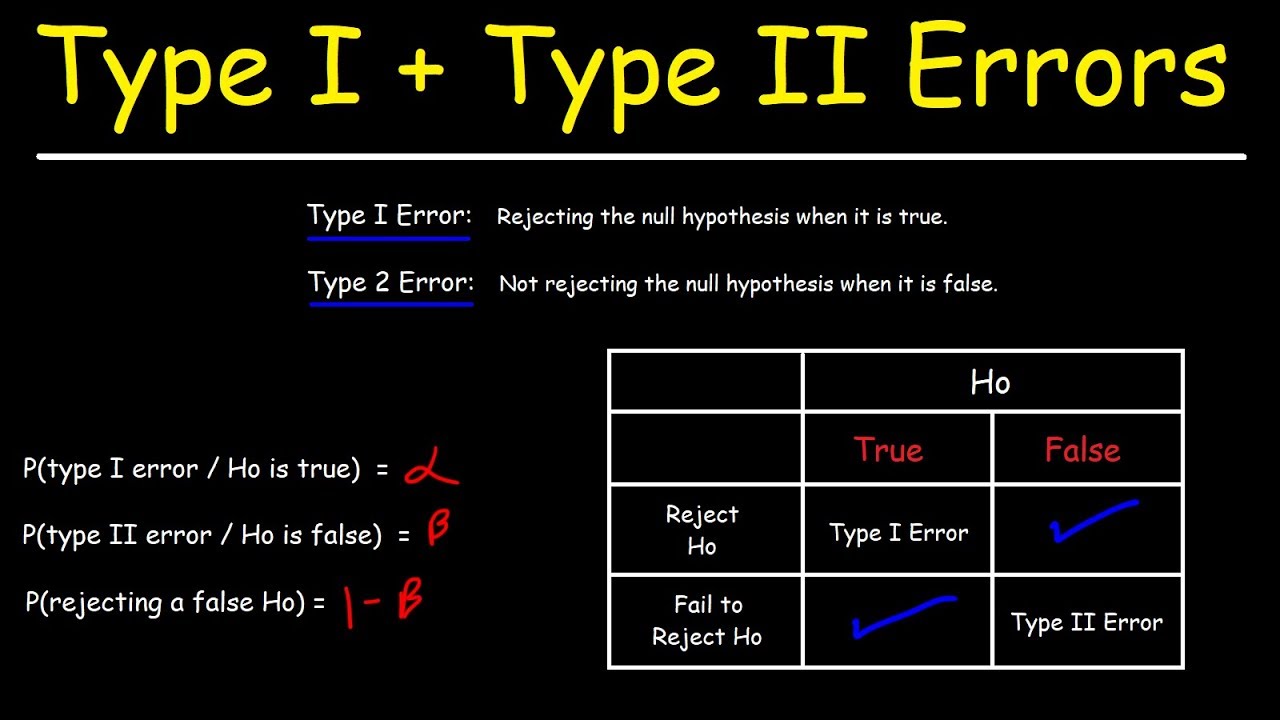
What is the probability of a Type II error? Step 1: Based on the above question, Power = 0.85. This means that the probability of correctly rejecting the null hypothesis is 0.85 or 85%. Step 2: We can use the formula 1 – Power = P(Type II Error) to find our probability.
What is a Type 2 error in math?
An error in a statistical test which occurs when a true hypothesis is rejected (a false negative in terms of the null hypothesis).
What is type II error explain with example?
Type II error, commonly referred to as ‘β’ error, is the probability of retaining an incorrect factual statement. It is an error of a false positive, i.e., a statement is factually false, and we are positive about it.
What is Type 2 error in statistics?
Type 2 errors happen when you inaccurately assume that no winner has been declared between a control version and a variation although there actually is a winner. In more statistically accurate terms, type 2 errors happen when the null hypothesis is false and you subsequently fail to reject it.
