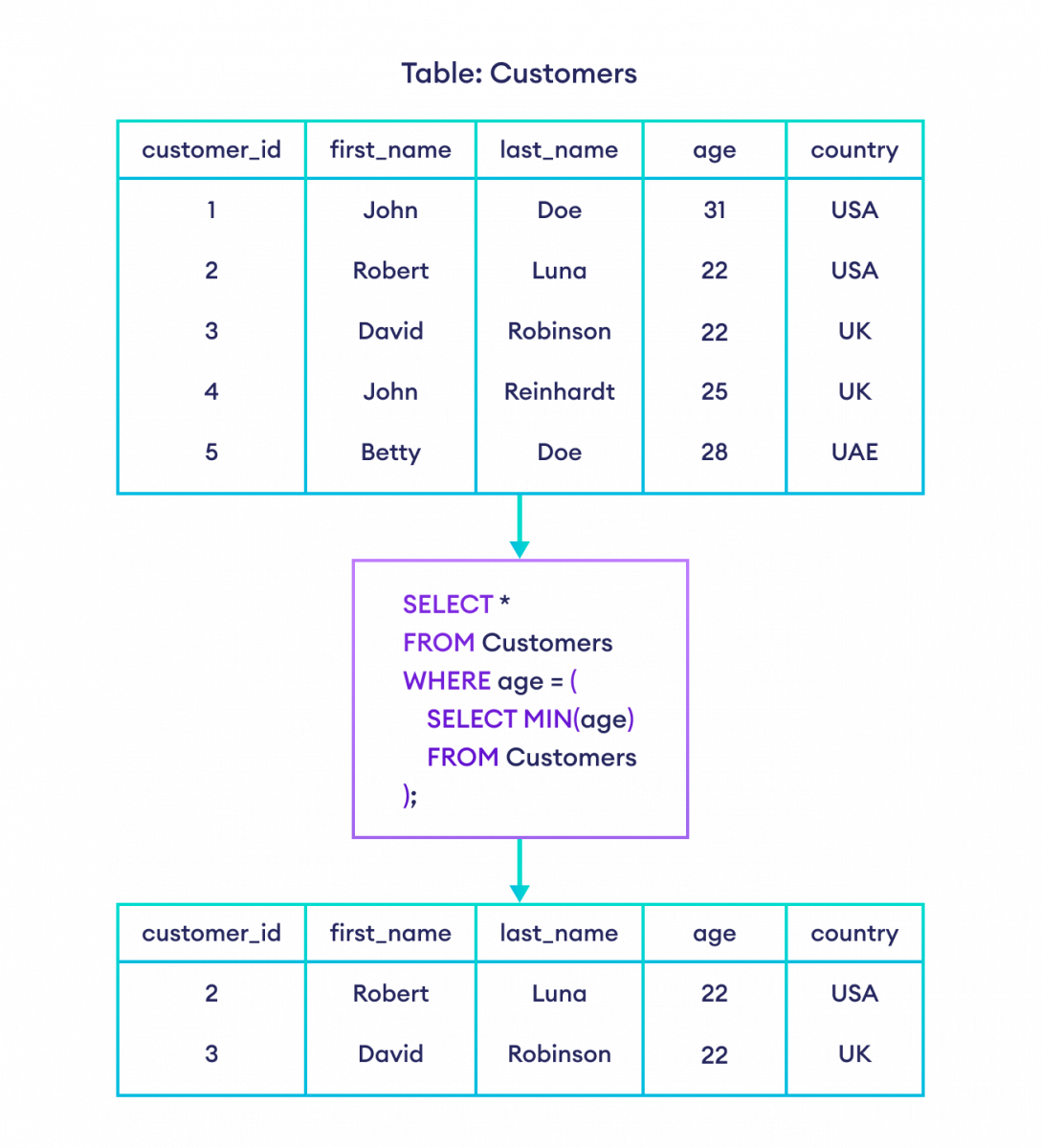
In SQL, it’s possible to place a SQL query inside another query known as subquery. For example, SELECT * FROM Customers WHERE age = ( SELECT MIN(age) FROM Customers ); Run Code. In a subquery, the outer query’s result is dependent on the result-set of the inner subquery.
What is subquery in SQL and its types?
They help us target specific rows to perform various operations in SQL. They are used to SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT and DELETE records in SQL. There are different types of SQL subquery, like Single-row subquery, multiple row subquery, multiple column subquery, correlated subquery, and nested subquery.
