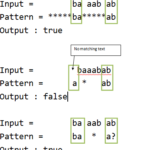
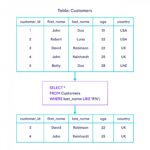
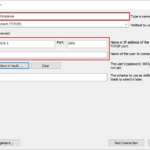
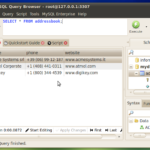
A SSL certificate is a small data file binding a cryptographic key to a firm’s details. When it is installed on a web server, the padlock and the https protocol get activated, allowing secure connections from a server to a browser. SSL is typically used to secure transactions via credit cards, logins, and data transfer, and most recently, SSL is also used in social media sites security.
Uses of SSL Protocol
SSL, or Secure Sockets Layer, is used to secure transactions done online via credit cards – Online transactions can be very sensitive, and they require high levels of security. In the modern world, technology has brought about a lot of positive changes, for example, SSL for online casinos is a welcome idea in a world where fraudsters were nearly taking over. User data is valid in the registration and login process of accounts, and therefore, securing it to prevent malicious entries is essential.
SSL is used to secure logins into systems as well as other sensitive details exchanged in the online space. To eliminate the chances of sensitive data leaking online, or getting into the hands of other parties, SSL ensures that system login is secured and cannot be accessed by third parties without authorization from the right party.
SSL is used to secure transfer of sensitive files over FTP(s) and https services, for example, owners of websites transferring large files or updating pages to their sites.
SSL is used to secure intranet-based flow of traffic such as internal networks, extranets, file sharing, and database connections.
SSL is used to secure network logins as well as other network traffic with VPNs, for example VPN Access Servers and other applications like Citrix Access Gateway.
SSL Handshake – the process
The handshake process can be a rather complex procedure, with a number of variations allowed by the protocol. These steps give a clear sense of how the process works.
Step 1. Client contacts server requesting secure connection. Server responds with a list of algorithmic toolkits for the client to make a comparison against its own list of supported toolkits, makes a choice of one, and notifies the server that they’ll both be using it.
Step 2. Server provides its digital certificate, which is an electronic document given by a third-party authority to confirm the identity of the server. Upon receiving the certificate, the client confirms the authenticity of the certificate.
Step 3. Using the public key of the server, both parties establish a session key to be used by both over the entire session to ensure that communication is encrypted. A number of techniques can be used to achieve encryption, where the client may encrypt a random number using the public key before sending it out to the server to decrypt. Also, both parties may use a more complex approach known as Diffie-Hellman key exchange to generate the session key.
Ideally, Secure Sockets Layer is a protocol designed specifically for securing connections between two parties; web servers and web clients over an insecure network. This ensures that there is web security, and personal data cannot be obtained or accessed illegally by third-parties.