How do you determine Type 1 and Type 2 error?
A type 1 error occurs when you wrongly reject the null hypothesis (i.e. you think you found a significant effect when there really isn’t one). A type 2 error occurs when you wrongly fail to reject the null hypothesis (i.e. you miss a significant effect that is really there).
What is Type 2 error in statistics?
Type 2 errors happen when you inaccurately assume that no winner has been declared between a control version and a variation although there actually is a winner. In more statistically accurate terms, type 2 errors happen when the null hypothesis is false and you subsequently fail to reject it.
What causes Type 2 error?
Causes of Type II Error Type II error is mainly caused by the statistical power of a test being low. A Type II error will occur if the statistical test is not powerful enough. The size of the sample can also lead to a Type I error because the outcome of the test will be affected.
What are Type 1 2 and 3 errors?
Type I error: “rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true”. Type II error: “failing to reject the null hypothesis when it is false”. Type III error: “correctly rejecting the null hypothesis for the wrong reason”. (1948, p.
What is power Type 2 error?
Statistical Power Power (1-β): the probability correctly rejecting the null hypothesis (when the null hypothesis isn’t true). Type II error (β): the probability of failing to rejecting the null hypothesis (when the null hypothesis is not true).
What is Type 2 error Mcq?
Type – II error means. We reject null hypothesis although no true difference exists. We accept the null hypothesis although no true difference exists. We accept the null hypothesis although a true difference exists.
Is a type 2 error a random error?
A Type II error occurs when there really is a difference (association, correlation) overall, but random sampling caused your data to not show a statistically significant difference.
How do we calculate standard error?
How do you calculate standard error? The standard error is calculated by dividing the standard deviation by the sample size’s square root. It gives the precision of a sample mean by including the sample-to-sample variability of the sample means.
What is a Type 1 error formula?
A type I error occurs when one rejects the null hypothesis when it is true. The probability of a type I error is the level of significance of the test of hypothesis, and is denoted by *alpha*. Usually a one-tailed test of hypothesis is is used when one talks about type I error.
How do we find Type 1 errors?
The probability of committing the type I error is measured by the significance level (α) of a hypothesis test. The significance level indicates the probability of erroneously rejecting the true null hypothesis.
Which of the following is the best example of a type II error?
So the best example of a type two error be that’s getting a negative test when you are actually pregnant.
What are the 2 types of errors?
As a consequence there are actually two different types of error here. If we reject a null hypothesis that is actually true, then we have made a type I error. On the other hand, if we retain the null hypothesis when it is in fact false, then we have made a type II error.
What is type II error in machine learning?
Type I and Type II errors are very common in machine learning and statistics. Type I error occurs when the Null Hypothesis (H0) is mistakenly rejected. This is also referred to as the False Positive Error. Type II error occurs when a Null Hypothesis that is actually false is accepted.
What is Type 2 error in statistics?
Type 2 errors happen when you inaccurately assume that no winner has been declared between a control version and a variation although there actually is a winner. In more statistically accurate terms, type 2 errors happen when the null hypothesis is false and you subsequently fail to reject it.
How is type 2 error related to sample size?
Type II errors are more likely to occur when sample sizes are too small, the true difference or effect is small and variability is large. The probability of a type II error occurring can be calculated or pre-defined and is denoted as β.
What affects a type 2 error?
A Type II error is when we fail to reject a false null hypothesis. Higher values of α make it easier to reject the null hypothesis, so choosing higher values for α can reduce the probability of a Type II error.
What is a Type 3 error example?
You can also think of a Type III error as giving the right answer (i.e. correctly rejecting the null) to the wrong question. Either way, you’re still arriving at the correct conclusion for the wrong reason. When we say the “wrong question”, that normally means you’ve formulated your hypotheses incorrectly.
What are the 3 types of error in programming?
When developing programs there are three types of error that can occur: syntax errors. logic errors. runtime errors.