What is the use of subquery in SQL?
A subquery is used to return data that will be used in the main query as a condition to further restrict the data to be retrieved. Subqueries can be used with the SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements along with the operators like =, <, >, >=, <=, IN, BETWEEN, etc.
What is the subquery?
A subquery is a query that appears inside another query statement. Subqueries are also referred to as sub- SELECT s or nested SELECT s. The full SELECT syntax is valid in subqueries.
What is subquery explain types of subqueries with example?
A subquery is best defined as a query within a query. Subqueries enable you to write queries that select data rows for criteria that are actually developed while the query is executing at run time. More formally, it is the use of a SELECT statement inside one of the clauses of another SELECT statement.
What is the use of subquery in SQL?
A subquery is used to return data that will be used in the main query as a condition to further restrict the data to be retrieved. Subqueries can be used with the SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements along with the operators like =, <, >, >=, <=, IN, BETWEEN, etc.
How many types of subquery are there?
There are three broad types of a subquery in SQL. This chapter from OCA Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals I Exam Guide explains differences between a single-row subquery, multiple-row subquery and correlated subquery .
What are the advantages of subquery?
Advantages Of Subquery: Subqueries divide the complex query into isolated parts so that a complex query can be broken down into a series of logical steps. It is easy to understand and code maintenance is also at ease. Subqueries allow you to use the results of another query in the outer query.
What are the rules of subquery?
Important rules for Subqueries: You can place the Subquery in a number of SQL clauses: WHERE clause, HAVING clause, FROM clause. Subqueries can be used with SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT, DELETE statements along with expression operator.
How subquery is executed?
Each subquery is executed once for every row of the outer query. A correlated subquery is evaluated once for each row processed by the parent statement. The parent statement can be a SELECT, UPDATE, or DELETE statement.
What is the use of subquery in SQL?
A subquery is used to return data that will be used in the main query as a condition to further restrict the data to be retrieved. Subqueries can be used with the SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements along with the operators like =, <, >, >=, <=, IN, BETWEEN, etc.
What are the 4 types of queries?
They are: Select queries • Action queries • Parameter queries • Crosstab queries • SQL queries. Select Queries Select query is the simplest and the most common type of query.
Which is faster subquery or function?
using function (included that subquery) has better performance, when you define a function, the function will not run while calling the function. I mean that you may have multiple sub-query, then using function makes to be called those that you need.
Is subquery faster than two queries?
For subqueries and joins, the data needs to be combined. Small amounts can easily be combined in memory, but if the data gets bigger, then it might not fit, causing the need to swap temporary data to disk, degrading performance. So, there is no general rule to say which one is faster.
Which subquery Cannot be executed?
Which subquery cannot be executed by itself as a separate statement? Explanation: An uncorrelated subquery contains references to the values from the outer query. So, it is dependent on it. Therefore, a correlated subquery cannot be executed by itself as a separate statement.
What is single row subquery?
Single-row subqueries are subqueries used with a comparison operator in a WHERE, or HAVING clause. Subqueries that can return more than one row (but only one column) to the outer statement are called multiple-row subqueries. Multiple-row subqueries are subqueries used with an IN, ANY, or ALL clause.
Why subquery is faster than JOIN?
I won’t leave you in suspense, between Joins and Subqueries, joins tend to execute faster. In fact, query retrieval time using joins will almost always outperform one that employs a subquery. The reason is that joins mitigate the processing burden on the database by replacing multiple queries with one join query.
Which JOIN is faster in mysql?
performance – Mysql – LEFT JOIN way faster than INNER JOIN – Stack Overflow. Stack Overflow for Teams – Start collaborating and sharing organizational knowledge.
What is the syntax for subquery?
A subquery can be placed in a number of SQL clauses like WHERE clause, FROM clause, HAVING clause. You can use Subquery with SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT, DELETE statements along with the operators like =, <, >, >=, <=, IN, BETWEEN, etc. A subquery is a query within another query.
Is subquery executed first?
Answer: D. The sub-query always executes before the execution of the main query. Subqueries are completed first. The result of the subquery is used as input for the outer query.
WHERE subquery can not be used?
Subqueries are not allowed in the defining query of a CREATE PROJECTION statement. Subqueries are supported within UPDATE statements with the following exceptions: You cannot use SET column = {expression} to specify a subquery.
Can subquery DELETE?
A subquery can be used in a DELETE statement. Always back up your data and test your DELETE statement before running it on live data.