any additional information to create a Type 1 SCD.
What is type 1 and type 2 dimension?
Type 1 Slowly Changing DimensionSlowly Changing DimensionA Slowly Changing Dimension (SCD) is a dimension that stores and manages both current and historical data over time in a data warehouse. It is considered and implemented as one of the most critical ETL tasks in tracking the history of dimension records.https://www.oracle.com › lesson3 › slowlychangingdimensionsSlowly Changing Dimensions – Oracle: This method overwrites the existing value with the new value and does not retain history. Type 2 Slowly Changing Dimension: This method adds a new row for the new value and maintains the existing row for historical and reporting purposes.
Which SCD type is better?
For dimensions, you need to decide which columns can change, and whether you need to know their previous value. If none of the columns can change, then SCD0 is usually the most appropriate.
What is the difference between between type 2 SCD and Type 4 SCD?
Most SCD types use a full outer join to match records from the original data source with records in the updated source based on equating a key from each. Type 4, however, accomplishes the update using a sort. The Type 4 model is similar to that for Type 2.
What is the benefit of using Type 1 SCD?
In Type 1 Slowly Changing Dimension, the new information simply overwrites the original information. In other words, no history is kept. Advantages: – This is the easiest way to handle the Slowly Changing Dimension problem, since there is no need to keep track of the old information.
How is SCD Type 2 implemented?
Open the mapping designer tool, source analyzer and either create or import the source definition. Go to the Warehouse designer or Target designer and import the target definition. Go to the mapping designer tab and create new mapping. Drag the source into the mapping.
What is a SCD in medical terms?
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of inherited red blood cell disorders. Red blood cells contain hemoglobin, a protein that carries oxygen. Healthy red blood cells are round, and they move through small blood vessels to carry oxygen to all parts of the body.
What is the mechanism of SCD?
It is caused by an A to T point mutation in the beta globin gene that produces hemoglobin S, which polymerizes in the deoxygenated state, resulting in physical deformation or sickling of erythrocytes. Sickle erythrocytes promote vaso-occlusion and hemolysis, which are two major hallmarks of the disease.
What is the benefit of using type 1 SCD?
In Type 1 Slowly Changing Dimension, the new information simply overwrites the original information. In other words, no history is kept. Advantages: – This is the easiest way to handle the Slowly Changing Dimension problem, since there is no need to keep track of the old information.
What is the difference between between type 2 SCD and type 4 SCD?
Most SCD types use a full outer join to match records from the original data source with records in the updated source based on equating a key from each. Type 4, however, accomplishes the update using a sort. The Type 4 model is similar to that for Type 2.
How many SCD types are there?
In reality, only types 0, 1 and 2 are widely used, with the others reserved for very specific requirements. Confusingly, there is no SCD type 5 in commonly agreed definitions. After you have implemented your chosen dimension type, you can then point your fact records at the relevant business or surrogate key.
What is SCD type1?
Type 1 SCDs – Overwriting. In a Type 1 SCD the new data overwrites the existing data. Thus the existing data is lost as it is not stored anywhere else. This is the default type of dimension you create. You do not need to specify any additional information to create a Type 1 SCD.
What is SCD type2?
As we discussed in SCD type 2, we maintain the history by adding a different version of the row to the dimension. However, if the changes are rapid in nature Type 2 SCD will not be scalable. For example, let us assume we want to keep the customer risk type depending on his previous payment.
What is dimension in ETL?
In data warehousing, a dimension is a collection of reference information about a measurable event. In this context, events are known as “facts.” Dimensions categorize and describe data warehouse facts and measures in ways that support meaningful answers to business questions.
What is an example of 1 dimension?
A line segment drawn on a surface is a one-dimensional object, as it has only length and no width.
What are the 3 types of dimensions?
Everything around us, from the houses we live in to the objects we use in everyday life, has three dimensions: height, length, and width.
What does SCD pain feel like?
Some noted that it feels like “multiple fractures” and “broken bones and glass flowing through my body.” Others mentioned being electrocuted, while some could not describe it but stated that the pain is truly immense.