“Sources of Error” are factors (causes) that may limit the accuracy and/or the precision of experimental results. Sources of error are factors inherent within the experimental set-up and procedures that cannot be “fixed”, no matter how hard you try.
What are 3 sources of error in an experiment?
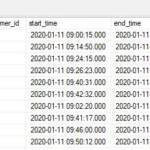
Physical and chemical laboratory experiments include three primary sources of error: systematic error, random error and human error.
What is the source of error in measurement?
Measurement errors are commonly ascribed to four sources: the respondent, the interviewer, the instrument (i.e., the survey questionnaire), and the mode of data collection.
What are 3 sources of error in an experiment?
Physical and chemical laboratory experiments include three primary sources of error: systematic error, random error and human error.
What are the types of errors explain?
Solution : Types of errors :
(a) Systematic error (b) Random error
( c) Gross error
(a) Systematic errors : They are reprducible inaccurales that are consistently in the same direction. These are the errors whose casuses are known.
What is source and types of error?
Common sources of error include instrumental, environmental, procedural, and human. All of these errors can be either random or systematic depending on how they affect the results. Instrumental error happens when the instruments being used are inaccurate, such as a balance that does not work (SF Fig.
What are sources of random error?
Sources of random errors natural variations in real world or experimental contexts. imprecise or unreliable measurement instruments. individual differences between participants or units. poorly controlled experimental procedures.
What are errors in an experiment?
Experimental error is the difference between a measured value and its true value. In other words, it is the inaccuracy or inaccuracies that stop us from seeing an absolutely correct measurement. Experimental error is very common and is to some degree inherent in every measurement.
What are 3 sources of error in an experiment?
Physical and chemical laboratory experiments include three primary sources of error: systematic error, random error and human error.
How many types are error?
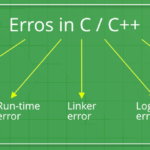
Generally errors are classified into three types: systematic errors, random errors and blunders. Gross errors are caused by mistake in using instruments or meters, calculating measurement and recording data results.
What do u mean by error?
error, mistake, and blunder mean an act or statement that is not right or true or proper. error is used for failure to follow a model correctly. There was an error in the addition. mistake is used when someone misunderstands something or does not intend to do wrong.
What type of error is accuracy?
Accuracy has two definitions: More commonly, it is a description of only systematic errors, a measure of statistical bias of a given measure of central tendency; low accuracy causes a difference between a result and a true value; ISO calls this trueness.
What is method error?
They can be defined as the difference between the value obtained during the process of measurement and the real value of the magnitude of measurement. 5. These errors, when significant and of great magnitude, affect the reliability of results by increasing or decreasing the real differences among the studied variables.
How do you find the source of error in an experiment?
One method of measuring error is by calculating absolute error, which is also called absolute uncertainty. This measure of accuracy is reported using the units of measurement. Absolute error is simply the difference between the measured value and either the true value or the average value of the data.
What is random error example?
An example of random error is putting the same weight on an electronic scales several times and obtaining readings that vary in random fashion from one reading to the next. The differences between these readings and the actual weight correspond to the random error of the scale measurements.
What is called random error?
: a statistical error that is wholly due to chance and does not recur.
How do you find the source of error in an experiment?
One method of measuring error is by calculating absolute error, which is also called absolute uncertainty. This measure of accuracy is reported using the units of measurement. Absolute error is simply the difference between the measured value and either the true value or the average value of the data.
What do u mean by error?
error, mistake, and blunder mean an act or statement that is not right or true or proper. error is used for failure to follow a model correctly. There was an error in the addition. mistake is used when someone misunderstands something or does not intend to do wrong.
What are sources of random error?
Sources of random errors natural variations in real world or experimental contexts. imprecise or unreliable measurement instruments. individual differences between participants or units. poorly controlled experimental procedures.
What type of error is human error?
Human error is an unintentional action or decision. Violations are intentional failures – deliberately doing the wrong thing. There are three types of human error: slips and lapses (skill-based errors), and mistakes.
What are examples of random errors?
An example of random error is putting the same weight on an electronic scales several times and obtaining readings that vary in random fashion from one reading to the next. The differences between these readings and the actual weight correspond to the random error of the scale measurements.
What are 3 sources of error in an experiment?
Physical and chemical laboratory experiments include three primary sources of error: systematic error, random error and human error.