What Is a Type II ErrorType II ErrorA false negative error, or false negative, is a test result which wrongly indicates that a condition does not hold. For example, when a pregnancy test indicates a woman is not pregnant, but she is, or when a person guilty of a crime is acquitted, these are false negatives.https://en.wikipedia.org › False_positives_and_false_negativesFalse positives and false negatives – Wikipedia? A type II error is a statistical term used within the context of hypothesis testing that describes the error that occurs when one fails to reject a null hypothesis that is actually false. A type II error produces a false negative, also known as an error of omission.
What are the 2 types of errors?
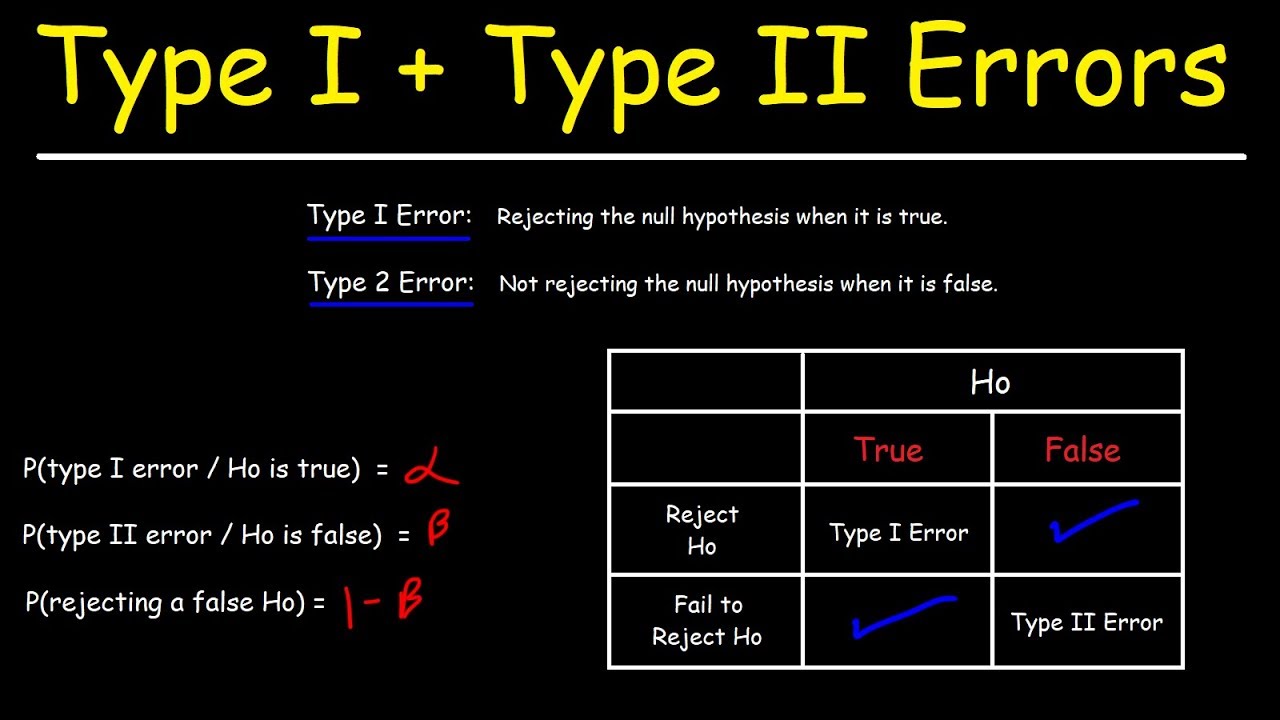
As a consequence there are actually two different types of error here. If we reject a null hypothesis that is actually true, then we have made a type I error. On the other hand, if we retain the null hypothesis when it is in fact false, then we have made a type II error.
What are the 2 types of error in hypothesis testing?
A type I error (false-positive) occurs if an investigator rejects a null hypothesis that is actually true in the population; a type II error (false-negative) occurs if the investigator fails to reject a null hypothesis that is actually false in the population.
Is a Type 2 error a random error?
A Type II error occurs when there really is a difference (association, correlation) overall, but random sampling caused your data to not show a statistically significant difference.
What is Type 1 Type 2 Type 3 error?
