vector, in mathematics, a quantity that has both magnitude and direction but not position. Examples of such quantities are velocity and acceleration.A quantity that can be completely described using both magnitude and direction is called a vector quantity. Example: Displacement, Force, Electric Field intensity, etc. Vector algebra is a huge world of math that uses pure logic. Geometrically, a vector is a directed line segment.
What is vector with example?
A vector is a quantity or phenomenon that has two independent properties: magnitude and direction. The term also denotes the mathematical or geometrical representation of such a quantity. Examples of vectors in nature are velocity, momentum, force, electromagnetic fields, and weight.
How do you define a vector in math?
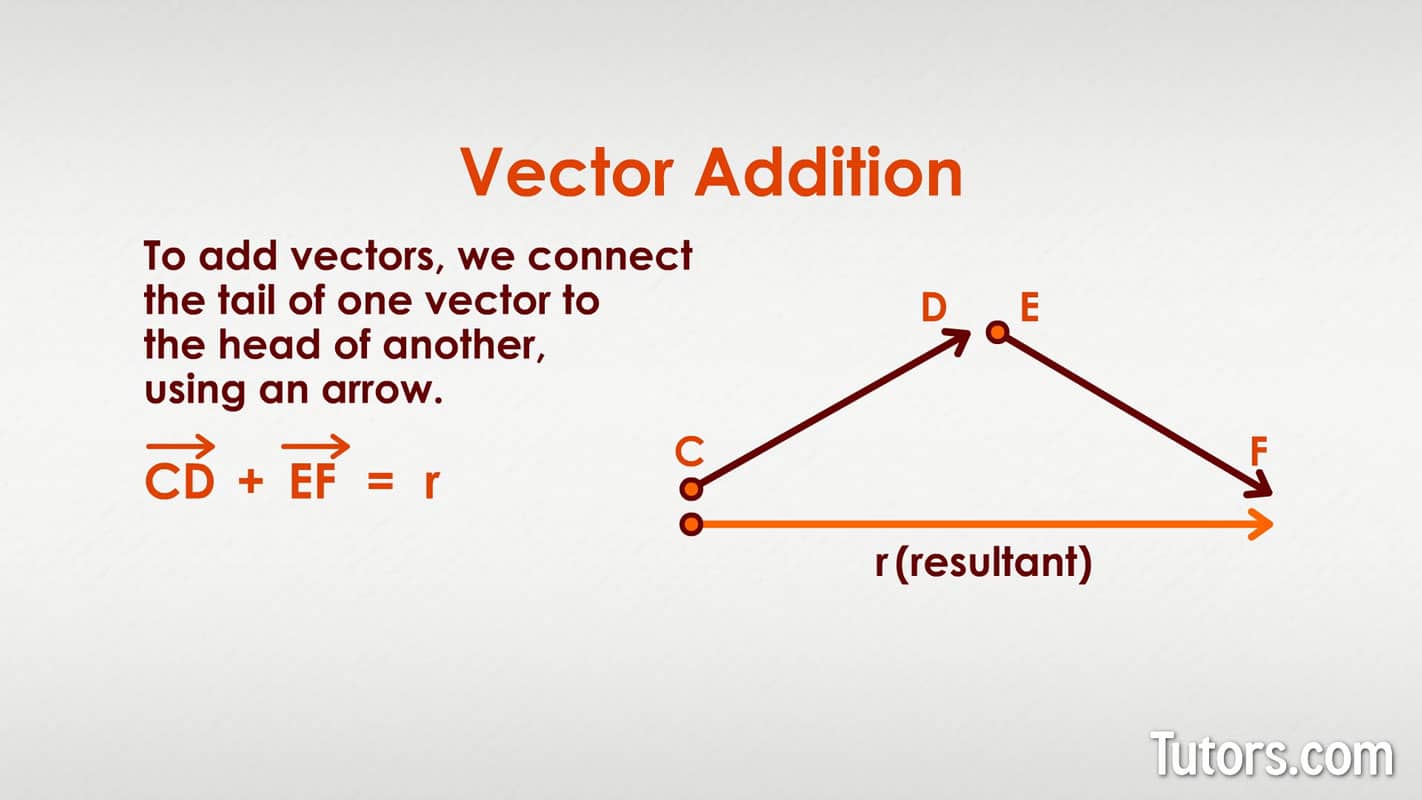
Definition of a vector. A vector is an object that has both a magnitude and a direction. Geometrically, we can picture a vector as a directed line segment, whose length is the magnitude of the vector and with an arrow indicating the direction. The direction of the vector is from its tail to its head.
What vector means?
vector, in physics, a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. It is typically represented by an arrow whose direction is the same as that of the quantity and whose length is proportional to the quantity’s magnitude.
What type of math is vectors?