Type I error: “rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true”. Type II error: “failing to reject the null hypothesis when it is false”. Type III error: “correctly rejecting the null hypothesis for the wrong reason”.
What are the 2 types of error in hypothesis testing?
A type I error (false-positive) occurs if an investigator rejects a null hypothesis that is actually true in the population; a type II error (false-negative) occurs if the investigator fails to reject a null hypothesis that is actually false in the population.
What is Type 2 error in statistics?
Type 2 errors happen when you inaccurately assume that no winner has been declared between a control version and a variation although there actually is a winner. In more statistically accurate terms, type 2 errors happen when the null hypothesis is false and you subsequently fail to reject it.
What causes Type 2 error?
Causes of Type II Error Type II error is mainly caused by the statistical power of a test being low. A Type II error will occur if the statistical test is not powerful enough. The size of the sample can also lead to a Type I error because the outcome of the test will be affected.
What are the 2 types of hypothesis explain each?
Here are a few different types of hypotheses: Simple hypothesis: A simple hypothesis predicts a relationship between an independent and a dependent variable. Complex hypothesis: A complex hypothesis looks at the relationship between two or more independent variables and two or more dependent variables.
Which type of error is a random error?
Random Error (indeterminate error) Caused by uncontrollable variables, which can not be defined/eliminated. 1. Instrument errors – failure to calibrate, degradation of parts in the instrument, power fluctuations, variation in temperature, etc.
Is Type 1 error random error?
There are two types of random error – type I error and type II error. In this study, type I and type II errors are explained, and the important concepts of statistical power and sample size estimation are discussed.
What are random or accidental error?
Random Errors Accidental errors are brought about by changing experimental conditions that are beyond the control of the experimenter; examples are vibrations in the equipment, changes in the humidity, fluctuating temperature, etc.
What are Type 3 and Type 4 errors?
A Type III error is directly related to a Type IV error; it’s actually a specific type of Type III error. When you correctly reject the null hypothesis, but make a mistake interpreting the results, you have committed a Type IV error.
What is Type 4 error?
A type IV error was defined as the incorrect interpretation of a correctly rejected null hypothesis. Statistically significant interactions were classified in one of the following categories: (1) correct interpretation, (2) cell mean interpretation, (3) main effect interpretation, or (4) no interpretation.
What are Type 1 errors called?
False Positive Type I Error This “false positive,” leading to an incorrect rejection of the null hypothesis, is called a type I error. A type I error rejects an idea that should not have been rejected.
What are the 2 types of error in hypothesis testing?
A type I error (false-positive) occurs if an investigator rejects a null hypothesis that is actually true in the population; a type II error (false-negative) occurs if the investigator fails to reject a null hypothesis that is actually false in the population.
What is Type 2 error formula?
What is the probability of a Type II error? Step 1: Based on the above question, Power = 0.85. This means that the probability of correctly rejecting the null hypothesis is 0.85 or 85%. Step 2: We can use the formula 1 – Power = P(Type II Error) to find our probability.
How do you remember Type 1 and Type 2 error?
So here’s the mnemonic: first, a Type I error can be viewed as a “false alarm” while a Type II error as a “missed detection”; second, note that the phrase “false alarm” has fewer letters than “missed detection,” and analogously the numeral 1 (for Type I error) is smaller than 2 (for Type I error).
What is the most common type of errors?
1. Syntax Errors. Just like human languages, computer languages have grammar rules. But while humans are able to communicate with less-than-perfect grammar, computers can’t ignore mistakes, i.e. syntax errors.
Why is null hypothesis called null?
Why is it Called the “Null”? The word “null” in this context means that it’s a commonly accepted fact that researchers work to nullify. It doesn’t mean that the statement is null (i.e. amounts to nothing) itself! (Perhaps the term should be called the “nullifiable hypothesis” as that might cause less confusion).
What is the definition of type 2 error quizlet?
type II error. An error that occurs when a researcher concludes that the independent variable had no effect on the dependent variable, when in truth it did; a “false negative” type II error. occurs when researchers fail to reject a false null hypotheses.
What type of error is bias?
Bias is any systematic error in an epidemiologic study that results in an incorrect estimate of the association between exposure and the health outcome. Bias occurs when an estimated association (risk ratio, rate ratio, odds ratio, difference in means, etc.) deviates from the true measure of association.