A vector has both magnitude and direction. We use vectors to, for example, describe the velocity of moving objects. In this video, you’ll learn how to write and draw vectors.
How do you define a vector in math?
Definition of a vector. A vector is an object that has both a magnitude and a direction. Geometrically, we can picture a vector as a directed line segment, whose length is the magnitude of the vector and with an arrow indicating the direction. The direction of the vector is from its tail to its head.
Why is it called vector?
The term vector comes from engineering/physics. Vectors represent 2 and 3 dimensional lines that have a direction.
What is the vector formula?
the formula to determine the magnitude of a vector (in two dimensional space) v = (x, y) is: |v| =√(x2 + y2). This formula is derived from the Pythagorean theorem.
How do you write a vector?
When a vector is just a list of numbers, we can visualize it as an arrow in space. For example, we visualize the vector (4,2)left parenthesis, 4, comma, 2, right parenthesis as an arrow whose tail is at the origin and whose tip is at the point ( 4 , 2 ) (4, 2) (4,2)left parenthesis, 4, comma, 2, right parenthesis.
What is vector and scalar in maths?
A scalar is an element of a field which is used to define a vector space. A quantity described by multiple scalars, such as having both direction and magnitude, is called a vector.
How is vector used in real life?
Vectors have many real-life applications, including situations involving force or velocity. For example, consider the forces acting on a boat crossing a river. The boat’s motor generates a force in one direction, and the current of the river generates a force in another direction. Both forces are vectors.
What is difference between scalar and vector?
A quantity that has magnitude but no particular direction is described as scalar. A quantity that has magnitude and acts in a particular direction is described as vector.
Are numbers vectors?
Since R is a vector space over itself, real numbers are both vectors and scalars in this context. In other contexts, a real number might be a vector but not a scalar (e.g. the vector √2 in R over Q), a scalar but not a vector (e.g. the scalar 1 in R2 over R), or neither a vector nor a scalar.
Who is the father of vector?
In their modern form, vectors appeared late in the 19th century when Josiah Willard Gibbs and Oliver Heaviside (of the United States and Britain, respectively) independently developed vector analysis to express the new laws of electromagnetism discovered by the Scottish physicist James Clerk Maxwell.
Why do we use vectors?
We know that vectors have both magnitude and direction. Hence, it is used in Physics to represent physical quantities. It has many applications in Physics to calculate force, velocity, acceleration, displacement, and so on. Also, the vectors are used to visually represent the position.
What is vector in C++ with example?
In C++, vectors are used to store elements of similar data types. However, unlike arrays, the size of a vector can grow dynamically. That is, we can change the size of the vector during the execution of a program as per our requirements. Vectors are part of the C++ Standard Template Library.
What is the vector formula?
the formula to determine the magnitude of a vector (in two dimensional space) v = (x, y) is: |v| =√(x2 + y2). This formula is derived from the Pythagorean theorem.
What is the vector in biology?
A vector is a living organism that transmits an infectious agent from an infected animal to a human or another animal. Vectors are frequently arthropods, such as mosquitoes, ticks, flies, fleas and lice.
What is scalar and its examples?
scalar, a physical quantity that is completely described by its magnitude. Examples of scalars are volume, density, speed, energy, mass, and time. Other quantities, such as force and velocity, have both magnitude and direction and are called vectors.
How do you define a vector in math?
Definition of a vector. A vector is an object that has both a magnitude and a direction. Geometrically, we can picture a vector as a directed line segment, whose length is the magnitude of the vector and with an arrow indicating the direction. The direction of the vector is from its tail to its head.
What type of math is vectors?
A vector has both magnitude and direction. We use vectors to, for example, describe the velocity of moving objects. In this video, you’ll learn how to write and draw vectors.
What are two types of vectors?
The four major types of vectors are plasmids, viral vectors, cosmids, and artificial chromosomes. Of these, the most commonly used vectors are plasmids.
What is a vector in maths?
Vectors In Maths: Definition The vector is derived from Latin word Vectus, meaning to carry. Vector is defined as the quantity consisting of magnitude and direction. It represents the direction of objects from one position to another.
What are the types of vectors?
Some of the types of vectors are mentioned below: 1 Zero vector: The initial and terminal points coinciding with each other is called a zero vector. 2 Unit Vector: The vector whose magnitude is 1 unit called a unit vector. 3 Coinitial Vector: Vectors having two or more same initial points are called coinitial vectors. More items…
What is an example of a vector quantity?
The most common examples of the vector are Velocity, Acceleration, Force, Increase/Decrease in Temperature etc. All these quantities, have directions and magnitude both. Therefore, it is necessary to calculate them in their vector form.
What is vectorvector?
Vector is derived from the Latin word Vectus, meaning to carry. It is defined as the quantity consisting of magnitude and direction. Vectors represent the direction of objects from one position to another.